↗ arXiv ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Papers with Code
TL;DR#
Current text-based methods for controlling image generation in diffusion models have limitations, struggling to capture complex visual concepts or prevent generation of undesired content like copyrighted images. Negative prompts, while useful, are often insufficient. Additionally, some state-of-the-art models don’t even support negative prompts.
This paper introduces NegToMe, a novel training-free approach that uses images directly for adversarial guidance during reverse diffusion. By cleverly pushing apart visual features between generated and reference images, NegToMe significantly improves output diversity and reduces similarity to copyrighted material. It’s simple, efficient, compatible with various architectures, and demonstrably improves image quality and diversity in experiments.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it introduces a novel, training-free method for improving the diversity and quality of image generation, addressing limitations of existing text-based approaches. It’s highly relevant to current research trends in diffusion models and opens avenues for enhancing output diversity, mitigating copyright issues, and improving aesthetic control. This work is significant for researchers in computer vision, machine learning, and AI, particularly those working with generative models.
Visual Insights#

🔼 This figure demonstrates how NegToMe enhances the diversity of outputs from diffusion models. The top row shows the outputs of a state-of-the-art diffusion model without NegToMe, revealing a lack of diversity in terms of ethnicity, race, and gender. The bottom row displays the results when NegToMe is used. By guiding the features of each image away from one another during reverse diffusion, NegToMe increases the diversity of the generated images.
read the caption
(a) Adversarial Guidance across Different Outputs: State-of-the-art diffusion models are observed to suffer from limited diversity (e.g., ethnic, racial, gender etc.). NegToMe can be used to improve output diversity by simply guiding the features of each image away from each other during reverse diffusion.
| Method | Dreamsim ↓ | CLIPScore ↑ | IS ↑ | Inf. Time ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Prompt | 0.812 | 0.334 | 3.197 | 13.2 s |
| Base Prompt + Ours | 0.780 | 0.336 | 3.355 | 13.7 s |
PW (gpt-4o) | 0.743 | 0.332 | 3.686 | 15.4 s |
| PW + Ours | 0.712 | 0.333 | 3.747 | 15.9 s |
🔼 Table 1 presents a quantitative evaluation of NegToMe’s effectiveness in mitigating copyright infringement in image generation. It compares different methods (using negative prompts alone or in combination with NegToMe) for reducing visual similarity to copyrighted characters. The metrics used are Dreamsim (lower scores indicate less visual similarity), VQAScore (higher scores indicate better image quality), CLIPScore (higher scores mean better text-image alignment), and Inception Score (IS; higher scores indicate better image quality). The results show that NegToMe significantly reduces visual similarity to copyrighted material while maintaining or improving other performance metrics.
read the caption
Table 1: Copyright Mitigation. NegToMe reduces visual similarity to copyright characters while preserving T2I performance.
In-depth insights#
NegToMe: Image Guidance#
The concept of ‘NegToMe: Image Guidance’ presents a novel approach to adversarial guidance in image generation models. Instead of relying solely on textual negative prompts, which can be imprecise and insufficient for complex visual concepts or copyrighted material, NegToMe leverages visual features directly from a reference image. This image-based guidance allows for more nuanced control, effectively steering the generation process away from undesired visual elements with greater precision. The method’s training-free nature and simplicity make it easily implementable and adaptable to various diffusion model architectures, significantly broadening its applicability. By carefully selecting the reference image, NegToMe offers versatility in its applications, including enhancing output diversity (e.g., addressing biases in gender or ethnicity representation), mitigating copyright infringement, and improving image quality by guiding away from undesirable features. The ability to use masked images as references further refines its control, allowing for targeted manipulation of specific visual elements within the generated image. The results showcase the effectiveness of NegToMe in improving output diversity and reducing similarity to copyrighted content, demonstrating its potential as a valuable tool for enhancing existing image generation models and improving overall image quality.
Diversity & Copyright#
The research paper explores the crucial intersection of diversity and copyright in the context of AI-generated images. The core argument revolves around improving the diversity of outputs while simultaneously mitigating the risk of generating copyrighted content. The authors highlight the limitations of traditional negative prompting, suggesting that it is often insufficient for achieving both goals simultaneously. Instead, they propose a novel method, negative token merging (NegToMe), which directly leverages visual features from reference images to guide the generative process. This image-based approach proves particularly effective in scenarios where text-based prompts fall short, especially when dealing with complex visual concepts or copyrighted materials. NegToMe offers a training-free approach, enhancing the practicality and versatility of its application. Experiments reveal NegToMe’s success in increasing diversity across various dimensions (racial, gender, visual style) and significantly reducing the similarity of outputs to copyrighted images. The method’s simplicity and compatibility with diverse diffusion architectures position it as a significant advance in addressing the multifaceted challenges presented by diversity and copyright concerns within AI image generation.
Training-Free Approach#
The core idea behind the paper’s training-free approach is to leverage existing diffusion models without requiring additional training. This is achieved by introducing a novel technique called negative token merging (NegToMe). NegToMe cleverly guides the generation process by directly using visual features from reference images, rather than relying solely on text prompts. This approach is advantageous because it can address limitations of text-based guidance, such as difficulty capturing complex visual concepts or insufficient control over specific visual elements like copyrighted characters. The simplicity of the method is highlighted by the minimal code required and its compatibility with various diffusion architectures. By subtly adjusting the reference image, NegToMe enables a wide array of applications, including enhancing output diversity and mitigating copyrighted content concerns. The training-free nature of the method is key as it avoids the time and resource-intensive process of retraining or finetuning large diffusion models, making it efficient and readily adaptable.
MM-DiT Model Support#
The heading ‘MM-DiT Model Support’ suggests an important aspect of the research paper’s contribution: its compatibility and effectiveness when integrated with multi-modal diffusion transformer (MM-DiT) models. This is crucial because MM-DiT models, known for their advanced capabilities in generating high-quality and diverse images, often rely on complex architectures. The paper’s claim of seamless integration with such models, without requiring extensive retraining or modification, represents a significant advancement. This ease of implementation simplifies the adoption of the proposed technique, widening its accessibility to researchers and practitioners. Moreover, successful integration with different architectures validates the algorithm’s robustness and generalizability, moving beyond compatibility with specific diffusion models. This adaptability enhances the method’s practical use and potential in real-world applications. The discussion of MM-DiT model support should provide empirical evidence demonstrating the performance gains or lack thereof, addressing the efficiency and effectiveness of the algorithm in these advanced models, and potentially comparing its performance against traditional diffusion model approaches. The focus should be on demonstrating that the proposed method doesn’t hinder the performance of the MM-DiT models, while potentially enhancing certain aspects of image generation. A thorough analysis in this section would strengthen the paper’s overall impact and contribution to the field of image generation.
Future Enhancements#
Future enhancements for negative token merging (NegToMe) could explore several promising avenues. Improving the semantic token matching mechanism is crucial; exploring more sophisticated similarity metrics beyond cosine similarity, potentially incorporating contextual information or learned embeddings, could significantly boost performance. Expanding the types of adversarial guidance beyond simple linear extrapolation is also important. Investigating alternative methods like generative adversarial networks (GANs) or other sophisticated techniques could offer more nuanced control over feature manipulation. Furthermore, enhancing NegToMe’s compatibility with a wider range of diffusion models is vital, including those that don’t utilize transformer blocks or those with significantly different architectures. This would broaden the applicability of NegToMe and increase its impact on the broader diffusion model community. Finally, thorough investigation into the effects of hyperparameters such as the merging threshold and the affine coefficient (alpha) is needed to optimize NegToMe’s performance in diverse scenarios and across different model types. A comprehensive analysis of these aspects will lead to more robust and effective adversarial guidance via images.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 This figure demonstrates how NegToMe reduces the generation of copyrighted content by diffusion models. The standard approach of using negative prompts is often ineffective at preventing this. NegToMe improves upon this by directly guiding the diffusion model’s features away from copyrighted images, resulting in generated images with significantly reduced similarity to the protected material. This is illustrated by comparing outputs with and without NegToMe applied, showcasing its effectiveness in mitigating copyright infringement.
read the caption
(b) Adversarial Guidance with Copyrighted Content: Diffusion models can generate copyrighted content. Moreover, using negative prompt for avoiding this is often insufficient. NegToMe helps better reduce similarity to copyrighted characters, by guiding diffusion features away from copyrighted images.

🔼 This figure demonstrates the capabilities of NegToMe, a novel training-free method for adversarial guidance in image generation models. It showcases NegToMe’s ability to enhance diversity in generated images by guiding features away from each other (illustrated with examples showing improvements in visual, gender, and racial diversity). Additionally, it highlights NegToMe’s effectiveness in mitigating the generation of copyrighted content by guiding the generation process away from copyrighted reference images. Further applications are mentioned and detailed in Section 4 of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: We introduce NegToMe, a training-free approach for adversarial guidance directly using images instead of a negative prompt. Above we show its applications for a) improving output diversity (visual, gender, racial) by guiding each image away from others, b) reducing visual similarity to copyrighted characters, by guiding outputs away from copyrighted images. (refer Sec. 4 for further applications).

🔼 Figure 2 demonstrates the versatility of NegToMe in performing image-based adversarial guidance. Unlike text-based negative prompts, NegToMe uses reference images to directly steer the generation process. This allows for several applications: improving output diversity by guiding features away from each other (e.g., achieving more diverse representation across demographics); controlling style by excluding specific artistic styles; enhancing output quality by guiding away from blurry references; and performing object feature interpolation or extrapolation. The figure visually shows various scenarios illustrating these capabilities.
read the caption
Figure 2: Image-based adversarial guidance. NegToMe enables directly using images (instead of negative prompt alone) for adversarial guidance. By simply adjusting the used reference, NegToMe allows for a range of custom applications, 1) adversarial guidance for visually complex concepts to improve diversity, 2) Style control for excluding specific artistic styles (e.g., Van Gogh) from generated images, 3) improving output quality by guiding away from a blurry reference, 4) Object feature interpolation or extrapolation by guiding the outputs towards or away from the reference etc.

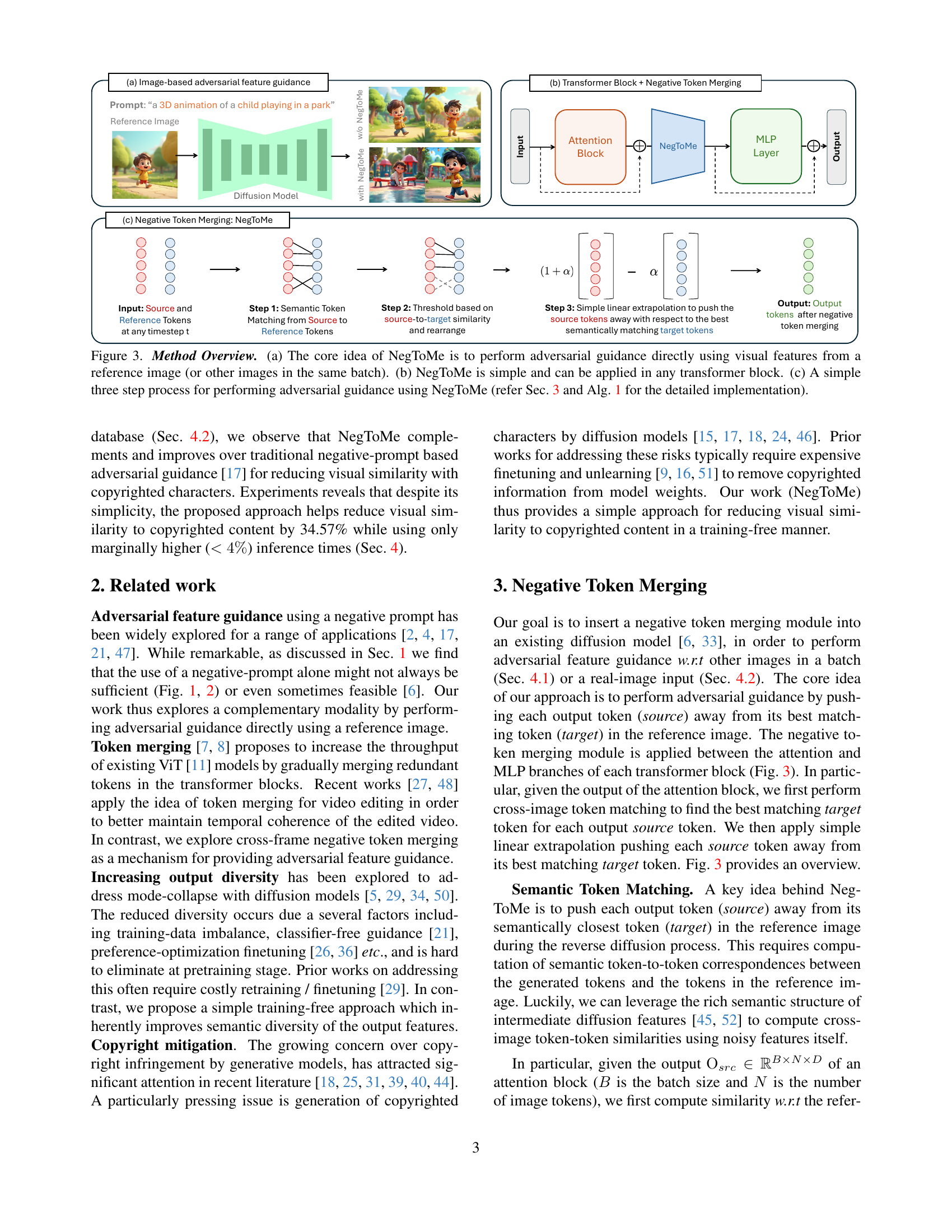
🔼 This figure illustrates the core concept and implementation of Negative Token Merging (NegToMe). (a) shows how NegToMe uses visual features from a reference image (or other images in a batch) to perform adversarial guidance. Instead of relying on text-based negative prompts, it leverages the visual similarity between the reference and generated images. (b) highlights the simplicity of NegToMe, demonstrating its applicability within any transformer block. (c) provides a step-by-step breakdown of the NegToMe process, which involves semantic token matching, thresholding for similarity, and linear extrapolation to push source tokens away from target tokens. More details can be found in Section 3 and Algorithm 1 of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 3: Method Overview. (a) The core idea of NegToMe is to perform adversarial guidance directly using visual features from a reference image (or other images in the same batch). (b) NegToMe is simple and can be applied in any transformer block. (c) A simple three step process for performing adversarial guidance using NegToMe (refer Sec. 3 and Alg. 1 for the detailed implementation).

🔼 This figure presents a quantitative analysis of the impact of NegToMe on the diversity and quality of generated images using two different diffusion models, SDXL and FLUX. The results are shown across a range of Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) scales. Lower DreamSim scores indicate improved diversity, while higher Entropy values also suggest increased diversity. Simultaneously, lower FID (Fréchet Inception Distance) and higher IS (Inception Score) demonstrate that NegToMe either maintains or enhances the quality of the generated images.
read the caption
Figure 4: Quantitative Results for Output Diversity. NegToMe (ours) helps improve output diversity (lower DreamSim score and higher Entropy) while preserving or improving quality (lower FID and higher IS) across different CFG scales for both SDXL and FLUX.

🔼 Figure 5 showcases the impact of NegToMe on enhancing the diversity of generated images. By using NegToMe with other images from the same batch (specifically, the first image in each batch), the model produces a wider range of outputs in terms of race, ethnicity, and overall visual style. Importantly, this increased diversity is achieved without sacrificing the quality of the generated images.
read the caption
Figure 5: Increasing Output Diversity. We observe that when performed w.r.t to images in the same batch (the first image of each batch in above), NegToMe significantly improves output diversity (racial, ethnic, visual) while preserving output image quality.

🔼 Figure 6 presents a comparison of image generation results using different methods. The top row shows images generated with a base prompt, while the second row shows images generated with NegToMe applied to the base prompt. The third row shows images generated with a prompt rewritten using GPT-4, and the fourth row presents images generated with NegToMe combined with a GPT-4 rewritten prompt. This illustrates that NegToMe improves image diversity both when used with and without explicit prompt rewriting.
read the caption
Figure 6: NegToMe helps improve output diversity both with (row-2) and without explicit prompt-rewriting (PW) (row-4).
Full paper#