↗ arXiv ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Papers with Code
TL;DR#
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
High-resolution image and video synthesis is a crucial area in generative AI. This paper offers a significant advancement by enabling the generation of high-fidelity 8k images and improved-quality videos from pre-trained models without fine-tuning. It addresses the limitations of current models that struggle with high resolutions, opening new possibilities for various applications. The tuning-free nature of the method makes it widely accessible. The fusion of multi-scale information and frequency extraction offers a novel approach to high-resolution generation. This research paves the way for future research in controllable detail generation.
Visual Insights#

🔼 FreeScale successfully generates images up to 8k resolution, while the baseline model SDXL can only generate images with a resolution of 1024x1024 without quality loss. The examples showcase various image generation prompts including a blue unicorn, an astronaut on mars, a chihuahua in an astronaut suit, and a woman’s body.
read the caption
Figure 1: Gallery of FreeScale. Original SDXL citesdxl can only generate images with a resolution of up to 10242superscript102421024^{2}1024 start_POSTSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_POSTSUPERSCRIPT without losing quality, while FreeScale successfully extends SDXL to generate 81922superscript819228192^{2}8192 start_POSTSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_POSTSUPERSCRIPT images without any fine-tuning. All generated images are produced using a single A800 GPU. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.
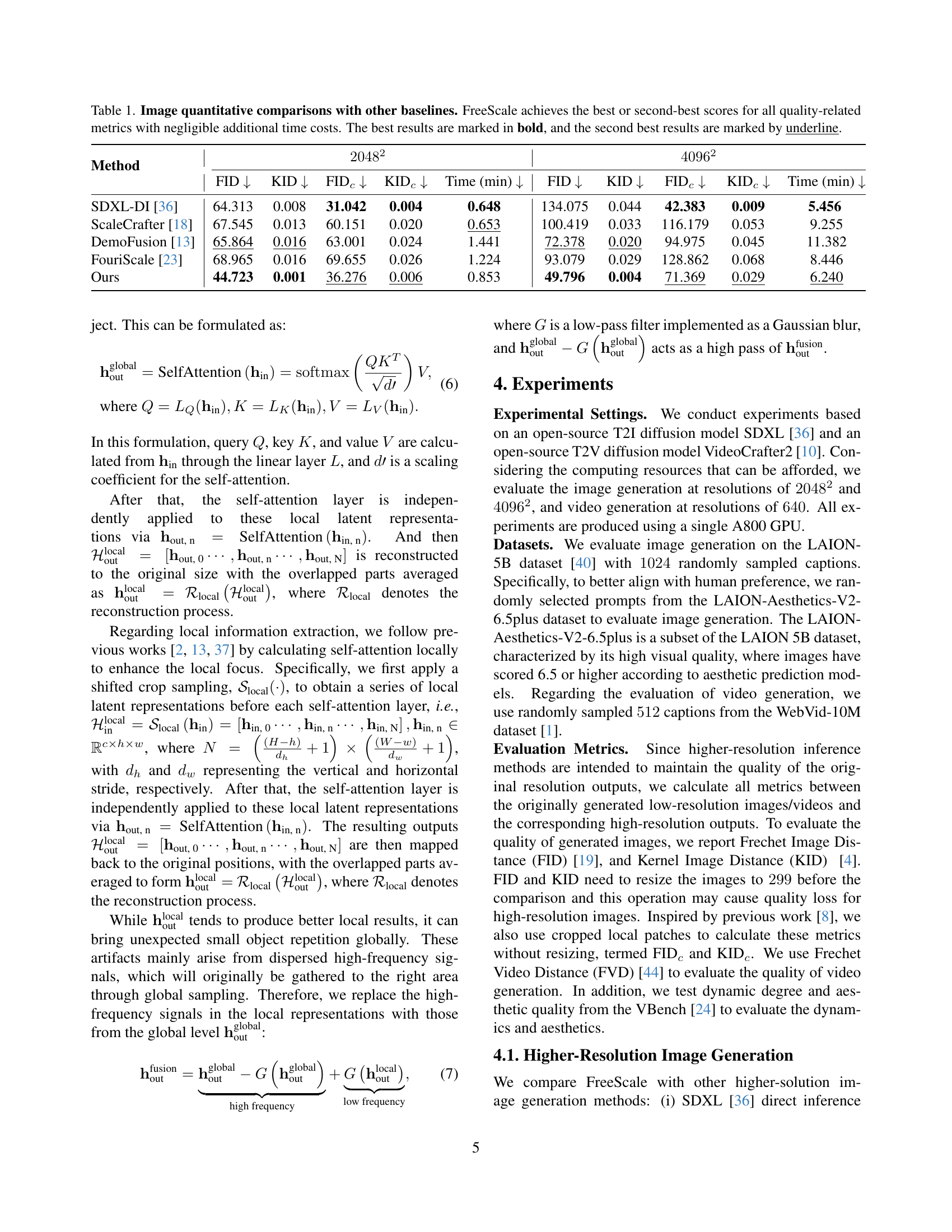
| Method | 2048² | 4096² | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FID ↓ | KID ↓ | FIDc ↓ | KIDc ↓ | Time (min) ↓ | FID ↓ | KID ↓ | FIDc ↓ | KIDc ↓ | Time (min) ↓ | |
| SDXL-DI [36] | 64.313 | 0.008 | 31.042 | 0.004 | 0.648 | 134.075 | 0.044 | 42.383 | 0.009 | 5.456 |
| ScaleCrafter [18] | 67.545 | 0.013 | 60.151 | 0.020 | 0.653 | 100.419 | 0.033 | 116.179 | 0.053 | 9.255 |
| DemoFusion [13] | 65.864 | 0.016 | 63.001 | 0.024 | 1.441 | 72.378 | 0.020 | 94.975 | 0.045 | 11.382 |
| FouriScale [23] | 68.965 | 0.016 | 69.655 | 0.026 | 1.224 | 93.079 | 0.029 | 128.862 | 0.068 | 8.446 |
| Ours | 44.723 | 0.001 | 36.276 | 0.006 | 0.853 | 49.796 | 0.004 | 71.369 | 0.029 | 6.240 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of our proposed FreeScale model with other baseline methods for higher-resolution image generation, using FID, KID, and inference time as metrics. It demonstrates FreeScale’s superior or competitive performance across different resolutions (2048² and 4096²) with minimal extra time cost.
read the caption
Table 1: Image quantitative comparisons with other baselines. FreeScale achieves the best or second-best scores for all quality-related metrics with negligible additional time costs. The best results are marked in bold, and the second best results are marked by underline.
In-depth insights#
Resolution Limits#
Resolution limits in current diffusion models primarily stem from training data limitations and computational constraints. While models excel at generating lower resolution outputs, extending to higher resolutions often introduces quality degradation, like repetitive patterns or blurry details. This limitation arises from the model’s receptive field and the information it can process. Upscaling methods partially address this by introducing a cascaded approach and fusing multi-scale information, but they still rely on the base model’s knowledge, and there are inherent limits to how far resolution can be pushed without distorting content. Future research must focus on improving the model’s ability to handle high-frequency details at scale.
Scale Fusion#
Scale Fusion is a key innovation for enhancing resolution in visual generation. It addresses limitations of previous methods like local repetitions in ScaleCrafter and small object repetitions in DemoFusion. By combining information from both global and local receptive scales, Scale Fusion refines details while maintaining structural coherence. The method extracts desired frequency components, fusing high-frequency details from global attention with low-frequency semantics from local attention. Notably, this fusion is within the self-attention layer, minimizing computational overhead. This approach allows FreeScale to generate higher resolution images with better quality.
Tuning-Free Upscaling#
Tuning-free upscaling methods for diffusion models aim to generate high-resolution images or videos without retraining. Existing techniques encounter challenges such as repetitive patterns and distortions. Addressing these issues requires innovative approaches like scale fusion, which combines information from different receptive fields. Methods like FreeScale address these limitations by extracting and combining frequency components, enabling high-fidelity generation of details without compromising overall structure. This approach allows leveraging pre-trained models to generate content at resolutions far exceeding their original training data, pushing the boundaries of image and video synthesis. Future work involves extending these capabilities to newer architectures and even higher resolutions.
8K Image Gen.#
FreeScale pushes image generation boundaries, achieving unprecedented 8K resolution. It leverages a novel scale fusion method, combining global and local information to enhance details without structural compromise or object repetition. This surpasses existing methods like ScaleCrafter and DemoFusion, which struggle with local or small-object repetitions. While computationally intensive, FreeScale offers flexible detail control, allowing targeted enhancements. It remains limited by base model knowledge and primarily supports UNet architectures, but opens doors for future ultra-high-resolution content creation.
Detail Control#
Detail control in image generation is crucial for achieving high fidelity and realism, especially at higher resolutions. Fine-grained control over details allows for the creation of intricate textures, patterns, and sharp features, enhancing the overall visual appeal. However, achieving precise detail control presents several challenges. Balancing global coherence with local details is essential to avoid artifacts and inconsistencies. Overemphasis on details can lead to noise and artifacts, while neglecting them results in blurry or unrealistic outputs. Therefore, sophisticated techniques are required to effectively manage details, preserving structural integrity while enhancing visual richness. Adaptive methods that vary detail levels based on image content or semantic regions can further enhance realism and artistic control. Efficient implementation of these techniques is also critical for practical applications, particularly when dealing with high-resolution images and videos.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 FreeScale enhances resolution of diffusion models via a two-step process: 1) Tailored Self-Cascade Upscaling: Initial denoising at training resolution, followed by upscaling and adding noise to higher-resolution latent, refined with restrained dilated convolution and region-aware detail control. 2) Scale Fusion: Combining global and local attention, Gaussian blur fuses details from global attention with semantics from local attention, producing the final self-attention output.
read the caption
Figure 2: Overall framework of FreeScale. (a) Tailored Self-Cascade Upscaling. FreeScale starts with pure Gaussian noise and progressively denoises it using the training resolution. An image is then generated via the VAE decoder, followed by upscaling to obtain a higher-resolution one. We gradually add noise to the latent of this higher-resolution image and incorporate this forward noise into the denoising process of the higher-resolution latent with the use of restrained dilated convolution. Additionally, for intermediate latent steps, we enhance high-frequency details by applying region-aware detail control using masks derived from the image. (b) Scale Fusion. During denoising, we adapt the self-attention layer to a global and local attention structure. By utilizing Gaussian blur, we fuse high-frequency details from global attention and low-frequency semantics from local attention, serving as the final output of the self-attention layer.

🔼 Qualitative comparison of FreeScale-generated images at 2048x2048 and 4096x4096 resolutions with other baseline models. FreeScale demonstrates superior image quality with better content coherence and richer local details.
read the caption
Figure 3: Image qualitative comparisons with other baselines. Our method generates both 20482superscript204822048^{2}2048 start_POSTSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_POSTSUPERSCRIPT and 40962superscript409624096^{2}4096 start_POSTSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_POSTSUPERSCRIPT vivid images with better content coherence and local details. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.

🔼 This figure showcases the impact of FreeScale’s flexible detail control on generated images. By adjusting coefficient weights assigned to specific regions within an image during generation, users can enhance or diminish the prominence of details in those areas. Specifically, in this example, increasing the coefficient weight on the Griffons and decreasing it elsewhere yields a superior visual result with more pronounced details on the creatures and a less detailed background. This demonstrates the granularity of control offered by FreeScale for tailoring generated image outputs.
read the caption
Figure 4: Qualitative results of flexible control for detail level. A better result will be generated by adding the coefficient weight in the area of Griffons and reducing the coefficient weight in the other regions. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.

🔼 Qualitative comparison of video generation between FreeScale and baseline methods (VC2-DI, ScaleCrafter, DemoFusion). FreeScale successfully generates high-resolution and high-fidelity videos, while the other methods fail, producing artifacts such as duplicated objects or local/small object repetitions, and blurry or distorted videos with strange patterns. The resolution of the videos generated by VC2-DI and VideoCrafter2 is 320x512 pixels. The two prompts used are: (1) ‘A chihuahua in an astronaut suit floating in space, cinematic lighting, glow effect.’, (2) ‘A bear running in the ruins, photorealistic, 4k, high definition.’
read the caption
Figure 5: Video qualitative comparisons with other baselines. While other baselines fail in video generation, FreeScale effectively generates higher-resolution videos with high fidelity. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.

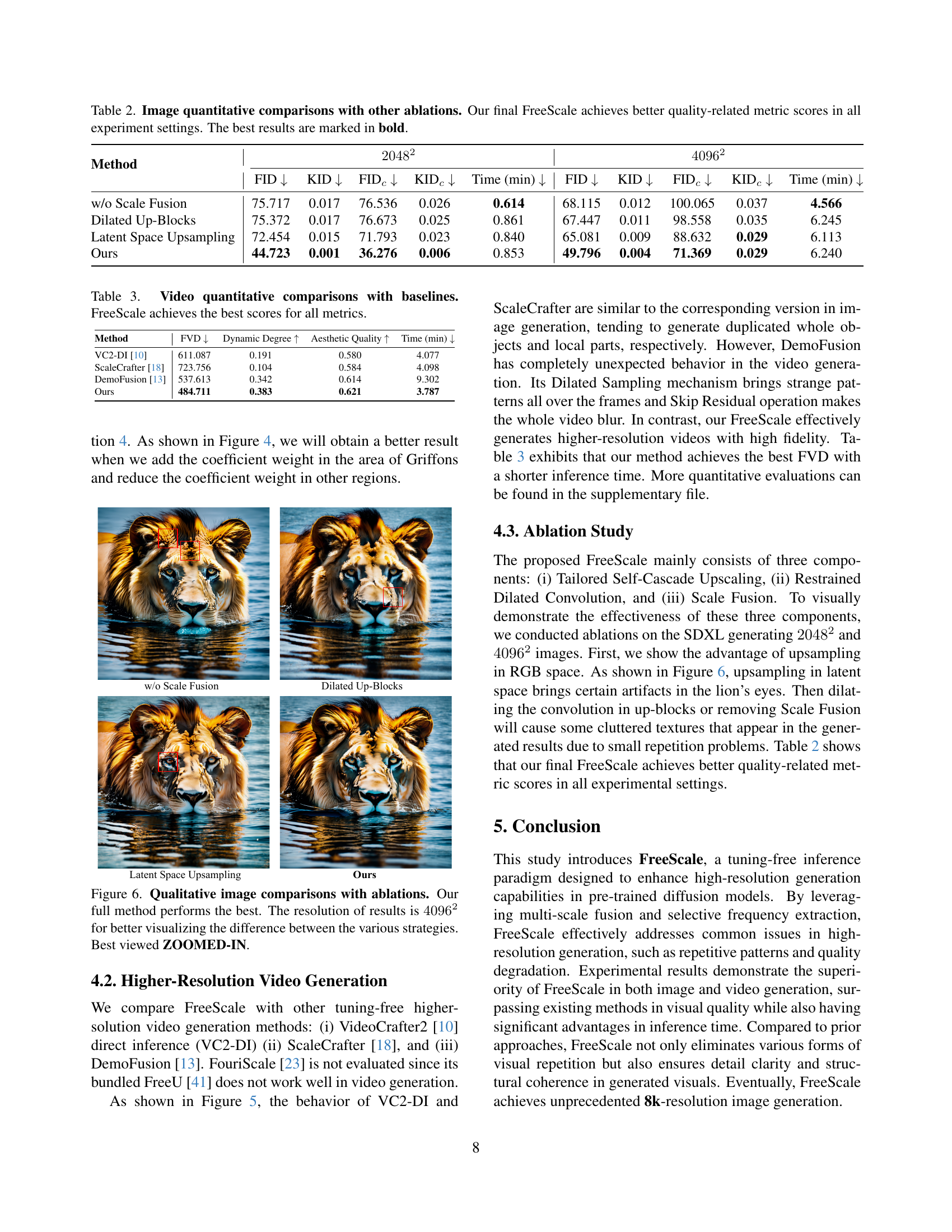
🔼 This figure shows qualitative results of 4096x4096 resolution image generation with different FreeScale ablations. It includes the results of removing Scale Fusion, applying dilated convolution to up-blocks, and using latent space upsampling, compared to the full FreeScale method. The comparison visually demonstrates the improved quality and reduced artifacts achieved by the complete FreeScale approach.
read the caption
Figure 6: Qualitative image comparisons with ablations. Our full method performs the best. The resolution of results is 40962superscript409624096^{2}4096 start_POSTSUPERSCRIPT 2 end_POSTSUPERSCRIPT for better visualizing the difference between the various strategies. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.

🔼 Close-up views of an 8k resolution image generated by FreeScale, comparing the upscaled image to the original lower resolution input. The bottom row specifically highlights how FreeScale regenerates facial details that were originally blurry and poorly defined in the lower resolution version, demonstrating improved clarity and detail at 8k. This showcases FreeScale’s ability to enhance existing images by extrapolating details based on learned priors, rather than simply upscaling the existing information.
read the caption
Figure 7: Zoomed in details for the 8k image. FreeScale may regenerate the original blurred areas at low resolution based on the prior knowledge that the model has learned. As shown in the bottom row, two originally chaotic and blurry faces are clearly outlined at 8k resolution. Best viewed ZOOMED-IN.
More on tables
| Method | 2048² | 4096² | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FID ↓ | KID ↓ | FIDc ↓ | KIDc ↓ | Time (min) ↓ | FID ↓ | KID ↓ | FIDc ↓ | KIDc ↓ | Time (min) ↓ | |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| w/o Scale Fusion | 75.717 | 0.017 | 76.536 | 0.026 | 0.614 | 68.115 | 0.012 | 100.065 | 0.037 | 4.566 |
| Dilated Up-Blocks | 75.372 | 0.017 | 76.673 | 0.025 | 0.861 | 67.447 | 0.011 | 98.558 | 0.035 | 6.245 |
| Latent Space Upsampling | 72.454 | 0.015 | 71.793 | 0.023 | 0.840 | 65.081 | 0.009 | 88.632 | 0.029 | 6.113 |
| Ours | 44.723 | 0.001 | 36.276 | 0.006 | 0.853 | 49.796 | 0.004 | 71.369 | 0.029 | 6.240 |
🔼 This table compares the performance of different versions of FreeScale, including the full model and versions with some components removed (ablated). The comparison uses FID and KID metrics at 2048x2048 and 4096x4096 resolutions, along with inference time. Lower FID and KID values indicate better image quality. The goal is to show that each component of FreeScale contributes to the final performance improvement by demonstrating lower FID and KID scores when using the full method.
read the caption
Table 2: Image quantitative comparisons with other ablations. Our final FreeScale achieves better quality-related metric scores in all experiment settings. The best results are marked in bold.
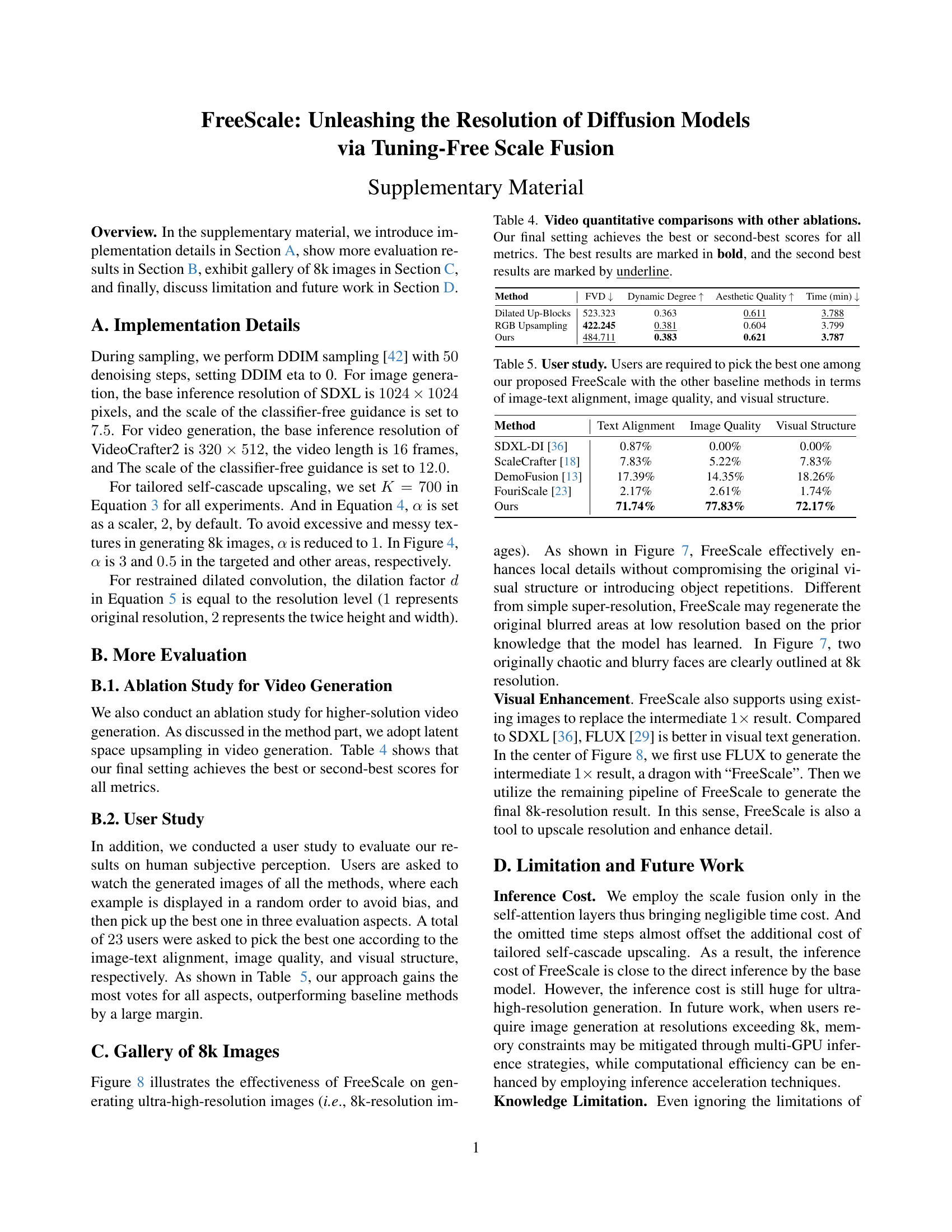
| Method | FVD ↓ | Dynamic Degree ↑ | Aesthetic Quality ↑ | Time (min) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VC2-DI [10] | 611.087 | 0.191 | 0.580 | 4.077 |
| ScaleCrafter [18] | 723.756 | 0.104 | 0.584 | 4.098 |
| DemoFusion [13] | 537.613 | 0.342 | 0.614 | 9.302 |
| Ours | 484.711 | 0.383 | 0.621 | 3.787 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of FreeScale and other tuning-free higher-solution video generation methods, including VideoCrafter2 direct inference (VC2-DI), ScaleCrafter, and DemoFusion. The table reports Frechet Video Distance (FVD), Dynamic Degree, Aesthetic Quality, and inference time (in minutes) to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of each method. FreeScale consistently outperforms competitors, achieving the best scores across all metrics.
read the caption
Table 3: Video quantitative comparisons with baselines. FreeScale achieves the best scores for all metrics.
| Method | FVD ↓ | Dynamic Degree ↑ | Aesthetic Quality ↑ | Time (min) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilated Up-Blocks | 523.323 | 0.363 | 0.611 | 3.788 |
| RGB Upsampling | 422.245 | 0.381 | 0.604 | 3.799 |
| Ours | 484.711 | 0.383 | 0.621 | 3.787 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of our proposed FreeScale method for higher-resolution video generation with different ablated versions. We used Frechet Video Distance (FVD), dynamic degree and aesthetic quality metrics from VBench benchmark to assess the quality of generated videos. Lower FVD indicates better performance. Our final configuration outperforms baseline methods in terms of best and second-best scores for all the selected quality metrics.
read the caption
Table 4: Video quantitative comparisons with other ablations. Our final setting achieves the best or second-best scores for all metrics. The best results are marked in bold, and the second best results are marked by underline.
| Method | Text Alignment | Image Quality | Visual Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDXL-DI [36] | 0.87% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| ScaleCrafter [18] | 7.83% | 5.22% | 7.83% |
| DemoFusion [13] | 17.39% | 14.35% | 18.26% |
| FouriScale [23] | 2.17% | 2.61% | 1.74% |
| Ours | 71.74% | 77.83% | 72.17% |
🔼 This table presents a user study comparing FreeScale with other higher-solution image generation models — SDXL-DI, ScaleCrafter, DemoFusion, and FouriScale. 23 users evaluated the generated images based on three criteria: image-text alignment, image quality, and visual structure. Participants selected the best image among the presented methods for each criterion. The table shows the percentage of votes each method received for each evaluation aspect.
read the caption
Table 5: User study. Users are required to pick the best one among our proposed FreeScale with the other baseline methods in terms of image-text alignment, image quality, and visual structure.
Full paper#