↗ arXiv ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Papers with Code
TL;DR#
Current text-to-video models struggle to generate videos with transparency (RGBA videos), primarily due to a lack of suitable datasets and the difficulty in adapting existing models to handle alpha channels. Alpha channels are crucial for special effects (VFX) as they allow for seamless blending of transparent elements into scenes. Existing approaches, like generating RGB first, then predicting alpha separately, often suffer from poor alignment and insufficient detail in challenging scenarios.
TransPixar directly addresses these issues by leveraging a diffusion transformer architecture and incorporating a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism. The key innovation is jointly generating RGB and alpha channels within the same model, enabling better alignment and consistency. This is achieved by optimizing attention mechanisms and employing LoRA-based fine-tuning. The results demonstrate that TransPixar generates high-quality, diverse RGBA videos while maintaining the strengths of the original RGB model. The code for the project is also publicly available, making it easier for other researchers to reproduce the results and further advance the field.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it addresses a significant challenge in text-to-video generation: creating videos with transparency. Its novel approach of jointly generating RGB and alpha channels offers a significant improvement over existing methods that struggle with alpha prediction and alignment. This work opens up new possibilities for VFX, AR/VR, and other applications requiring transparent elements in videos, and provides a strong foundation for future research in this area. The research also meticulously analyzes the attention mechanisms, offering valuable insights that can guide future developments in video generation.
Visual Insights#

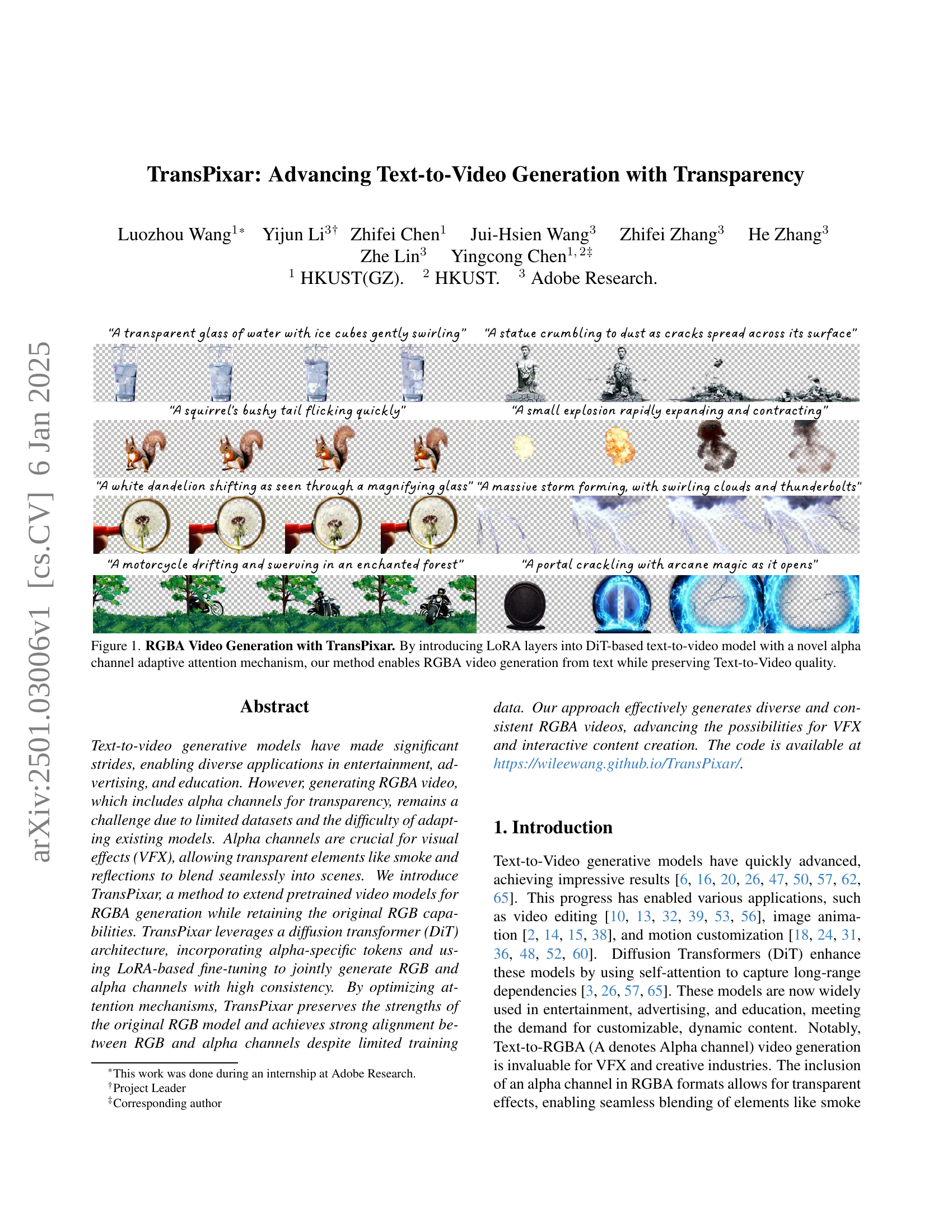
🔼 Figure 1 showcases the capabilities of TransPixar in generating RGBA videos from textual descriptions. TransPixar integrates Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) layers into a Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based text-to-video model. A key innovation is the inclusion of a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism which allows for the simultaneous and consistent generation of both RGB (red, green, blue) and alpha (transparency) video channels. The result is high-quality RGBA videos that maintain the visual fidelity of the original text-to-video model, enabling the seamless integration of transparent elements into generated video scenes.
read the caption
Figure 1: RGBA Video Generation with TransPixar. By introducing LoRA layers into DiT-based text-to-video model with a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism, our method enables RGBA video generation from text while preserving Text-to-Video quality.
| RGBA Alignment | Motion Quality | |
|---|---|---|
| AnimateDiff [16]+LayerDiff [64] | 6.7% | 21.7% |
| Ours + CogVideoX [57] | 93.3% | 78.3% |
🔼 This table presents the results of a user study comparing two different methods for generating RGBA videos. The study evaluated two key aspects of the generated videos: 1) the alignment between the RGB and alpha channels (how well they match), and 2) the quality of the motion in the videos (how well the motion matches the intended description in the text prompt). The table shows the percentage of users who rated each method positively for each aspect.
read the caption
Table 1: User Study.
In-depth insights#
RGBA VideoGen#
RGBA VideoGen represents a significant advancement in text-to-video generation by enabling the creation of videos with transparency. This functionality, achieved by incorporating alpha channels, opens exciting possibilities for various applications. The core challenge addressed is the scarcity of RGBA video data for training. The proposed approach cleverly leverages pretrained RGB video models, extending their capabilities through innovative techniques such as alpha-specific tokens and LoRA-based fine-tuning. The key to success lies in a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism that ensures high consistency between RGB and alpha channels, preserving the quality of the original RGB model while significantly enhancing its capabilities. This demonstrates a resource-efficient approach, as it avoids the need to train a separate model from scratch. The successful handling of diverse and complex visual effects such as smoke and reflections also highlights the robustness and potential of this innovative method for applications demanding high-quality visual effects and seamless integration with existing content. The research provides a thoughtful analysis of attention mechanisms crucial to the success of RGBA video generation, leading to a refined model that carefully manages information flow. The experimental results showcase that this method surpasses existing techniques, proving its effectiveness and advancement in the field.
TransPixar Model#
The hypothetical “TransPixar Model” presented in the research paper focuses on advancing text-to-video generation with transparency, a significant challenge in the field. The core idea revolves around extending pre-trained RGB video generation models to produce RGBA videos, which incorporate an alpha channel for transparency effects. Key innovations include the introduction of alpha-specific tokens and a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism. The model uses a diffusion transformer architecture, and leverages low-rank adaptation (LoRA) for fine-tuning, effectively preserving the quality of the original RGB model while generating consistent and high-quality alpha channels. The significance lies in the ability to generate diverse and realistic RGBA videos for various applications, including VFX and interactive content creation, which were previously hindered by the limited availability of RGBA video datasets. Further analysis focuses on attention mechanisms within the model to ensure optimal alignment and quality between RGB and alpha channels. The effectiveness of this model is demonstrated through various experiments and a user study, highlighting the improvements over generation-then-prediction methods.
Attention Analysis#
The core of the paper’s contribution lies in its novel approach to attention mechanisms for joint RGB-alpha video generation. The authors meticulously analyze the interplay between different attention components, focusing on the impact of various attention paths on the final RGBA output. This in-depth analysis reveals crucial insights into how information flows between text, RGB, and alpha tokens. The study highlights the importance of RGB-attend-to-alpha attention, emphasizing its role in refining RGB tokens based on alpha information and ensuring strong RGB-alpha alignment. Conversely, the authors demonstrate that text-attend-to-alpha attention is detrimental, potentially due to the limited training data and the significant domain gap between the modalities, leading to decreased generation quality. By strategically removing the detrimental attention while preserving the beneficial ones, the authors improve the model’s performance and maintain consistency between the RGB and alpha channels. This targeted approach to attention rectification is a key innovation, effectively leveraging the pretrained model’s strengths while adapting it for the new RGBA generation task.
Ablation Study#
The ablation study systematically evaluates the contribution of different components within the proposed TransPixar model. By selectively removing or modifying specific parts—such as attention mechanisms and network designs—the researchers isolate their individual effects on the overall performance. This process is crucial for understanding the model’s strengths and weaknesses. The results reveal the importance of the RGB-to-Alpha attention mechanism for achieving high-quality alignment between RGB and alpha channels, highlighting the effectiveness of the proposed joint generation approach over the typical generation-then-prediction method. Furthermore, it demonstrates that unnecessary attention pathways, like Text-to-Alpha, can negatively impact performance. The findings confirm the design choices made, validating the model’s architecture and contributing to its overall success.
Future of RGBA#
The future of RGBA in text-to-video generation hinges on overcoming current data limitations. The scarcity of readily available RGBA video datasets significantly hampers model training and generalization. Future progress will require larger, more diverse datasets, potentially through synthetic data generation or improved annotation techniques. Furthermore, algorithmic advancements are needed to efficiently and effectively handle the complexities of jointly generating both RGB and alpha channels. This may involve novel attention mechanisms, improved loss functions, or alternative model architectures. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve high-quality, seamless integration of transparent elements in videos generated from text prompts, unlocking potential for enhanced realism in VFX, animation, and interactive media. Real-time RGBA video generation also remains a key aspiration, requiring optimization of existing models and perhaps the development of entirely new approaches. Efficient training strategies will be crucial for handling the increased computational demands of RGBA video generation.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 This figure compares three different approaches to generating RGBA (Red, Green, Blue, Alpha) videos. The first method (b) uses a generation-then-prediction approach. It first generates an RGB video (a), then uses a video matting technique to predict the alpha channel (top of (b)) representing transparency. The result of combining the RGB and the predicted alpha channel is shown in the bottom of (b). The second method (c) also uses a generation-then-prediction approach, but instead uses a generative model that includes a prior for transparency (MariGold or Lotus model). Its alpha channel and composite are shown in the top and bottom of (c). The third method (d) demonstrates the authors’ proposed joint generation approach, where RGB and alpha channels are generated simultaneously. This produces the jointly generated alpha channel and the final composite result shown in the top and bottom of (d). The figure visually demonstrates that the joint generation approach (d) achieves better consistency and alignment between the RGB and alpha channels than the generation-then-prediction approaches (b, c).
read the caption
Figure 2: Comparison between Generation-Then-Prediction and our Joint Generation approach. Given the generated RGB in (a), (b) and (c) show the predicted alpha (top) and the composited result (bottom). In (d), the top shows the jointly generated alpha.

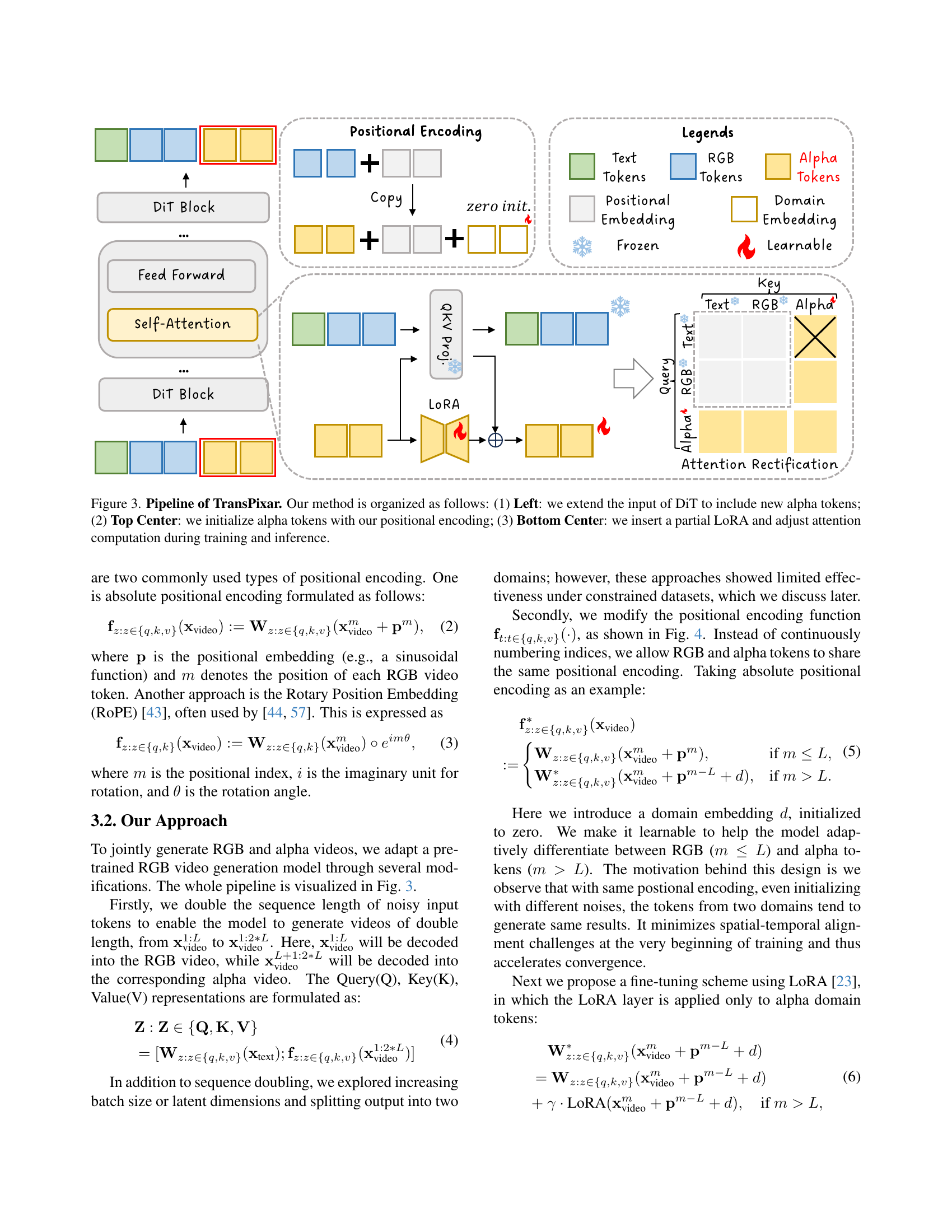
🔼 TransPixar’s architecture modifies a pre-trained Diffusion Transformer (DiT) model for generating RGBA videos. The figure details three key steps: (1) extending the input sequence to include alpha tokens alongside the text and RGB tokens; (2) initializing these alpha tokens with a custom positional encoding; and (3) incorporating a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) layer and adjusting the attention mechanism during training to ensure the model effectively learns to generate consistent RGB and alpha channels.
read the caption
Figure 3: Pipeline of TransPixar. Our method is organized as follows: (1) Left: we extend the input of DiT to include new alpha tokens; (2) Top Center: we initialize alpha tokens with our positional encoding; (3) Bottom Center: we insert a partial LoRA and adjust attention computation during training and inference.

🔼 This figure compares different positional encoding strategies for generating RGBA videos. It shows that using the same positional encoding for both RGB and alpha channels leads to faster model convergence during training. Specifically, after 1000 training iterations, the model trained with the shared positional encoding shows improved performance compared to models trained with other encoding strategies. This suggests that this approach helps align the RGB and alpha channels effectively, leading to more efficient and potentially higher-quality RGBA video generation.
read the caption
Figure 4: Positional Encoding Design for RGBA Generation. Assigning alpha tokens the same positional encoding as RGB yields similar results, resulting in faster convergence after 1000 iterations compared to standard encoding strategies.

🔼 This figure demonstrates the impact of different attention mechanisms on the quality and alignment of generated RGBA videos. Panel (a) shows that removing all attention from the alpha channel as a key input maintains the quality of RGB generation but results in a misalignment between the RGB and alpha channels. Panel (b) illustrates that including all possible attention paths significantly reduces the overall video quality and causes a loss of motion. Panel (c) displays the results of the proposed method that achieves a balance between preserving the original RGB video quality and generating a well-aligned alpha channel.
read the caption
Figure 5: Attention Rectification. (a) Eliminating all attention from alpha as a key preserves 100% RGB generation but leads to poor alignment. (b) Retaining all attention significantly degrades quality, causing a lack of motion in bicycles. (c) Our method achieves an effective balance.

🔼 This figure showcases the applications of TransPixar in two scenarios: text-to-video generation and image-to-video generation, both incorporating transparency. The top row displays examples of text prompts used to generate videos, demonstrating the model’s capability to produce videos with transparent elements. The bottom row illustrates the generation of videos from input images, also highlighting the ability to produce transparent effects in these scenarios.
read the caption
Figure 6: Applications. Top: Text-to-Video with Transparency. Bottom: Image-to-Video generation with transparency. .

🔼 Figure 7 compares the results of TransPixar with two other approaches for generating RGBA videos: a generation-then-prediction pipeline using video matting (Lotus + RGBA and SAM-2). TransPixar demonstrates better alignment between the generated RGB and alpha channels, resulting in more realistic and seamlessly integrated transparent elements.
read the caption
Figure 7: Comparison with Generation-then-Prediction Pipelines. Our method demonstrates superior alignment.

🔼 Figure 8 compares the results of two different approaches to generating RGBA videos: LayerDiffusion combined with AnimateDiff (top) and the authors’ proposed TransPixar method (bottom). The comparison highlights the superior alignment between RGB and alpha channels achieved by TransPixar, as well as its ability to more accurately generate motion consistent with the text prompts used to generate the videos. The image shows several example videos created with each method, illustrating the differences in alpha channel quality and motion consistency.
read the caption
Figure 8: Comparison with Joint Generation Pipelines. Top: LayerDiffusion + AnimateDiff; Bottom: Ours. Our method achieves better alignment and generates corresponding motion described by prompts.

🔼 Figure 9 explores different architectural approaches for jointly generating RGB and alpha video channels within a Diffusion Transformer (DiT) framework. It compares three variations: (a) batch extension, (b) sequence extension (the authors’ proposed method), and (c) latent dimension extension. Each approach modifies the input to the DiT model differently to handle both RGB and alpha information, aiming to achieve consistent and high-quality joint generation. The figure highlights how the authors’ chosen sequence extension method (b) integrates alpha information by extending the input sequence length, facilitating the generation of both RGB and alpha videos simultaneously within the same DiT architecture.
read the caption
Figure 9: Alternative Designs for Joint Generation with DiT. Sequence extension (b) represents our method.

🔼 This ablation study analyzes the impact of different design choices and attention mechanisms on the performance of the TransPixar model for generating RGBA videos. The results demonstrate the importance of the RGB-attend-to-Alpha attention mechanism for achieving good alignment between the RGB and Alpha channels, while maintaining high quality motion generation. Removing this mechanism leads to misalignment, while adding the Text-attend-to-Alpha mechanism introduces interference and negatively impacts quality. Alternative strategies for handling batch size and latent dimension are also evaluated, showcasing the effectiveness of the proposed sequence extension approach. Specific examples include the generation of butterflies, where the quality of wing movement is used to illustrate successful or unsuccessful alignment between the generated RGB and Alpha components.
read the caption
Figure 10: Ablation Study. (a) Ours; (b) Ours without RGB-attend-to-Alpha; (c) Ours with Text-attend-to-alpha; (d) Batch Extension Strategy; (e) Latent Dimension Extension Strategy. Our method maintains high-quality motion generation (e.g., butterflies waving their wings) while achieving good alignment.
Full paper#