↗ arXiv ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Papers with Code
TL;DR#
Many Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) primarily use English data, limiting their effectiveness with non-English inputs and outputs. Existing work tries to fix this by adding more multilingual data, but it’s often done without a clear strategy, leading to inconsistent results. This study explores different approaches to improve LVLMs’ multilingual capabilities.
The researchers systematically investigated optimal multilingual training strategies using various language combinations and data distributions for both pre-training and instruction tuning. They introduced a new benchmark for multilingual text-in-image understanding and found that including large numbers of training languages (up to 100) can greatly improve multilingual performance without harming English performance. They also determined the optimal balance between English and non-English training data, with a surprisingly high amount of non-English data being beneficial.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is crucial because it systematically investigates the optimal training strategies for multilingual Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), a critical area in the current AI research landscape. The findings challenge existing assumptions and offer valuable insights for researchers working to develop more inclusive and performant LVLMs. The novel benchmark introduced opens up new avenues for future research on multilingual text-in-image understanding, which is vital for improving the accessibility and usefulness of these powerful models.
Visual Insights#

🔼 This figure illustrates the key factors investigated in the paper to understand multilingual capabilities in large vision-language models (LVLMs). It’s broken down into three parts: (1) Training Data Languages: Shows a tiered structure of languages included in the training data, categorized from high to low-resource languages. This helps to visualize the different language mixes used in experiments. (2) Language Data Distribution: Illustrates different proportions of English versus multilingual data in the training. It demonstrates how altering this ratio affects the model’s performance. (3) Multilingual Text in Images: Presents examples of how multilingual text is incorporated into images in the training data. This element specifically focuses on improving the model’s ability to understand OCR data from various languages. The figure is designed to show the various ways in which language is introduced in the data for LVLMs, aiming to improve multilingual performance.
read the caption
Figure 1: Exploring drivers of multilingual ability: (1) Languages in the training data; (2) Distribution of languages in the training data; (3) Incorporating multilingual OCR samples to understand non-English text in images.
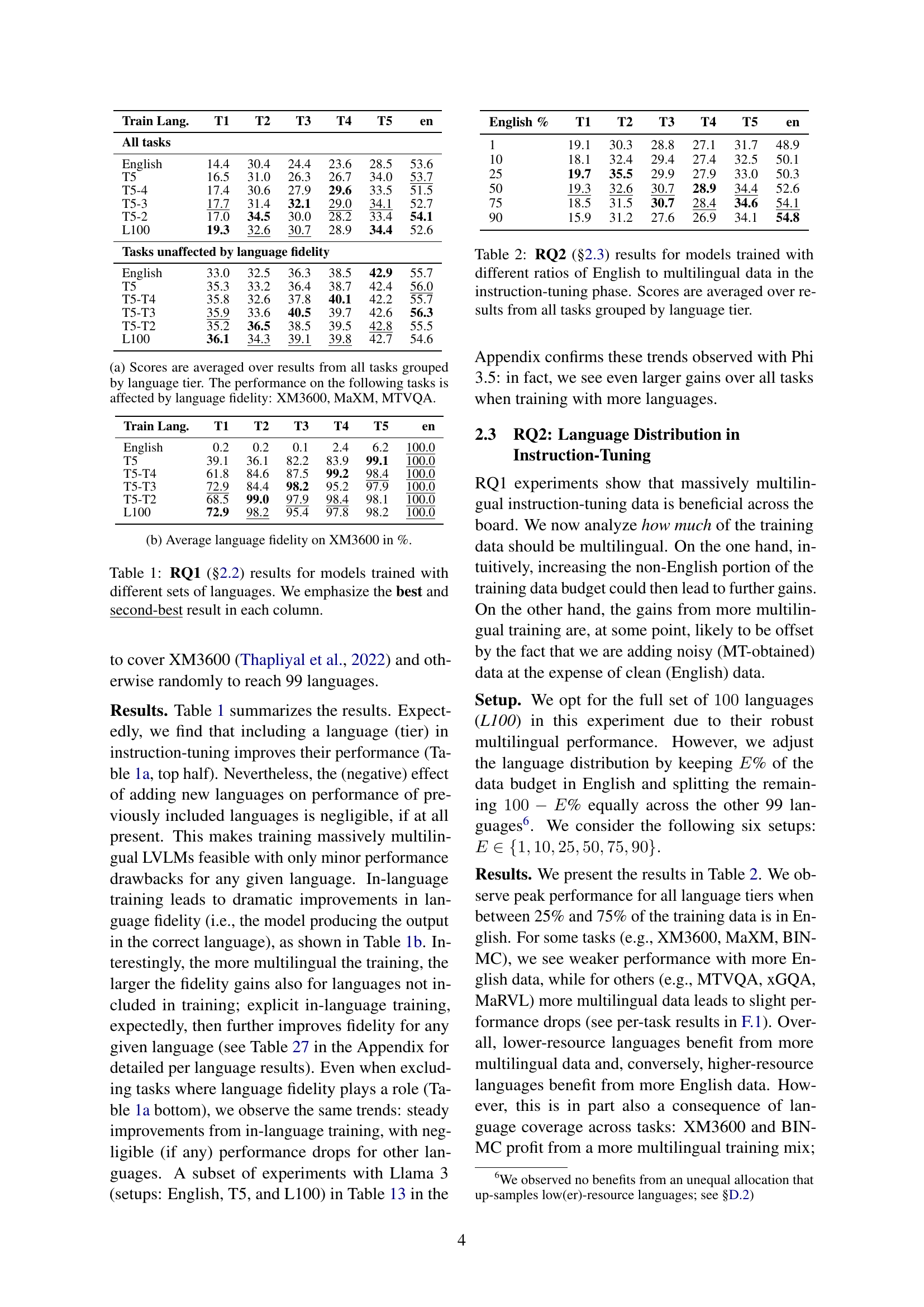
| Train Lang. | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All tasks | ||||||
| English | 14.4 | 30.4 | 24.4 | 23.6 | 28.5 | 53.6 |
| T5 | 16.5 | 31.0 | 26.3 | 26.7 | 34.0 | 53.7 |
| T5-4 | 17.4 | 30.6 | 27.9 | 29.6 | 33.5 | 51.5 |
| T5-3 | 17.7 | 31.4 | 32.1 | 29.0 | 34.1 | 52.7 |
| T5-2 | 17.0 | 34.5 | 30.0 | 28.2 | 33.4 | 54.1 |
| L100 | 19.3 | 32.6 | 30.7 | 28.9 | 34.4 | 52.6 |
| Tasks unaffected by language fidelity | ||||||
| English | 33.0 | 32.5 | 36.3 | 38.5 | 42.9 | 55.7 |
| T5 | 35.3 | 33.2 | 36.4 | 38.7 | 42.4 | 56.0 |
| T5-T4 | 35.8 | 32.6 | 37.8 | 40.1 | 42.2 | 55.7 |
| T5-T3 | 35.9 | 33.6 | 40.5 | 39.7 | 42.6 | 56.3 |
| T5-T2 | 35.2 | 36.5 | 38.5 | 39.5 | 42.8 | 55.5 |
| L100 | 36.1 | 34.3 | 39.1 | 39.8 | 42.7 | 54.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of an experiment evaluating the performance of models trained with different sets of languages. The scores represent an average across multiple tasks, grouped by language tier. It shows that for some tasks (XM3600, MaXM, MTVQA), language fidelity (accuracy of the generated language) is a significant factor influencing the overall score. This table is crucial for understanding the impact of language diversity in the training data on model performance.
read the caption
(a) Scores are averaged over results from all tasks grouped by language tier. The performance on the following tasks is affected by language fidelity: XM3600, MaXM, MTVQA.
In-depth insights#
Multilingual LVLM Training#
Multilingual Large Vision-Language Model (LVLM) training presents significant challenges and opportunities. A naive approach of simply adding multilingual data to an existing English-centric training pipeline often yields suboptimal results, a phenomenon sometimes called the “curse of multilingualism.” Effective multilingual LVLM training requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the optimal number of languages to include in the training set, the ideal distribution of data across languages, and the impact of different training strategies like pre-training and instruction-tuning. Research suggests that a surprisingly large number of languages can be included without significantly harming English performance, and that a balanced approach with a substantial portion of non-English data is beneficial. Furthermore, incorporating multilingual OCR data, particularly for instruction-tuning, can greatly improve performance on tasks involving text within images. Finding the optimal balance between data quantity and quality across many languages is crucial, as the cost of acquiring and processing high-quality multilingual data can be prohibitive. Ultimately, successful multilingual LVLM training hinges on a well-defined strategy that accounts for these multifaceted linguistic and computational complexities, leading to more robust and inclusive models.
Optimal Data Mixes#
The concept of “Optimal Data Mixes” in multilingual vision-language models (LVLMs) is crucial. The paper investigates the impact of various training data compositions on model performance across multiple languages. A key finding is that a balanced approach, rather than prioritizing English data, yields superior multilingual performance. The research explores the optimal proportion of English versus non-English data, suggesting a sweet spot where a significant portion of non-English data improves results without severely compromising English performance. Furthermore, the study delves into the optimal number of languages to include in training, highlighting a surprising finding: including a large number of languages can be beneficial. Finally, the role of instruction tuning data and the integration of multilingual OCR data are discussed, demonstrating that these can be critical factors for enhancing performance in lower-resource languages. The research emphasizes the need for careful consideration of data distribution and the absence of a one-size-fits-all solution. These findings have significant implications for training cost-effective and highly performant multilingual LVLMs.
OCR Data Impact#
The integration of OCR (Optical Character Recognition) data significantly impacts the performance of multilingual vision-language models (LVLMs). The study reveals that including even a small amount of synthetic multilingual OCR data during pre-training and instruction-tuning substantially improves the model’s ability to understand text within images, especially in low-resource languages. This improvement is particularly notable for Latin-script languages. However, the impact is less pronounced for languages with non-Latin scripts, suggesting a need for more extensive OCR data for these languages to achieve similar gains in performance. The findings highlight the importance of incorporating diverse and high-quality multilingual OCR data in training, emphasizing the trade-off between the quantity of data and its overall quality. While machine-translated data can be cost-effective, its inherent limitations necessitate a strategic balance between cost and accuracy. Therefore, a well-designed multilingual OCR data strategy is critical for building robust and effective LVLMs capable of handling various languages with varying levels of available data.
Centurio: A Case Study#
A hypothetical case study on Centurio would delve into its multilingual capabilities and the factors influencing its performance across various languages and tasks. It would likely involve a detailed analysis of Centurio’s architecture, training data, and evaluation metrics. The study would likely compare Centurio’s performance against other state-of-the-art multilingual vision-language models (LVLMs), highlighting its strengths and weaknesses in handling different language families and resource levels. It would also focus on the effect of different training strategies on performance, such as the optimal number of languages included in training and the distribution of the data across languages. A key aspect would be examining Centurio’s ability to handle text-in-image tasks effectively, as this is often a major challenge for multilingual LVLMs. This involves understanding the impact of training data with multilingual OCR samples and the overall performance improvements and cost-benefit analysis. Ultimately, the case study should provide valuable insights into the drivers of multilingual ability in LVLMs and offer recommendations for future research and development.
Future Research#
Future research directions stemming from this multilingual large vision-language model (LVLM) study should prioritize addressing the performance gap between Latin and non-Latin script languages in text-in-image understanding. This suggests a need for significantly more training data for non-Latin scripts, potentially through crowdsourcing or improved synthetic data generation techniques. Further investigation into optimal training data compositions beyond the 50/50 English/multilingual split explored here is also warranted, exploring the impact of varying data quality and language family representation. A crucial area for future work is rigorously evaluating the impact of machine translation on data quality, developing benchmarks that explicitly account for translation artifacts. Finally, this research could be extended by incorporating multicultural aspects into LVLM training, moving beyond language proficiency to encompass cultural knowledge and understanding in model outputs, better reflecting the complexity of human understanding.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 This figure details the prompts used for each dataset in the paper’s evaluation suite. It highlights the diversity of input types across different tasks. For instance, some tasks involve single images, while others require multiple images as inputs. Furthermore, the options within certain multiple-choice questions (e.g., M3Exam and xMMMU) can also include images. The figure provides a concise visualization of the variations in question design and the complexity of the visual and textual elements required for each task.
read the caption
Figure 2: Prompts used for the different datasets of our test suite. For M3Exam and xMMMU, the questions contain images at individual positions, and also the options can consist of images. In total, a sample of M3Exam can contain up to 8 images and 8 options, and a sample of xMMMU can contain up to 4 images and 4 options.

🔼 The figure shows two types of questions for a bar chart. Grounding questions verify the understanding of the chart’s structure, for example, identifying the tallest bar or the color of a specific bar. Reading questions test the ability to extract information from the chart, such as identifying the label of the tallest bar or the color of a specific bar. The example uses an English bar chart, but the paper states that the SMPQA dataset includes various languages and scripts.
read the caption
(a) Example of a bar plot in SMPQA for English. Questions for Grounding: 'Is the bar with label ’reward’ the biggest?', 'Is the bar with label ’incredible’ the biggest?', 'Is the bar with label ’reverse’ the smallest?', 'Is the bar with label ’sunset’ the smallest?', 'Is the bar with label ’closed’ colored in yellow?', 'Is the bar with label ’closed’ colored in purple?', 'Is the bar with label ’twitter’ colored in purple?', 'Is the bar with label ’twitter’ colored in red?' Questions for Reading: 'What is the label of the biggest bar?', 'What is the label of the smallest bar?', 'What is the label of the yellow bar?', 'What is the label of the red bar?', 'What is the label of the purple bar?'
More on tables
| Train Lang. | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 6.2 | 100.0 |
| T5 | 39.1 | 36.1 | 82.2 | 83.9 | 99.1 | 100.0 |
| T5-T4 | 61.8 | 84.6 | 87.5 | 99.2 | 98.4 | 100.0 |
| T5-T3 | 72.9 | 84.4 | 98.2 | 95.2 | 97.9 | 100.0 |
| T5-T2 | 68.5 | 99.0 | 97.9 | 98.4 | 98.1 | 100.0 |
| L100 | 72.9 | 98.2 | 95.4 | 97.8 | 98.2 | 100.0 |
🔼 This table presents the average language fidelity scores achieved by various multilingual large vision-language models (LVLMs) on the XM3600 dataset. Language fidelity refers to the model’s ability to generate outputs (image captions in this case) in the target language specified in the input prompt. The table shows how well each model can generate captions in the correct language for a range of languages, indicating the model’s multilingual performance level. Higher percentages indicate better language fidelity. The scores are broken down by language tiers (T1-T5) representing different language resource levels, with T5 being the high-resource languages and T1 being the low-resource languages. This allows for analysis of how the models perform across different language groups. The column ’en’ represents the English language results.
read the caption
(b) Average language fidelity on XM3600 in %.
| English % | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.1 | 30.3 | 28.8 | 27.1 | 31.7 | 48.9 |
| 10 | 18.1 | 32.4 | 29.4 | 27.4 | 32.5 | 50.1 |
| 25 | 19.7 | 35.5 | 29.9 | 27.9 | 33.0 | 50.3 |
| 50 | 28.9 | 52.6 | ||||
| 75 | 18.5 | 31.5 | 30.7 | 34.6 | ||
| 90 | 15.9 | 31.2 | 27.6 | 26.9 | 34.1 | 54.8 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments evaluating the impact of the number of training languages on the performance of large vision-language models (LVLMs). Different model configurations were trained with varying sets of languages, ranging from a small number to a large number (100). The table shows the performance of each model configuration on various downstream vision-language tasks, providing average scores across all tasks and per-language scores grouped by language resource tiers. The best and second-best performance in each column (task) are highlighted to show the relative gains from increasing the number of languages included in training. This helps in determining an optimal multilingual training mix without compromising performance on English, a common challenge in multilingual LVLMs.
read the caption
Table 1: RQ1 (§2.2) results for models trained with different sets of languages. We emphasize the best and second-best result in each column.
| English % | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No pre-training | 19.3 | 32.6 | 30.7 | 28.9 | 34.4 | 52.6 |
| 100 | 19.3 | 33.3 | 32.1 | 29.4 | 34.5 | 55.2 |
| 50 | 22.8 | 39.5 | 33.8 | 30.8 | 35.7 | 54.9 |
| 1 | 22.7 | 38.9 | 33.7 | 31.2 | 35.4 | 55.1 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments evaluating the impact of different ratios of English to multilingual data in the instruction-tuning phase of training large vision-language models (LVLMs). It shows the average performance across 13 downstream vision-language tasks, broken down by language tier (T1-T5). The table helps to understand the optimal balance between English and multilingual data during instruction tuning to achieve strong performance across diverse languages, while maintaining good English performance. The different language tiers represent different levels of resource availability for those languages, helping to assess the impact of the training data balance on resource-constrained languages.
read the caption
Table 2: RQ2 (§2.3) results for models trained with different ratios of English to multilingual data in the instruction-tuning phase. Scores are averaged over results from all tasks grouped by language tier.
| Setup | SMPQA Ground | SMPQA Read | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| en | Latin | other | en | Latin | other | |
| No pre-training | 69.6 | 67.2 | 51.9 | 33.4 | 12.8 | 0.1 |
| No OCR | 76.1 | 73.0 | 55.3 | 41.8 | 23.1 | 0.2 |
| 100% Eng. | 78.4 | 74.7 | 57.9 | 55.8 | 39.9 | 3.9 |
| 50% Eng. | 81.2 | 76.7 | 60.0 | 53.8 | 41.8 | 7.1 |
| 50% (frozen) | 76.1 | 70.8 | 56.3 | 47.2 | 34.1 | 3.5 |
| 1% Eng. | 81.0 | 78.3 | 64.1 | 54.8 | 43.5 | 8.0 |
| Latin down | 78.9 | 74.2 | 59.5 | 54.6 | 41.0 | 9.9 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments investigating the impact of different English-to-multilingual ratios in pre-training data on the performance of a large vision-language model (LVM). The model was trained with 100 languages, and the instruction-tuning phase consistently used a 50% English, 50% multilingual data split across the 100 languages. The table shows how varying the proportion of English data in pre-training (from 1% to 100%) affects performance across different language tiers (T1-T5), which represent language resourceness, for both overall tasks and tasks not affected by language fidelity. This allows for an assessment of the trade-off between the inclusion of more languages and overall performance, revealing whether an optimal multilingual pre-training data mix exists, and if so, what its characteristics might be.
read the caption
Table 3: RQ3 (§2.4) results with different English-to-multilingual ratios (L100) for pre-training. All variants are identically instruction-tuned (L100, 50% En.).
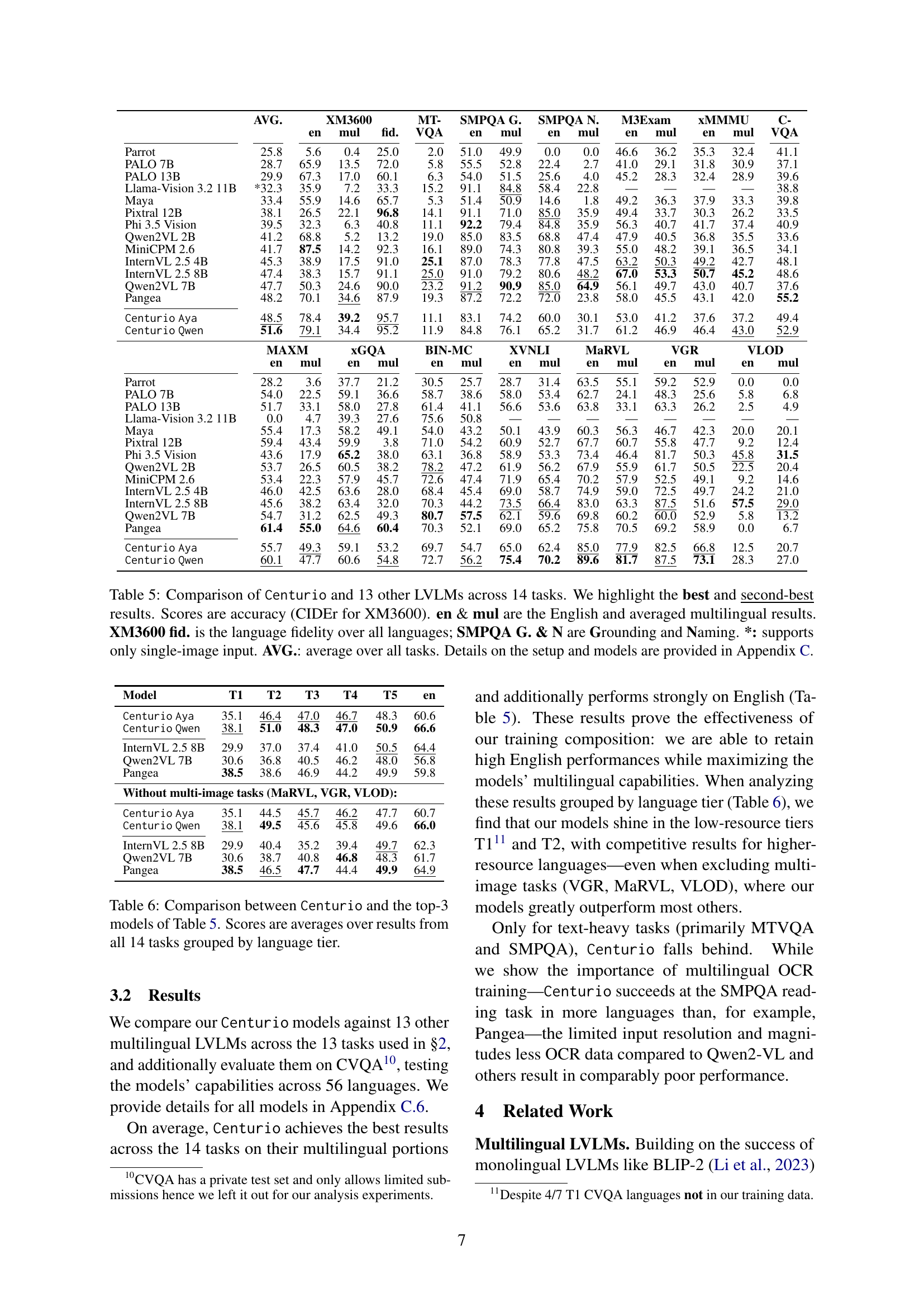
| Model Name | AVG. | XM3600 en | XM3600 mul | XM3600 fid. | MT-VQA | SMPQA G. en | SMPQA G. mul | SMPQA N. en | SMPQA N. mul | M3Exam en | M3Exam mul | xMMMU en | xMMMU mul | C-VQA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parrot | 25.8 | 5.6 | 0.4 | 25.0 | 2.0 | 51.0 | 49.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 46.6 | 36.2 | 35.3 | 32.4 | 41.1 |
| PALO 7B | 28.7 | 65.9 | 13.5 | 72.0 | 5.8 | 55.5 | 52.8 | 22.4 | 2.7 | 41.0 | 29.1 | 31.8 | 30.9 | 37.1 |
| PALO 13B | 29.9 | 67.3 | 17.0 | 60.1 | 6.3 | 54.0 | 51.5 | 25.6 | 4.0 | 45.2 | 28.3 | 32.4 | 28.9 | 39.6 |
| Llama-Vision 3.2 11B | *32.3 | 35.9 | 7.2 | 33.3 | 15.2 | 91.1 | 84.8 | 58.4 | 22.8 | - | - | - | - | 38.8 |
| Maya | 33.4 | 55.9 | 14.6 | 65.7 | 5.3 | 51.4 | 50.9 | 14.6 | 1.8 | 49.2 | 36.3 | 37.9 | 33.3 | 39.8 |
| Pixtral 12B | 38.1 | 26.5 | 22.1 | 96.8 | 14.1 | 91.1 | 71.0 | 85.0 | 35.9 | 49.4 | 33.7 | 30.3 | 26.2 | 33.5 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 39.5 | 32.3 | 6.3 | 40.8 | 11.1 | 92.2 | 79.4 | 84.8 | 35.9 | 56.3 | 40.7 | 41.7 | 37.4 | 40.9 |
| Qwen2VL 2B | 41.2 | 68.8 | 5.2 | 13.2 | 19.0 | 85.0 | 83.5 | 68.8 | 47.4 | 47.9 | 40.5 | 36.8 | 35.5 | 33.6 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 41.7 | 87.5 | 14.2 | 92.3 | 16.1 | 89.0 | 74.3 | 80.8 | 39.3 | 55.0 | 48.2 | 39.1 | 36.5 | 34.1 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 45.3 | 38.9 | 17.5 | 91.0 | 25.1 | 87.0 | 78.3 | 77.8 | 47.5 | 63.2 | 50.3 | 49.2 | 42.7 | 48.1 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 47.4 | 38.3 | 15.7 | 91.1 | 25.0 | 91.0 | 79.2 | 80.6 | 48.2 | 67.0 | 53.3 | 50.7 | 45.2 | 48.6 |
| Qwen2VL 7B | 47.7 | 50.3 | 24.6 | 90.0 | 23.2 | 91.2 | 90.9 | 85.0 | 64.9 | 56.1 | 49.7 | 43.0 | 40.7 | 37.6 |
| Pangea | 48.2 | 70.1 | 34.6 | 87.9 | 19.3 | 87.2 | 72.2 | 72.0 | 23.8 | 58.0 | 45.5 | 43.1 | 42.0 | 55.2 |
| Centurio Aya | 48.5 | 78.4 | 39.2 | 95.7 | 11.1 | 83.1 | 74.2 | 60.0 | 30.1 | 53.0 | 41.2 | 37.6 | 37.2 | 49.4 |
| Centurio Qwen | 51.6 | 79.1 | 34.4 | 95.2 | 11.9 | 84.8 | 76.1 | 65.2 | 31.7 | 61.2 | 46.9 | 46.4 | 43.0 | 52.9 |
Table 2: MAXM, xGQA, BIN-MC, XVNLI, MaRVL, VGR, and VLOD Performance Comparison#
| Model Name | MAXM en | MAXM mul | xGQA en | xGQA mul | BIN-MC en | BIN-MC mul | XVNLI en | XVNLI mul | MaRVL en | MaRVL mul | VGR en | VGR mul | VLOD en | VLOD mul |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parrot | 28.2 | 3.6 | 37.7 | 21.2 | 30.5 | 25.7 | 28.7 | 31.4 | 63.5 | 55.1 | 59.2 | 52.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| PALO 7B | 54.0 | 22.5 | 59.1 | 36.6 | 58.7 | 38.6 | 58.0 | 53.4 | 62.7 | 24.1 | 48.3 | 25.6 | 5.8 | 6.8 |
| PALO 13B | 51.7 | 33.1 | 58.0 | 27.8 | 61.4 | 41.1 | 56.6 | 53.6 | 63.8 | 33.1 | 63.3 | 26.2 | 2.5 | 4.9 |
| Llama-Vision 3.2 11B | 0.0 | 4.7 | 39.3 | 27.6 | 75.6 | 50.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Maya | 55.4 | 17.3 | 58.2 | 49.1 | 54.0 | 43.2 | 50.1 | 43.9 | 60.3 | 56.3 | 46.7 | 42.3 | 20.0 | 20.1 |
| Pixtral 12B | 59.4 | 43.4 | 59.9 | 3.8 | 71.0 | 54.2 | 60.9 | 52.7 | 67.7 | 60.7 | 55.8 | 47.7 | 9.2 | 12.4 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 43.6 | 17.9 | 65.2 | 38.0 | 63.1 | 36.8 | 58.9 | 53.3 | 73.4 | 46.4 | 81.7 | 50.3 | 45.8 | 31.5 |
| Qwen2VL 2B | 53.7 | 26.5 | 60.5 | 38.2 | 78.2 | 47.2 | 61.9 | 56.2 | 67.9 | 55.9 | 61.7 | 50.5 | 22.5 | 20.4 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 53.4 | 22.3 | 57.9 | 45.7 | 72.6 | 47.4 | 71.9 | 65.4 | 70.2 | 57.9 | 52.5 | 49.1 | 9.2 | 14.6 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 46.0 | 42.5 | 63.6 | 28.0 | 68.4 | 45.4 | 69.0 | 58.7 | 74.9 | 59.0 | 72.5 | 49.7 | 24.2 | 21.0 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 45.6 | 38.2 | 63.4 | 32.0 | 70.3 | 44.2 | 73.5 | 66.4 | 83.0 | 63.3 | 87.5 | 51.6 | 57.5 | 29.0 |
| Qwen2VL 7B | 54.7 | 31.2 | 62.5 | 49.3 | 80.7 | 57.5 | 62.1 | 59.6 | 69.8 | 60.2 | 60.0 | 52.9 | 5.8 | 13.2 |
| Pangea | 61.4 | 55.0 | 64.6 | 60.4 | 70.3 | 52.1 | 69.0 | 65.2 | 75.8 | 70.5 | 69.2 | 58.9 | 0.0 | 6.7 |
| Centurio Aya | 55.7 | 49.3 | 59.1 | 53.2 | 69.7 | 54.7 | 65.0 | 62.4 | 85.0 | 77.9 | 82.5 | 66.8 | 12.5 | 20.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 60.1 | 47.7 | 60.6 | 54.8 | 72.7 | 56.2 | 75.4 | 70.2 | 89.6 | 81.7 | 87.5 | 73.1 | 28.3 | 27.0 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments evaluating the impact of adding synthetic OCR data to the training of multilingual vision-language models (LVLMs). The experiments are performed on the SMPQA benchmark, which assesses the model’s ability to read and understand text within images. Multiple model configurations are examined varying in several key aspects: 1. Pre-training: Models are tested with and without a pre-training phase, using the data distribution found optimal in previous sections of the paper. 2. Image Encoder: Models are tested with frozen versus unfrozen image encoders. 3. OCR Data Distribution: The proportion of English vs. non-English OCR data is varied (1%, 25%, 50%, 100%). 4. Latin Script Emphasis: A specific condition where Latin-script languages receive 2.5k samples while others get 10k.
read the caption
Table 4: RQ4 (§2.5) results of models trained with additional synthetic OCR data on SMPQA for English, Latin-script languages, and languages with other scripts. No pre-training: from Table 2; No OCR: from Table 3; frozen: image encoder frozen; N% Eng.: N%percent𝑁N\%italic_N % of OCR data is English, rest uniform distributed over L100 languages; Latin down: 2.5k samples for all Latin-script languages, 10k samples for others.
| Model | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 35.1 | 46.4 | 47.0 | 46.7 | 48.3 | 60.6 |
| Centurio Qwen | 38.1 | 51.0 | 48.3 | 47.0 | 50.9 | 66.6 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 29.9 | 37.0 | 37.4 | 41.0 | 50.5 | 64.4 |
| Qwen2VL 7B | 30.6 | 36.8 | 40.5 | 46.2 | 48.0 | 56.8 |
| Pangea | 38.5 | 38.6 | 46.9 | 44.2 | 49.9 | 59.8 |
| Without multi-image tasks (MaRVL, VGR, VLOD): | ||||||
| Centurio Aya | 35.1 | 44.5 | 45.7 | 46.2 | 47.7 | 60.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 38.1 | 49.5 | 45.6 | 45.8 | 49.6 | 66.0 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 29.9 | 40.4 | 35.2 | 39.4 | 49.7 | 62.3 |
| Qwen2VL 7B | 30.6 | 38.7 | 40.8 | 46.8 | 48.3 | 61.7 |
| Pangea | 38.5 | 46.5 | 47.7 | 44.4 | 49.9 | 64.9 |
🔼 This table presents a comprehensive comparison of Centurio’s performance against 13 other Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) across 14 diverse tasks. The evaluation metrics include accuracy scores (using CIDEr for the XM3600 task) and language fidelity, along with more granular results for specific tasks like SMPQA grounding and naming. The table distinguishes between English-only performance and averaged multilingual performance across various language tiers, providing insights into the models’ multilingual capabilities. The ‘*’ indicates models that only support single-image input, and ‘AVG’ represents the average performance across all tasks. Additional details about the experimental setup and models are available in Appendix C.
read the caption
Table 5: Comparison of Centurio and 13 other LVLMs across 14 tasks. We highlight the best and second-best results. Scores are accuracy (CIDEr for XM3600). en & mul are the English and averaged multilingual results. XM3600 fid. is the language fidelity over all languages; SMPQA G. & N are Grounding and Naming. *: supports only single-image input. AVG.: average over all tasks. Details on the setup and models are provided in Appendix C.
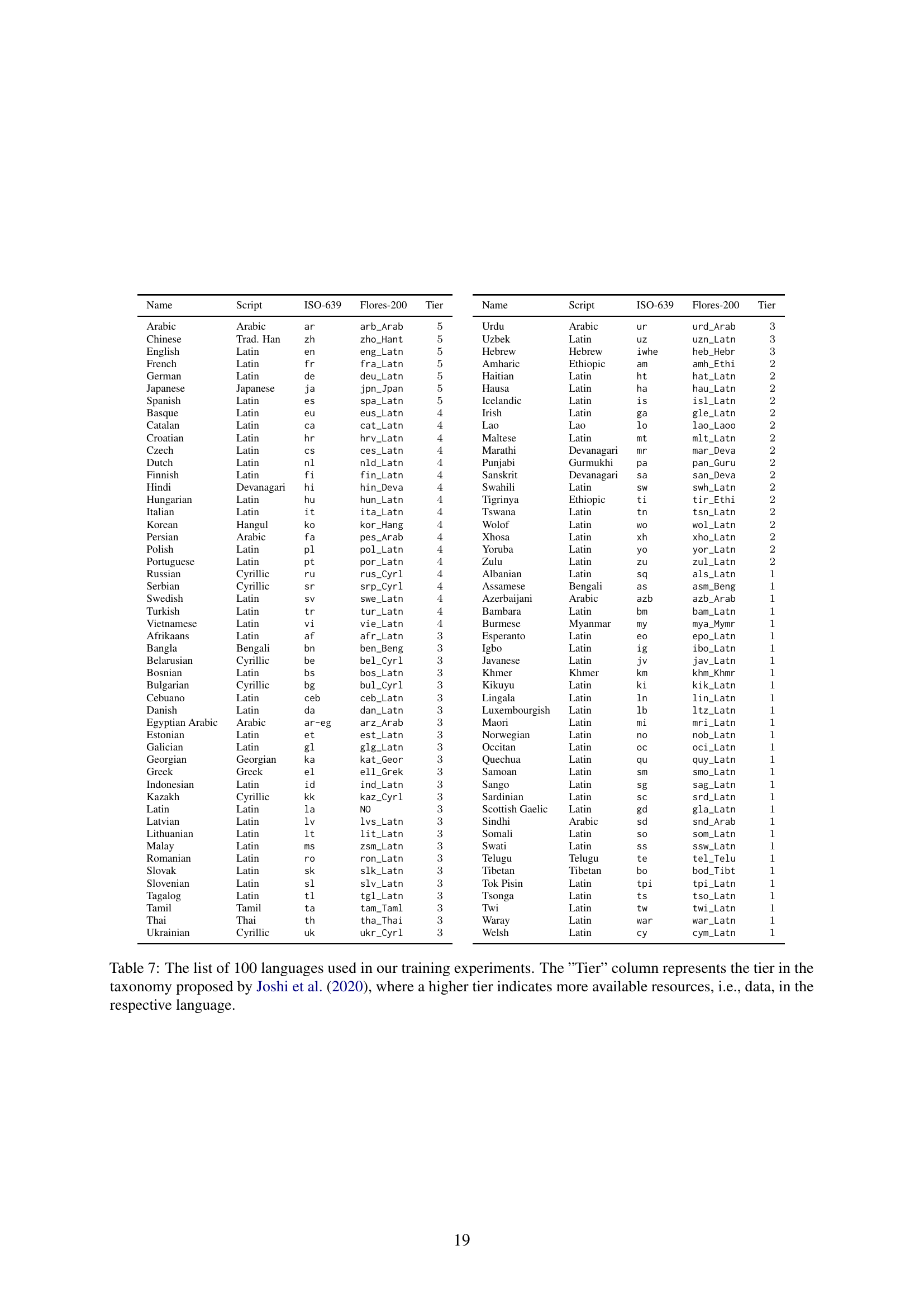
| Name | Script | ISO-639 | Flores-200 | Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic | Arabic | ar | arb_Arab | 5 |
| Chinese | Trad. Han | zh | zho_Hant | 5 |
| English | Latin | en | eng_Latn | 5 |
| French | Latin | fr | fra_Latn | 5 |
| German | Latin | de | deu_Latn | 5 |
| Japanese | Japanese | ja | jpn_Jpan | 5 |
| Spanish | Latin | es | spa_Latn | 5 |
| Basque | Latin | eu | eus_Latn | 4 |
| Catalan | Latin | ca | cat_Latn | 4 |
| Croatian | Latin | hr | hrv_Latn | 4 |
| Czech | Latin | cs | ces_Latn | 4 |
| Dutch | Latin | nl | nld_Latn | 4 |
| Finnish | Latin | fi | fin_Latn | 4 |
| Hindi | Devanagari | hi | hin_Deva | 4 |
| Hungarian | Latin | hu | hun_Latn | 4 |
| Italian | Latin | it | ita_Latn | 4 |
| Korean | Hangul | ko | kor_Hang | 4 |
| Persian | Arabic | fa | pes_Arab | 4 |
| Polish | Latin | pl | pol_Latn | 4 |
| Portuguese | Latin | pt | por_Latn | 4 |
| Russian | Cyrillic | ru | rus_Cyrl | 4 |
| Serbian | Cyrillic | sr | srp_Cyrl | 4 |
| Swedish | Latin | sv | swe_Latn | 4 |
| Turkish | Latin | tr | tur_Latn | 4 |
| Vietnamese | Latin | vi | vie_Latn | 4 |
| Afrikaans | Latin | af | afr_Latn | 3 |
| Bangla | Bengali | bn | ben_Beng | 3 |
| Belarusian | Cyrillic | be | bel_Cyrl | 3 |
| Bosnian | Latin | bs | bos_Latn | 3 |
| Bulgarian | Cyrillic | bg | bul_Cyrl | 3 |
| Cebuano | Latin | ceb | ceb_Latn | 3 |
| Danish | Latin | da | dan_Latn | 3 |
| Egyptian Arabic | Arabic | ar-eg | arz_Arab | 3 |
| Estonian | Latin | et | est_Latn | 3 |
| Galician | Latin | gl | glg_Latn | 3 |
| Georgian | Georgian | ka | kat_Geor | 3 |
| Greek | Greek | el | ell_Grek | 3 |
| Indonesian | Latin | id | ind_Latn | 3 |
| Kazakh | Cyrillic | kk | kaz_Cyrl | 3 |
| Latin | Latin | la | NO | 3 |
| Latvian | Latin | lv | lvs_Latn | 3 |
| Lithuanian | Latin | lt | lit_Latn | 3 |
| Malay | Latin | ms | zsm_Latn | 3 |
| Romanian | Latin | ro | ron_Latn | 3 |
| Slovak | Latin | sk | slk_Latn | 3 |
| Slovenian | Latin | sl | slv_Latn | 3 |
| Tagalog | Latin | tl | tgl_Latn | 3 |
| Tamil | Tamil | ta | tam_Taml | 3 |
| Thai | Thai | th | tha_Thai | 3 |
| Ukrainian | Cyrillic | uk | ukr_Cyrl | 3 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of Centurio’s performance against the top three models from Table 5 across fourteen vision-language tasks. The results are averaged across all fourteen tasks and grouped by language tier (T1-T5, representing language resource levels, with T5 being high-resource and T1 low-resource), providing a comprehensive evaluation of multilingual capabilities. The table highlights Centurio’s performance relative to other state-of-the-art models across different language groups, illustrating its strengths and weaknesses in various tasks and language scenarios.
read the caption
Table 6: Comparison between Centurio and the top-3 models of Table 5. Scores are averages over results from all 14 tasks grouped by language tier.
| Name | Script | ISO-639 | Flores-200 | Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urdu | Arabic | ur | urd_Arab | 3 |
| Uzbek | Latin | uz | uzn_Latn | 3 |
| Hebrew | Hebrew | iwhe | heb_Hebr | 3 |
| Amharic | Ethiopic | am | amh_Ethi | 2 |
| Haitian | Latin | ht | hat_Latn | 2 |
| Hausa | Latin | ha | hau_Latn | 2 |
| Icelandic | Latin | is | isl_Latn | 2 |
| Irish | Latin | ga | gle_Latn | 2 |
| Lao | Lao | lo | lao_Laoo | 2 |
| Maltese | Latin | mt | mlt_Latn | 2 |
| Marathi | Devanagari | mr | mar_Deva | 2 |
| Punjabi | Gurmukhi | pa | pan_Guru | 2 |
| Sanskrit | Devanagari | sa | san_Deva | 2 |
| Swahili | Latin | sw | swh_Latn | 2 |
| Tigrinya | Ethiopic | ti | tir_Ethi | 2 |
| Tswana | Latin | tn | tsn_Latn | 2 |
| Wolof | Latin | wo | wol_Latn | 2 |
| Xhosa | Latin | xh | xho_Latn | 2 |
| Yoruba | Latin | yo | yor_Latn | 2 |
| Zulu | Latin | zu | zul_Latn | 2 |
| Albanian | Latin | sq | als_Latn | 1 |
| Assamese | Bengali | as | asm_Beng | 1 |
| Azerbaijani | Arabic | azb | azb_Arab | 1 |
| Bambara | Latin | bm | bam_Latn | 1 |
| Burmese | Myanmar | my | mya_Mymr | 1 |
| Esperanto | Latin | eo | epo_Latn | 1 |
| Igbo | Latin | ig | ibo_Latn | 1 |
| Javanese | Latin | jv | jav_Latn | 1 |
| Khmer | Khmer | km | khm_Khmr | 1 |
| Kikuyu | Latin | ki | kik_Latn | 1 |
| Lingala | Latin | ln | lin_Latn | 1 |
| Luxembourgish | Latin | lb | ltz_Latn | 1 |
| Maori | Latin | mi | mri_Latn | 1 |
| Norwegian | Latin | no | nob_Latn | 1 |
| Occitan | Latin | oc | oci_Latn | 1 |
| Quechua | Latin | qu | quy_Latn | 1 |
| Samoan | Latin | sm | smo_Latn | 1 |
| Sango | Latin | sg | sag_Latn | 1 |
| Sardinian | Latin | sc | srd_Latn | 1 |
| Scottish Gaelic | Latin | gd | gla_Latn | 1 |
| Sindhi | Arabic | sd | snd_Arab | 1 |
| Somali | Latin | so | som_Latn | 1 |
| Swati | Latin | ss | ssw_Latn | 1 |
| Telugu | Telugu | te | tel_Telu | 1 |
| Tibetan | Tibetan | bo | bod_Tibt | 1 |
| Tok Pisin | Latin | tpi | tpi_Latn | 1 |
| Tsonga | Latin | ts | tso_Latn | 1 |
| Twi | Latin | tw | twi_Latn | 1 |
| Waray | Latin | war | war_Latn | 1 |
| Welsh | Latin | cy | cym_Latn | 1 |
🔼 Table 7 presents a comprehensive list of the 100 languages included in the training data for the multilingual vision-language model. Each language is categorized into one of five tiers (T1-T5) based on the resource availability, as defined in the taxonomy by Joshi et al. (2020). A higher tier number indicates a greater abundance of resources (like training data and other linguistic tools) for that language. This tiering system helps to understand the relative scarcity or abundance of training data across the different languages used, which is crucial for evaluating the impact of various multilingual training strategies on model performance.
read the caption
Table 7: The list of 100 languages used in our training experiments. The ”Tier” column represents the tier in the taxonomy proposed by Joshi et al. (2020), where a higher tier indicates more available resources, i.e., data, in the respective language.
| Dataset | Size (Images) | Translated? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Image: | |||
| LLaVA Instruct Liu et al. (2023b) | 160k | yes | |
| VQAv2 Goyal et al. (2017) | 83k | yes | |
| GQA Hudson and Manning (2019) | 72k | yes | |
| OKVQA Marino et al. (2019) | 9k | yes | |
| A-OKVQA Schwenk et al. (2022) | 30k | yes | |
| RefCOCO Kazemzadeh et al. (2014); Mao et al. (2016) | 48k | yes | |
| VG Krishna et al. (2017) | 86k | yes | |
| MSCOCO Lin et al. (2014) | 50k (subset) | yes | |
| Multiple Images: | |||
| NLVR Suhr et al. (2019) | 86k | yes | |
| Spot-the-difference Jhamtani and Berg-Kirkpatrick (2018) | 8k | yes | |
| OCR: | |||
| OCRVQA Mishra et al. (2019) | 50k (subset) | no | |
| DocVQA Mathew et al. (2021) | 10k | no | |
| AI2D Kembhavi et al. (2016) | 3k | no | |
| ChartQA Masry et al. (2022) | 18k | no | |
| DVQA Kafle et al. (2018) | 50k (subset) | no | |
| ScienceQA Lu et al. (2022) | 6k | no | |
| Total | 766k |
🔼 This table lists the datasets used for the instruction-tuning phase of the experiments in the paper. The datasets are categorized into those containing natural images, those containing multiple images (where each data point includes several images), and those with OCR text. The table provides the name of each dataset, the number of unique images in the dataset, and whether machine translation was used to make the dataset multilingual. Note that for datasets with multiple images or text, only unique image examples are counted, so if multiple sentences pertain to a single image, it’s still only counted as one image.
read the caption
Table 8: List of datasets included in the instruct tuning phase in our analysis experiments. All sizes are based on unique images; examples about the same image are packed into one sequence.
| Dataset | Size (Images) | Translated? |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Image: | ||
| ALLaVA Instruct1 Chen et al. (2024a) | 760k | yes |
| LVIS Instruct4V Wang et al. (2023) | 223k | yes |
| Visual7W Zhu et al. (2016) | 14k | no |
| VizWiz QA Gurari et al. (2018) | 21k | no |
| TallyQA Acharya et al. (2019) | 133k | yes |
| SketchyVQA Tu et al. (2023) | 4k | yes |
| OODVQA Tu et al. (2023) | 3k | no |
| OCR: | ||
| ScienceQA (Cambrian version) | 6k | no |
| AI2D (Cambrian version) | 4k | no |
| Rendered Text2 | 10k | no |
| ScreenQA Hsiao et al. (2022) | 33k | no |
| LLaVAR Zhang et al. (2023b) | 20k | no |
| ArxivQA Li et al. (2024) | 54k | no |
| Chart2Text Obeid and Hoque (2020) | 25k | no |
| InfographicVQA Mathew et al. (2022) | 2k | no |
| VisText Tang et al. (2023) | 10k | no |
| TQA Kembhavi et al. (2017) | 1k | no |
| STVQA Biten et al. (2019) | 17k | no |
| TAT-QA Zhu et al. (2021) | 2k | no |
| TabMWP Lu et al. (2023) | 23k | no |
| HiTab Cheng et al. (2022) | 2k | no |
| IconQA Lu et al. (2021b) | 27k | no |
| VisualMRC Tanaka et al. (2021) | 3k | no |
| RobuT Zhao et al. (2023) | 113k | no |
| FinQA Chen et al. (2021) | 5k | no |
| Math & Code: | ||
| WebSight Laurençon et al. (2024b) | 10k | yes |
| Design2Code Si et al. (2024) | 0k | yes |
| DaTikz Belouadi et al. (2024) | 48k | no |
| CLEVR Johnson et al. (2017) | 70k | yes |
| CLEVR-Math Lindström and Abraham (2022) | 70k | yes |
| Geo170k Gao et al. (2023) | 9k | no |
| GeomVerse Kazemi et al. (2023) | 9k | no |
| Inter-GPS Lu et al. (2021a) | 1k | no |
| MathVision Wang et al. (2024a) | 3k | no |
| Raven Zhang et al. (2019) | 42k | no |
| Text (no images): | ||
| Aya Dataset Singh et al. (2024) | 202k | – |
| Tagengo-GPT4 Devine (2024) | 70k | – |
| Magpie2 Xu et al. (2024) | 400k | – |
| Total | 2.47M |
🔼 Table 9 details the datasets used in the instruction tuning phase for the Centurio model. It builds upon the datasets listed in Table 8. The table shows the name of each additional dataset, the number of images in the dataset, and whether or not machine translation was used. Note that one dataset includes web-scraped images from LAION (which contain textual elements), and another dataset combines three separate subsets from different sources.
read the caption
Table 9: Datasets used on top of the datasets from Table 8 for the instruct tuning phase of Centurio. 1: also contains web-scraped images from LAION Schuhmann et al. (2022) which contain textual elements. 2222:%****␣A1_details.tex␣Line␣275␣****https://huggingface.co/datasets/wendlerc/RenderedText. 2: Combining magpie-ultra-v0.1 (50k), Magpie-Qwen2-Pro-200K-English (200k), Magpie-Llama-3.1-Pro-MT-300K-Filtered (150k subset).
| Dataset | Task | Visual Input | Textual Input | Target Output | Metric | #Lang. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaXM | VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | WoP (TL) | E. Acc. | 6 |
| xGQA | VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | WoP (EN) | E. Acc. | 8 |
| XVNLI | VNLI | Single-Image | Hypothesis (TL) | ‘yes’ / ’no’ / ’maybe’ | E. Acc. | 5 |
| M5B-VLOD | VLOD | Multi-Image | Hypothesis (TL) | LoC | R. Acc. | 12 |
| M5B-VGR | VGR | Multi-Image | Hypothesis (TL) | ‘yes’ / ’no’ | E. Acc. | 12 |
| MaRVL | VGR | Multi-Image | Hypothesis (TL) | ‘yes’ / ’no’ | E. Acc. | 6 |
| MTVQA | TH VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | WoP (TL) | E. Acc. | 9 |
| SMPQA - Name | TH VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | WoP (TL) | E. Acc. | 11 |
| SMPQA - Ground | TH VGR | Single-Image | Question (TL) | ‘yes’ / ’no’ | E. Acc. | 11 |
| M3Exam | TH MC VQA | Single or Multi-Image | Question (TL) | LoC | R. Acc. | 7 |
| MMMU | TH MC VQA | Single or Multi-Image | Question (EN) | LoC | R. Acc. | 1 |
| xMMMU | TH MC VQA | Single or Multi-Image | Question (TL) | LoC | R. Acc. | 7 |
| BabelImageNet-MC | MC VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | LoC | R. Acc. | 20 |
| CVQA | MC VQA | Single-Image | Question (TL) | LoC | R. Acc. | 39 |
| XM3600 | Captioning | Single-Image | Prompt (EN) | Caption (TL) | CIDEr | 36 |
🔼 Table 10 details the datasets used to evaluate the Centurio model’s performance. It lists 15 vision-language datasets, specifying the task type (Visual Question Answering (VQA), Visual Natural Language Inference (VNLI), Visio-Linguistic Outlier Detection (VLOD), Visually Grounded Reasoning (VGR), Text-Heavy (TH), and Multiple-Choice (MC)), the type of visual input (single image, multiple images), the textual input, target output (single word or phrase (WoP), Letter of Correct Choice (LoC), in Target Language (TL), or in English (EN)), and evaluation metric (Exact Accuracy (E. Acc.) or Relaxed Accuracy (R. Acc.)). The table notes that CVQA is excluded from section 2 of the paper because its test set is not publicly available.
read the caption
Table 10: List of datasets contained in our test suite. In the Task column, ”VQA” ”VNLI”, ”VLOD”, ”VGR”, ”TH”, and ”MC” are acronyms for ”Visual Question Answering”, ”Visual Natural Language Inference”, ”Visio-Linguistic Outlier Detection”, ”Visually Grounded Reasoning”, ”Text-Heavy”, and ”Multiple-Choice”, respectively. In the ”Textual Input” and ”Target Output” columns, the acronyms ”WoP”, ”LoC”, ”TL”, and ”EN” stand for ”(Single) Word or Phrase”, ”Letter of the correct Choice”, ”Target Language”, and ”English”, respectively. Further, ”E. Acc.” is ”Exact Accuracy” and ”R. Acc.” is ”Relaxed Accuracy”. CVQA is not used in §2 due to its hidden test set with limited submissions.
| Name | Tier | ISO-639-3 | ISO-639-1 | Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrikaans | 3 | afr | af | BabelImageNet-MC, M3Exam |
| Amharic | 2 | amh | am | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD |
| Arabic | 5 | ara | ar | MTVQA, SMPQA, XM3600, xMMMU, XVNLI |
| Bengali | 3 | ben | bn | CVQA, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, xGQA, XM3600 |
| Berber (macrolanguage) | 0 | ber | - | M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD |
| Breton | 1 | bre | br | CVQA |
| Bulgarian | 3 | bul | bg | CVQA |
| Chinese | 5 | zho | zh | CVQA, M3Exam, MaRVL, MaXM, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600 |
| Croatian | 4 | hrv | hr | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Cusco Quechua | 1 | quz | - | XM3600 |
| Czech | 4 | ces | cs | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Danish | 3 | dan | da | XM3600 |
| Dutch | 4 | nld | nl | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Egyptian Arabic | 3 | arz | - | CVQA |
| English | 5 | eng | en | BabelImageNet-MC, M3Exam, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MaRVL, MaXM, MME, MMMU, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600, xMMMU, XVNLI |
| Filipino | 3 | fil | - | CVQA, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, XM3600 |
| Finnish | 4 | fin | fi | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| French | 5 | fra | fr | MaXM, MTVQA, XM3600, xMMMU, XVNLI |
| German | 5 | deu | de | M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MTVQA, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600 |
| Hausa | 2 | hau | ha | BabelImageNet-MC, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD |
| Hebrew | 3 | heb | he | XM3600 |
| Hindi | 4 | hin | hi | M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MaXM, SMPQA, XM3600, xMMMU |
| Hungarian | 4 | hun | hu | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Igbo | 1 | ibo | ig | CVQA |
| Indonesian | 3 | ind | id | CVQA, MaRVL, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600, xMMMU |
| Irish | 2 | gle | ga | CVQA |
| Italian | 4 | ita | it | M3Exam, MTVQA, SMPQA, XM3600 |
| Japanese | 5 | jpn | ja | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, MTVQA, XM3600, xMMMU |
| Javanese | 1 | jav | jv | CVQA |
| Kanuri | 0 | kau | kr | CVQA |
| Kinyarwanda | 1 | kin | rw | CVQA |
| Korean | 4 | kor | ko | CVQA, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600 |
| Malay (macrolanguage) | 3 | msa | ms | CVQA |
| Maori | 1 | mri | mi | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Mi-gkabau | 1 | min | - | CVQA |
| Modern Greek | 3 | ell | el | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Mongolian | 1 | mon | mn | CVQA |
| Norwegian | 1 | nor | no | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, XM3600 |
| Oromo | 1 | orm | om | CVQA |
| Persian | 4 | fas | fa | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Polish | 4 | pol | pl | BabelImageNet-MC, XM3600 |
| Portuguese | 4 | por | pt | CVQA, M3Exam, xGQA, XM3600, xMMMU |
| Romanian | 3 | ron | ro | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, MaXM, XM3600 |
| Russian | 4 | rus | ru | CVQA, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MTVQA, SMPQA, xGQA, XM3600, XVNLI |
| Sinhala | 0 | sin | si | CVQA |
| Spanish | 5 | spa | es | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, XM3600, XVNLI |
| Sundanese | 1 | sun | su | CVQA |
| Swahili (macrolanguage) | 2 | swa | sw | CVQA, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MaRVL, XM3600 |
| Swedish | 4 | swe | sv | XM3600 |
| Tamil | 3 | tam | ta | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, MaRVL |
| Telugu | 1 | tel | te | BabelImageNet-MC, CVQA, XM3600 |
| Thai | 3 | tha | th | M3Exam, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, MaXM, MTVQA, SMPQA, XM3600 |
| Turkish | 4 | tur | tr | MaRVL, XM3600 |
| Ukrainian | 3 | ukr | uk | XM3600 |
| Urdu | 3 | urd | ur | CVQA |
| Vietnamese | 4 | vie | vi | M3Exam, MTVQA, XM3600 |
| Zulu | 2 | zul | zu | BabelImageNet-MC, M5B-VGR, M5B-VLOD, SMPQA |
| Unique Languages | 56 (43 without CVQA) |
🔼 This table lists the 56 languages used in the evaluation of the Centurio model, categorized by their resource tier according to the Joshi et al. (2020) taxonomy. Tier 5 represents high-resource languages with ample available data, while Tier 1 indicates low-resource languages with limited resources. The table also notes that the CVQA dataset was excluded from the analysis in Section 2 due to its closed-off test set and limited submission opportunities.
read the caption
Table 11: List of languages covered in the datasets of our test suite. The ”Tier” column represents the tier in the taxonomy proposed by Joshi et al. (2020), where a higher tier indicates more available resources, i.e., data, in the respective language. CVQA is not used in §2 due to its hidden test set with limited submissions.
| HuggingFace Model ID | Params |
|---|---|
| Qwen/Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct [2024c] | 2B |
| Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct [2024c] | 7B |
| microsoft/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct [2024a] | 4B |
| neulab/Pangea-7B-hf [2024b] | 7B |
| openbmb/MiniCPM-V-2_6 [2024b] | 8B |
| meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct [2024] | 11B |
| mistralai/Pixtral-12B-2409 [2024] | 12B |
| AIDC-AI/Parrot-7B [2024b] | 7B |
| MBZUAI/PALO-7B [2024a] | 7B |
| MBZUAI/PALO-13B [2024a] | 13B |
| OpenGVLab/InternVL2_5-4B [2024e] | 4B |
| OpenGVLab/InternVL2_5-8B [2024e] | 8B |
| maya-multimodal/maya [2024] | 8B |
🔼 This table lists the large vision-language models (LVLMs) used in the paper’s experiments to evaluate the models’ multilingual capabilities. The models are listed along with their sizes (number of parameters), allowing for a comparison of performance across models of different scales. The table is crucial for understanding which LVLMs were considered and used as baselines for comparison against the Centurio model developed in the paper.
read the caption
Table 12: List of models considered in our evaluation experiments.
| Train Lang. | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 16.1 | 34.7 | 26.3 | 24.3 | 26.2 | 56.4 |
| T5 | 19.1 | 32.5 | 29.3 | 27.2 | 35.5 | 54.3 |
| L100 | 31.1 | 43.0 | 39.4 | 35.9 | 36.4 | 56.6 |
| Without tasks affected by language fidelity: | ||||||
| English | 36.6 | 37.1 | 39.0 | 39.6 | 40.0 | 54.6 |
| T5 | 38.8 | 34.8 | 40.1 | 40.2 | 40.4 | 53.5 |
| L100 | 46.3 | 44.0 | 45.0 | 42.8 | 42.9 | 55.3 |
🔼 This table replicates the results from Table 1, but uses the Llama 3 language model instead of Phi 3.5. It compares the performance of models trained with only English, the top 6 high-resource languages (T5), and all 100 languages (L100) across multiple downstream tasks. This allows for analysis of the impact of increasing the number of training languages on model performance.
read the caption
Table 13: Experimental setup of Table 1 repeated with Llama 3 and the setups: just English, T5 languages, and L100 languages.
| English % | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 32.9 | 43.1 | 38.7 | 35.4 | 35.4 | 54.2 |
| 50 | 31.1 | 43.0 | 39.4 | 35.9 | 36.4 | 56.6 |
| 90 | 26.9 | 38.7 | 36.9 | 34.2 | 35.8 | 56.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments investigating the effect of different proportions of English and multilingual data in the instruction-tuning phase of training a large vision-language model (LLM). The experiment setup replicates that of Table 2 but uses the Llama 3 LLM. It systematically varies the percentage of English data (10%, 50%, and 90%), while keeping the multilingual portion constant, and evaluates performance across multiple language tiers and tasks. The table provides insights into the optimal balance between English and multilingual data for instruction tuning in multilingual LVLMs, highlighting the impact of different data distributions on the overall performance.
read the caption
Table 14: Experimental setup of Table 2 repeated with Llama 3 and the setups: 10, 50, and 90% English instruct tune data.
| English % | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No pretrain | 31.1 | 43.0 | 39.4 | 35.9 | 36.4 | 56.6 |
| 100 | 33.9 | 44.7 | 43.3 | 39.9 | 39.9 | 60.8 |
| 1 | 37.8 | 47.4 | 45.0 | 41.1 | 40.7 | 61.4 |
🔼 This table presents the results of experiments evaluating the impact of different English-to-multilingual ratios in pre-training data on the performance of a large vision-language model (LLM). It expands upon the findings of Table 3, specifically showing how performance varies when pre-training is performed using either 1% or 100% English data. The model used is Llama 3, and the results are presented for various language tiers (T1-T5), and the English performance is also included as a separate metric.
read the caption
Table 15: Results of Table 3 repeated with Llama 3 and the setups: 1 and 100% English pre-train data.
| Distribution | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uniform | 18.9 | 32.6 | 30.7 | 28.8 | 34.4 | 52.6 |
| Stratified-1 | 18.6 | 32.5 | 30.7 | 28.0 | 33.8 | 53.0 |
| Stratified-2 | 19.2 | 32.6 | 29.5 | 27.4 | 33.9 | 52.0 |
🔼 This table presents a comparative analysis of three different language data allocation strategies for training a multilingual vision-language model. The strategies are: a uniform distribution across all languages, a stratified distribution that gives more weight to low-resource languages (Stratified-1), and another stratified distribution that gives even more weight to low-resource languages (Stratified-2). The table shows the performance of models trained with these different strategies on multiple evaluation tasks, allowing researchers to understand the effects of varying language data distributions on overall multilingual model performance.
read the caption
Table 16: Comparison between our uniform allocation of data compared to two stratified allocations that upsample low-resource languages.
| LLM | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | en |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi-3.5-mini-instruct | 18.9 | 32.6 | 30.7 | 28.8 | 34.4 | 52.6 |
| gemma-2-9b-it | 29.2 | 40.9 | 36.4 | 33.5 | 35.3 | 52.8 |
| Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 31.1 | 43.0 | 39.4 | 35.9 | 36.4 | 56.6 |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct | 30.7 | 43.7 | 42.0 | 38.1 | 40.5 | 62.7 |
| aya-expanse-8b | 28.3 | 42.5 | 43.0 | 39.8 | 40.9 | 59.9 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of the performance achieved by different large language models (LLMs) after being fine-tuned using instruction tuning data. The key characteristic of this fine-tuning is that it involves 100 languages and a training data composition where 50% is in English, with the other 50% distributed equally across the remaining 99 languages. The models are evaluated across different language tiers (T1-T5), allowing for an assessment of performance across varying resource levels for different languages. The results highlight the impact of different LLM architectures on multilingual performance under these specific training conditions.
read the caption
Table 17: Comparison between different LLM backbones all trained with the instruct tuning data with L100 languages and 50% English (as in §2.3).
| English | avg. | af | am | cs | el | es | fa | fi | ha | hr | hu | ja | mi | nl | no | pl | ro | ta | te | zu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 64.7 | 38.1 | 43.3 | 29.7 | 41.5 | 35.5 | 55.9 | 33.6 | 36.4 | 24.5 | 43.3 | 39.0 | 49.8 | 27.8 | 47.3 | 44.2 | 41.4 | 42.8 | 30.0 | 27.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 66.0 | 39.6 | 46.0 | 30.3 | 43.1 | 36.3 | 56.3 | 33.4 | 36.5 | 35.1 | 45.1 | 40.7 | 50.9 | 30.1 | 48.4 | 46.2 | 41.1 | 43.1 | 31.0 | 29.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 65.2 | 40.6 | 46.8 | 29.6 | 44.6 | 37.9 | 59.1 | 36.7 | 37.5 | 29.0 | 46.4 | 42.5 | 52.0 | 31.1 | 50.7 | 47.4 | 43.0 | 43.5 | 31.5 | 29.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 65.5 | 40.6 | 50.0 | 28.8 | 43.3 | 37.4 | 58.6 | 34.4 | 38.4 | 33.0 | 46.1 | 41.4 | 50.9 | 31.2 | 49.7 | 47.0 | 41.9 | 43.8 | 32.5 | 29.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 64.8 | 39.1 | 47.2 | 25.6 | 41.9 | 35.8 | 57.9 | 34.0 | 36.0 | 29.8 | 44.8 | 39.5 | 50.0 | 30.5 | 47.7 | 45.8 | 41.2 | 42.4 | 30.4 | 29.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 64.7 | 39.9 | 48.1 | 28.2 | 42.8 | 36.8 | 57.2 | 34.7 | 37.0 | 28.2 | 44.7 | 40.4 | 51.2 | 31.6 | 47.8 | 46.4 | 40.9 | 43.8 | 30.6 | 30.1 |
| Llama 3 - English | 65.4 | 40.9 | 44.0 | 28.2 | 46.9 | 42.2 | 53.0 | 42.4 | 38.7 | 31.1 | 47.6 | 46.3 | 48.6 | 30.1 | 48.2 | 47.4 | 44.0 | 44.9 | 31.6 | 32.5 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 63.9 | 43.7 | 50.6 | 28.7 | 49.2 | 46.4 | 54.6 | 46.6 | 41.7 | 35.4 | 50.7 | 50.8 | 51.9 | 30.0 | 51.2 | 50.9 | 47.0 | 48.4 | 31.1 | 35.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 66.2 | 48.8 | 55.3 | 35.1 | 54.2 | 51.2 | 56.2 | 47.6 | 46.2 | 37.2 | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.3 | 33.7 | 54.6 | 54.3 | 50.8 | 51.9 | 43.6 | 50.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 63.1 | 39.7 | 47.4 | 26.8 | 42.9 | 36.7 | 56.2 | 34.3 | 35.9 | 33.5 | 46.8 | 40.5 | 49.0 | 32.7 | 48.4 | 46.7 | 41.3 | 43.1 | 29.0 | 29.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 62.7 | 39.4 | 47.1 | 27.1 | 43.1 | 36.8 | 56.5 | 34.4 | 36.5 | 29.3 | 43.8 | 40.9 | 49.8 | 29.8 | 47.2 | 48.2 | 41.4 | 43.6 | 30.2 | 28.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 63.3 | 40.4 | 48.0 | 29.0 | 43.3 | 37.7 | 56.5 | 35.2 | 36.7 | 32.4 | 46.9 | 40.7 | 50.7 | 33.0 | 49.3 | 47.2 | 41.8 | 44.4 | 31.9 | 31.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 64.7 | 39.9 | 48.1 | 28.2 | 42.8 | 36.8 | 57.2 | 34.7 | 37.0 | 28.2 | 44.7 | 40.4 | 51.2 | 31.6 | 47.8 | 46.4 | 40.9 | 43.8 | 30.6 | 30.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 65.4 | 39.8 | 47.1 | 26.0 | 42.0 | 37.1 | 57.4 | 34.7 | 36.9 | 32.2 | 44.2 | 40.4 | 51.3 | 31.5 | 49.4 | 46.8 | 41.6 | 42.9 | 31.1 | 28.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 64.7 | 37.5 | 43.8 | 24.1 | 40.3 | 35.8 | 57.1 | 31.8 | 35.7 | 25.0 | 43.1 | 39.2 | 49.1 | 24.9 | 47.9 | 44.4 | 39.3 | 42.8 | 28.7 | 27.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 65.9 | 49.8 | 58.4 | 38.1 | 55.0 | 50.9 | 58.5 | 49.3 | 45.7 | 40.7 | 59.4 | 56.3 | 54.1 | 34.9 | 53.7 | 56.8 | 51.8 | 51.3 | 42.6 | 51.9 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 66.2 | 48.8 | 55.3 | 35.1 | 54.2 | 51.2 | 56.2 | 47.6 | 46.2 | 37.2 | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.3 | 33.7 | 54.6 | 54.3 | 50.8 | 51.9 | 43.6 | 50.9 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 64.4 | 45.3 | 52.5 | 26.8 | 51.0 | 47.2 | 54.8 | 45.9 | 44.0 | 29.5 | 54.1 | 50.0 | 51.2 | 31.3 | 52.1 | 51.8 | 48.6 | 49.8 | 36.5 | 48.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 64.7 | 39.9 | 48.1 | 28.2 | 42.8 | 36.8 | 57.2 | 34.7 | 37.0 | 28.2 | 44.7 | 40.4 | 51.2 | 31.6 | 47.8 | 46.4 | 40.9 | 43.8 | 30.6 | 30.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 66.3 | 38.9 | 48.4 | 25.0 | 42.7 | 36.0 | 57.3 | 33.2 | 36.5 | 22.3 | 44.8 | 39.8 | 49.9 | 31.3 | 48.6 | 46.4 | 41.3 | 43.2 | 30.5 | 30.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 65.7 | 42.2 | 50.0 | 37.8 | 44.2 | 40.0 | 57.8 | 36.0 | 36.5 | 33.0 | 45.2 | 41.8 | 49.3 | 35.0 | 49.0 | 48.1 | 42.0 | 44.1 | 33.7 | 37.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 65.8 | 42.8 | 50.1 | 35.1 | 44.8 | 38.9 | 56.9 | 37.9 | 37.5 | 41.2 | 49.1 | 42.1 | 49.6 | 33.4 | 49.6 | 48.2 | 43.6 | 45.9 | 34.9 | 36.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 66.2 | 48.8 | 55.3 | 35.1 | 54.2 | 51.2 | 56.2 | 47.6 | 46.2 | 37.2 | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.3 | 33.7 | 54.6 | 54.3 | 50.8 | 51.9 | 43.6 | 50.9 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 69.6 | 55.5 | 62.4 | 44.0 | 60.4 | 60.4 | 62.9 | 55.3 | 51.7 | 40.4 | 63.0 | 62.1 | 59.9 | 36.6 | 59.4 | 62.1 | 58.0 | 58.6 | 50.6 | 60.6 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 68.7 | 53.6 | 63.4 | 36.8 | 59.6 | 58.1 | 62.5 | 54.1 | 50.8 | 37.5 | 63.1 | 61.6 | 60.7 | 36.9 | 59.9 | 61.0 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 46.5 | 54.0 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 60.5 | 44.8 | 49.1 | 42.5 | 47.5 | 45.3 | 52.0 | 44.8 | 41.6 | 30.9 | 50.7 | 47.6 | 51.4 | 32.8 | 49.8 | 51.1 | 47.2 | 47.5 | 41.8 | 45.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 66.2 | 48.8 | 55.3 | 35.1 | 54.2 | 51.2 | 56.2 | 47.6 | 46.2 | 37.2 | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.3 | 33.7 | 54.6 | 54.3 | 50.8 | 51.9 | 43.6 | 50.9 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 68.2 | 50.6 | 62.4 | 37.1 | 57.9 | 50.8 | 63.4 | 49.6 | 42.6 | 28.7 | 61.0 | 48.3 | 63.1 | 33.5 | 58.8 | 58.2 | 57.2 | 55.4 | 36.8 | 55.6 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 67.6 | 52.0 | 62.2 | 31.0 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 63.2 | 58.9 | 39.8 | 33.2 | 60.8 | 46.3 | 65.1 | 33.1 | 61.3 | 55.5 | 60.2 | 61.9 | 43.5 | 43.2 |
Centurio Aya | 69.7 | 54.7 | 63.6 | 29.4 | 66.2 | 67.8 | 65.1 | 60.0 | 43.3 | 37.5 | 63.6 | 49.8 | 66.7 | 37.0 | 62.4 | 59.1 | 62.6 | 64.0 | 46.9 | 50.9 |
Centurio Qwen | 72.7 | 56.2 | 65.3 | 47.4 | 62.2 | 56.7 | 67.0 | 53.6 | 48.8 | 36.7 | 65.4 | 54.1 | 67.6 | 39.1 | 63.7 | 63.6 | 60.4 | 58.5 | 45.2 | 63.4 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the BIN-MC (Babel ImageNet Multiple Choice) task, which evaluates the model’s ability to correctly identify objects in images across various languages. It shows the accuracy scores for different models trained with varying numbers of languages, and different data composition strategies. The scores are shown per language and averaged, allowing for a comparison of performance based on language type and training setup.
read the caption
Table 18: BIN-MC
| en | avg. | af | zh | it | pt | th | vi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 52.9 | 32.7 | 32.5 | 37.0 | 49.6 | 39.7 | 25.4 | 12.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 51.2 | 35.3 | 39.9 | 35.9 | 46.4 | 39.7 | 28.2 | 21.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 52.2 | 34.2 | 40.5 | 32.4 | 49.1 | 38.6 | 25.2 | 19.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 51.3 | 35.3 | 43.6 | 34.0 | 47.4 | 37.3 | 27.9 | 21.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 49.2 | 33.7 | 39.3 | 32.9 | 45.1 | 38.4 | 22.2 | 24.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 50.8 | 36.0 | 39.3 | 36.1 | 50.9 | 40.1 | 26.2 | 23.5 |
| Llama 3 - English | 46.1 | 32.5 | 38.6 | 32.6 | 41.6 | 35.0 | 25.9 | 20.9 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 45.0 | 33.8 | 40.5 | 34.3 | 41.9 | 34.1 | 25.7 | 26.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 46.6 | 34.2 | 44.2 | 31.0 | 42.4 | 34.6 | 27.2 | 26.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 50.3 | 35.1 | 39.9 | 35.4 | 46.6 | 39.2 | 23.9 | 25.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 48.8 | 33.9 | 35.0 | 33.6 | 48.1 | 36.1 | 24.7 | 26.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 50.8 | 36.5 | 41.7 | 37.0 | 51.6 | 35.9 | 27.7 | 25.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 50.8 | 36.0 | 39.3 | 36.1 | 50.9 | 40.1 | 26.2 | 23.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 48.0 | 36.1 | 44.2 | 35.9 | 47.1 | 38.4 | 26.7 | 24.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 51.7 | 35.1 | 36.8 | 38.0 | 48.1 | 36.8 | 26.4 | 24.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 43.7 | 33.6 | 41.7 | 29.4 | 44.9 | 35.3 | 23.7 | 27.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 46.6 | 34.2 | 44.2 | 31.0 | 42.4 | 34.6 | 27.2 | 26.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 43.3 | 34.6 | 37.4 | 32.2 | 44.9 | 35.3 | 30.2 | 27.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 50.8 | 36.0 | 39.3 | 36.1 | 50.9 | 40.1 | 26.2 | 23.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 50.3 | 35.8 | 41.7 | 37.5 | 49.4 | 36.6 | 24.2 | 25.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 49.7 | 33.1 | 41.1 | 36.1 | 44.4 | 35.0 | 21.7 | 20.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 48.4 | 33.8 | 41.7 | 35.9 | 46.4 | 34.8 | 23.2 | 20.9 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 46.6 | 34.2 | 44.2 | 31.0 | 42.4 | 34.6 | 27.2 | 26.1 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 50.2 | 37.9 | 44.8 | 34.7 | 48.1 | 40.6 | 31.4 | 27.8 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 52.9 | 37.1 | 50.3 | 33.8 | 46.6 | 37.5 | 30.2 | 24.3 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 42.5 | 33.4 | 43.6 | 33.6 | 41.6 | 30.4 | 27.7 | 23.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 46.6 | 34.2 | 44.2 | 31.0 | 42.4 | 34.6 | 27.2 | 26.1 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 53.6 | 39.6 | 46.0 | 44.7 | 50.6 | 42.4 | 29.7 | 24.3 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 49.3 | 36.5 | 46.6 | 36.8 | 51.9 | 39.0 | 26.2 | 18.3 |
Centurio Aya | 53.0 | 41.2 | 52.8 | 40.3 | 51.4 | 47.7 | 27.4 | 27.8 |
Centurio Qwen | 61.2 | 46.9 | 50.9 | 64.1 | 55.6 | 49.0 | 31.9 | 29.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the M3Exam task, a multiple-choice visual question-answering task, across various language models and training configurations. It shows the accuracy scores obtained by different models, categorized by language tier and training setup (English-only, multilingual mixes with varying proportions of English data, different numbers of training languages, etc.). The metrics show how different amounts of English vs. multilingual data, different language distributions, and the presence or absence of pre-training affect performance on this task, allowing for a comparison of model effectiveness in multilingual settings. The performance is broken down by language tiers (T1-T5), revealing performance differences across resource levels.
read the caption
Table 19: M3Exam
| en | avg. | am | ber | bn | de | fil | ha | hi | ru | sw | th | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 80.8 | 54.1 | 45.0 | 50.8 | 41.5 | 71.7 | 55.8 | 41.7 | 62.7 | 85.0 | 35.8 | 68.3 | 36.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 75.8 | 50.9 | 49.2 | 49.2 | 40.7 | 72.5 | 55.0 | 42.5 | 54.2 | 60.8 | 37.5 | 60.8 | 37.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 83.3 | 55.1 | 51.7 | 43.3 | 49.2 | 70.8 | 65.8 | 42.5 | 61.9 | 70.8 | 38.3 | 75.0 | 36.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 83.3 | 56.6 | 43.3 | 50.8 | 50.8 | 74.2 | 69.2 | 42.5 | 57.6 | 76.7 | 43.3 | 71.7 | 42.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 81.7 | 57.5 | 45.8 | 52.5 | 44.1 | 73.3 | 64.2 | 39.2 | 59.3 | 73.3 | 60.0 | 60.8 | 59.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 76.7 | 56.4 | 46.7 | 46.7 | 54.2 | 71.7 | 60.0 | 45.0 | 57.6 | 70.8 | 57.5 | 65.8 | 44.0 |
| Llama 3 - English | 82.5 | 56.3 | 66.7 | 30.8 | 49.2 | 77.5 | 50.8 | 48.3 | 63.6 | 75.8 | 46.7 | 70.0 | 39.7 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 77.5 | 55.9 | 47.5 | 49.2 | 49.2 | 71.7 | 63.3 | 42.5 | 62.7 | 73.3 | 45.8 | 70.8 | 38.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 80.0 | 64.8 | 58.3 | 47.5 | 64.4 | 75.8 | 61.7 | 67.5 | 64.4 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 67.5 | 73.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 65.0 | 47.5 | 42.5 | 50.0 | 38.1 | 65.0 | 58.3 | 40.0 | 45.8 | 58.3 | 39.2 | 42.5 | 42.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 73.3 | 54.5 | 43.3 | 50.0 | 51.7 | 67.5 | 60.0 | 45.0 | 51.7 | 63.3 | 53.3 | 63.3 | 50.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 73.3 | 60.3 | 54.2 | 47.5 | 58.5 | 72.5 | 55.0 | 58.3 | 60.2 | 72.5 | 64.2 | 59.2 | 61.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 76.7 | 56.4 | 46.7 | 46.7 | 54.2 | 71.7 | 60.0 | 45.0 | 57.6 | 70.8 | 57.5 | 65.8 | 44.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 80.0 | 56.7 | 51.7 | 53.3 | 55.1 | 70.8 | 67.5 | 41.7 | 63.6 | 75.8 | 38.3 | 69.2 | 36.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 79.2 | 54.6 | 43.3 | 50.0 | 44.9 | 80.8 | 60.0 | 42.5 | 55.9 | 77.5 | 45.0 | 55.8 | 44.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 77.5 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 45.0 | 63.6 | 76.7 | 58.3 | 70.8 | 64.4 | 74.2 | 63.3 | 69.2 | 69.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 80.0 | 64.8 | 58.3 | 47.5 | 64.4 | 75.8 | 61.7 | 67.5 | 64.4 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 67.5 | 73.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 82.5 | 63.0 | 45.8 | 39.2 | 66.1 | 80.8 | 58.3 | 68.3 | 61.9 | 75.0 | 63.3 | 75.0 | 59.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 76.7 | 56.4 | 46.7 | 46.7 | 54.2 | 71.7 | 60.0 | 45.0 | 57.6 | 70.8 | 57.5 | 65.8 | 44.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 80.8 | 58.6 | 44.2 | 49.2 | 56.8 | 78.3 | 56.7 | 47.5 | 65.3 | 75.0 | 47.5 | 73.3 | 50.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 80.0 | 63.2 | 58.3 | 50.0 | 55.1 | 78.3 | 63.3 | 60.0 | 61.9 | 76.7 | 55.0 | 75.0 | 61.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 80.0 | 62.0 | 55.8 | 50.0 | 51.7 | 81.7 | 62.5 | 60.0 | 66.1 | 75.0 | 50.0 | 66.7 | 62.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 80.0 | 64.8 | 58.3 | 47.5 | 64.4 | 75.8 | 61.7 | 67.5 | 64.4 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 67.5 | 73.3 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 87.5 | 71.2 | 70.0 | 50.8 | 65.3 | 79.2 | 63.3 | 83.3 | 68.6 | 82.5 | 66.7 | 85.8 | 68.1 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 85.0 | 68.8 | 65.8 | 49.2 | 67.8 | 80.8 | 61.7 | 70.0 | 66.9 | 85.0 | 70.0 | 74.2 | 65.5 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 77.5 | 61.8 | 64.2 | 52.5 | 48.3 | 70.8 | 51.7 | 64.2 | 58.5 | 71.7 | 54.2 | 70.8 | 73.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 80.0 | 64.8 | 58.3 | 47.5 | 64.4 | 75.8 | 61.7 | 67.5 | 64.4 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 67.5 | 73.3 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 91.7 | 71.2 | 76.7 | 50.0 | 69.5 | 81.7 | 77.5 | 57.5 | 72.9 | 83.3 | 71.7 | 80.8 | 62.1 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 92.5 | 69.9 | 52.5 | 54.2 | 55.9 | 80.8 | 85.0 | 72.5 | 79.7 | 83.3 | 63.3 | 78.3 | 63.8 |
Centurio Aya | 82.5 | 66.8 | 71.7 | 54.2 | 59.3 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 65.0 | 71.2 | 75.8 | 67.5 | 72.5 | 65.5 |
Centurio Qwen | 87.5 | 73.1 | 77.5 | 49.2 | 62.7 | 80.8 | 78.3 | 76.7 | 72.9 | 85.0 | 70.0 | 81.7 | 69.0 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of various Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on the Visually Grounded Reasoning (VGR) task. The models’ performance is evaluated across multiple languages, grouped into tiers based on resource availability (T1-T5, with T5 representing high-resource languages like English and T1 representing low-resource languages). The table shows the accuracy scores achieved by each model in each language tier, illustrating the models’ multilingual capabilities and the impact of different training strategies. English performance is also shown separately for each model. The results help determine which models handle multilingual VGR effectively and which training techniques, such as varying the proportion of English versus multilingual data, lead to the best outcomes.
read the caption
Table 20: VGR
| en | avg. | am | ber | bn | de | fil | ha | hi | ru | sw | th | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 16.7 | 21.3 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 19.2 | 16.7 | 25.8 | 28.3 | 17.0 | 12.5 | 25.0 | 26.7 | 22.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 23.3 | 20.0 | 15.0 | 18.3 | 20.8 | 21.7 | 16.7 | 20.0 | 23.2 | 27.5 | 22.3 | 15.8 | 18.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 17.5 | 18.2 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 13.3 | 20.8 | 17.5 | 16.7 | 21.4 | 26.7 | 16.1 | 10.0 | 17.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 25.8 | 19.8 | 16.7 | 17.5 | 21.7 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 21.7 | 23.2 | 20.8 | 18.8 | 16.7 | 18.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 21.7 | 20.5 | 21.7 | 18.3 | 16.7 | 22.5 | 27.5 | 27.5 | 17.9 | 21.7 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 21.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 18.3 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 19.2 | 25.8 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 25.0 | 20.8 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 18.6 |
| Llama 3 - English | 12.5 | 20.8 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 29.2 | 15.2 | 12.5 | 28.6 | 29.2 | 19.5 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 20.8 | 20.1 | 18.3 | 19.2 | 17.5 | 16.7 | 25.0 | 21.7 | 24.1 | 15.0 | 19.6 | 23.3 | 20.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 12.5 | 20.6 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 30.0 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 27.5 | 19.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 24.2 | 19.3 | 15.0 | 21.7 | 17.5 | 20.0 | 29.2 | 22.5 | 17.9 | 14.2 | 16.1 | 22.5 | 16.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 23.3 | 19.2 | 23.3 | 15.0 | 16.7 | 21.7 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 20.5 | 24.2 | 10.7 | 15.8 | 22.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 25.0 | 18.3 | 20.8 | 18.3 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 17.9 | 21.7 | 14.3 | 16.7 | 16.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 18.3 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 19.2 | 25.8 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 25.0 | 20.8 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 18.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 16.7 | 18.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 19.2 | 19.2 | 16.7 | 23.3 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 20.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 22.5 | 19.0 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 15.8 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 23.3 | 21.4 | 23.3 | 16.1 | 15.8 | 19.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 13.3 | 20.4 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 19.2 | 10.8 | 23.3 | 26.7 | 17.9 | 10.0 | 28.6 | 28.3 | 19.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 12.5 | 20.6 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 30.0 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 27.5 | 19.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 12.5 | 19.9 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 15.0 | 10.8 | 22.5 | 28.3 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 28.3 | 19.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 18.3 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 19.2 | 25.8 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 25.0 | 20.8 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 18.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 23.3 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 24.2 | 20.0 | 25.0 | 21.7 | 19.6 | 15.0 | 20.5 | 20.0 | 20.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 20.0 | 18.6 | 18.3 | 17.5 | 15.0 | 15.8 | 14.2 | 21.7 | 17.9 | 23.3 | 20.5 | 20.8 | 19.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 25.0 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 22.5 | 19.2 | 22.5 | 16.7 | 15.8 | 20.5 | 21.7 | 16.1 | 15.0 | 22.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 12.5 | 20.6 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 30.0 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 27.5 | 19.5 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 19.2 | 20.5 | 15.8 | 19.2 | 22.5 | 15.0 | 23.3 | 23.3 | 17.9 | 13.3 | 25.9 | 28.3 | 21.2 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 13.3 | 20.8 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 12.5 | 23.3 | 29.2 | 17.0 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 28.3 | 19.5 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 14.2 | 21.1 | 18.3 | 22.5 | 20.8 | 10.8 | 25.0 | 28.3 | 16.1 | 11.7 | 27.7 | 30.0 | 20.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 12.5 | 20.6 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 30.0 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 27.5 | 19.5 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 26.7 | 27.3 | 25.0 | 21.7 | 26.7 | 27.5 | 27.5 | 25.0 | 29.5 | 25.0 | 29.5 | 40.0 | 22.9 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 12.5 | 20.7 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 24.2 | 29.2 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 29.2 | 19.5 |
| Centurio Aya | 12.5 | 20.7 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 11.7 | 24.2 | 29.2 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 29.2 | 19.5 |
| Centurio Qwen | 28.3 | 27.0 | 18.3 | 20.0 | 33.3 | 32.5 | 29.2 | 22.5 | 25.0 | 22.5 | 30.4 | 30.0 | 33.1 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the Visio-Linguistic Outlier Detection (VLOD) task, which involves identifying the outlier image among a set of images. The performance of several models is evaluated across different languages, categorized into tiers based on resource availability, showing the accuracy achieved by each model for each language tier. The table also includes results for models trained with various data distributions and settings, offering insights into the impact of different training strategies on the model’s performance.
read the caption
Table 21: VLOD
| en | avg. | id | sw | ta | tr | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 82.1 | 61.4 | 65.6 | 50.8 | 53.3 | 63.8 | 73.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 81.5 | 61.8 | 66.4 | 53.4 | 53.7 | 61.6 | 73.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 81.2 | 64.3 | 68.7 | 52.3 | 54.3 | 70.2 | 76.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 81.5 | 65.9 | 70.8 | 56.4 | 56.7 | 68.9 | 76.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 79.7 | 66.4 | 70.2 | 62.2 | 57.5 | 66.7 | 75.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 79.6 | 64.4 | 69.0 | 59.0 | 53.6 | 67.5 | 73.0 |
| Llama 3 - English | 85.2 | 65.0 | 68.8 | 52.5 | 54.3 | 69.7 | 79.8 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 84.5 | 67.1 | 73.8 | 55.7 | 53.6 | 72.7 | 79.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 83.7 | 74.2 | 75.3 | 71.4 | 68.4 | 79.8 | 76.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 71.9 | 61.4 | 65.1 | 56.1 | 54.3 | 65.2 | 66.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 74.1 | 63.4 | 66.8 | 58.1 | 57.2 | 65.1 | 70.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 76.0 | 61.6 | 63.4 | 57.6 | 56.9 | 64.0 | 66.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 79.6 | 64.4 | 69.0 | 59.0 | 53.6 | 67.5 | 73.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 81.7 | 64.7 | 71.3 | 54.4 | 56.1 | 64.8 | 77.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 83.1 | 64.3 | 70.7 | 56.3 | 53.8 | 62.8 | 77.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 80.0 | 72.9 | 71.9 | 70.8 | 71.7 | 75.7 | 74.2 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 83.7 | 74.2 | 75.3 | 71.4 | 68.4 | 79.8 | 76.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 85.1 | 71.1 | 73.4 | 63.7 | 65.1 | 75.7 | 77.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 79.6 | 64.4 | 69.0 | 59.0 | 53.6 | 67.5 | 73.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 82.0 | 65.6 | 68.6 | 59.4 | 57.9 | 67.6 | 74.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 82.5 | 69.9 | 75.2 | 64.0 | 64.1 | 71.1 | 74.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 81.9 | 67.9 | 74.0 | 64.0 | 60.2 | 68.0 | 73.4 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 83.7 | 74.2 | 75.3 | 71.4 | 68.4 | 79.8 | 76.0 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 87.5 | 80.4 | 82.5 | 75.5 | 77.1 | 84.5 | 82.3 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 86.5 | 78.9 | 81.3 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 83.4 | 81.5 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 82.5 | 73.0 | 72.6 | 71.4 | 68.3 | 76.4 | 76.2 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 83.7 | 74.2 | 75.3 | 71.4 | 68.4 | 79.8 | 76.0 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 89.6 | 79.4 | 84.8 | 73.9 | 65.2 | 86.6 | 86.6 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 87.0 | 80.2 | 83.9 | 75.6 | 71.7 | 86.9 | 83.0 |
Centurio Aya | 85.0 | 77.9 | 79.5 | 70.9 | 73.4 | 83.4 | 82.4 |
Centurio Qwen | 89.6 | 81.7 | 85.0 | 76.8 | 76.0 | 84.2 | 86.7 |
🔼 Table 22 presents the results of the MaRVL (Multilingual Reasoning over Vision and Language) task. The table compares the performance of various large vision-language models (LVLMs) on this task across different languages, grouped into five tiers (T1-T5) based on resource availability. Each language tier represents a range of languages with similar levels of available training data. The table shows the performance (accuracy) of each model on the MaRVL dataset for each language tier, as well as the overall average performance across all tiers. It allows for an analysis of how well these models generalize to low-resource languages compared to higher-resource languages.
read the caption
Table 22: MaRVL
| en | avg. | fr | hi | he | ro | th | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 53.0 | 9.2 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 7.9 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 7.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 51.3 | 25.6 | 41.0 | 30.6 | 17.5 | 15.6 | 27.5 | 21.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 51.0 | 33.1 | 45.4 | 50.7 | 27.0 | 23.7 | 32.5 | 19.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 53.7 | 36.7 | 41.0 | 45.9 | 33.0 | 36.6 | 40.4 | 23.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 53.4 | 35.9 | 42.3 | 48.0 | 33.3 | 35.1 | 32.8 | 23.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 54.4 | 36.6 | 43.0 | 48.0 | 30.8 | 35.1 | 39.1 | 23.5 |
| Llama 3 - English | 55.4 | 7.7 | 9.2 | 10.9 | 6.7 | 4.5 | 8.3 | 6.8 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 41.3 | 20.2 | 45.1 | 12.6 | 2.9 | 24.3 | 14.6 | 21.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 52.7 | 42.3 | 42.3 | 54.4 | 40.6 | 40.5 | 52.6 | 23.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 48.0 | 33.8 | 39.9 | 45.2 | 32.4 | 32.4 | 32.8 | 19.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 52.0 | 35.4 | 44.7 | 45.6 | 34.6 | 36.0 | 29.5 | 22.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 50.7 | 35.1 | 44.0 | 44.6 | 29.8 | 33.0 | 38.1 | 21.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 54.4 | 36.6 | 43.0 | 48.0 | 30.8 | 35.1 | 39.1 | 23.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 51.0 | 32.5 | 42.0 | 36.4 | 29.8 | 33.3 | 31.8 | 21.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 54.7 | 29.7 | 41.6 | 28.2 | 27.3 | 28.5 | 30.5 | 21.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 49.0 | 41.9 | 37.9 | 53.4 | 45.7 | 41.4 | 51.0 | 21.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 52.7 | 42.3 | 42.3 | 54.4 | 40.6 | 40.5 | 52.6 | 23.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 52.7 | 40.6 | 43.3 | 52.7 | 36.2 | 40.2 | 49.0 | 22.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 54.4 | 36.6 | 43.0 | 48.0 | 30.8 | 35.1 | 39.1 | 23.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 54.0 | 36.2 | 44.0 | 48.6 | 32.4 | 33.9 | 36.8 | 21.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 53.4 | 39.0 | 45.7 | 49.3 | 39.4 | 36.6 | 40.7 | 22.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 55.7 | 39.7 | 44.7 | 52.0 | 41.0 | 40.8 | 40.1 | 19.9 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 52.7 | 42.3 | 42.3 | 54.4 | 40.6 | 40.5 | 52.6 | 23.1 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 55.0 | 48.5 | 47.4 | 57.1 | 56.2 | 47.4 | 57.3 | 25.7 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 58.1 | 47.4 | 44.7 | 54.8 | 54.0 | 47.1 | 57.3 | 26.4 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 51.7 | 41.5 | 39.6 | 52.4 | 44.1 | 39.3 | 48.7 | 24.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 52.7 | 42.3 | 42.3 | 54.4 | 40.6 | 40.5 | 52.6 | 23.1 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 58.7 | 45.8 | 46.4 | 51.4 | 50.2 | 41.7 | 57.9 | 27.0 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 53.4 | 47.2 | 46.4 | 58.8 | 59.4 | 49.9 | 41.4 | 27.4 |
Centurio Aya | 55.7 | 49.3 | 45.1 | 62.9 | 58.7 | 51.1 | 46.7 | 31.6 |
Centurio Qwen | 60.1 | 47.7 | 47.1 | 56.8 | 45.1 | 47.7 | 57.0 | 32.2 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the MaXM (Massively Multilingual Cross-lingual Visual Question Answering) dataset experiment. It compares the performance of various large vision-language models (LVLMs) across different language groups and configurations, including different multilingual training data ratios and various pre-training strategies. The evaluation metrics likely involve accuracy scores, averaged across different language tiers (e.g., low-resource, high-resource languages). Each row represents a different model and training configuration, enabling a comparison of multilingual abilities and the impact of various training parameters. The columns likely represent different languages or groups of languages, showing performance scores for each model in those language groups.
read the caption
Table 23: MaXM
| Model | avg. | ar | de | fr | it | ja | ko | ru | th | vi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 3.2 | 0.9 | 6.5 | 9.3 | 8.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 5.7 | 1.7 | 12.0 | 15.9 | 10.1 | 2.4 | 3.8 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 5.9 | 2.7 | 14.0 | 15.1 | 9.6 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 5.8 | 2.0 | 13.5 | 14.6 | 9.4 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 2.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 6.6 | 5.3 | 15.9 | 15.1 | 9.4 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 6.3 | 2.8 | 15.8 | 16.8 | 8.9 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.9 |
| Llama 3 - English | 3.2 | 0.3 | 6.9 | 8.0 | 8.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 2.7 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 5.6 | 2.0 | 14.2 | 15.0 | 9.1 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 6.0 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 15.8 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 4.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 4.7 | 2.0 | 12.0 | 9.4 | 7.5 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 2.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 5.7 | 3.0 | 12.1 | 14.2 | 8.6 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 6.2 | 3.6 | 14.0 | 15.8 | 8.7 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 2.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 6.3 | 2.8 | 15.8 | 16.8 | 8.9 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 6.3 | 2.6 | 13.8 | 18.3 | 8.7 | 4.3 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 2.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 7.0 | 2.6 | 14.7 | 19.3 | 10.4 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 1.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 11.3 | 13.8 | 7.5 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 6.0 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 15.8 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 4.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 14.0 | 17.8 | 9.7 | 2.5 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 3.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 6.3 | 2.8 | 15.8 | 16.8 | 8.9 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 6.9 | 3.7 | 16.0 | 15.9 | 11.3 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 3.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 6.1 | 1.8 | 14.8 | 15.8 | 10.5 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 2.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 6.2 | 1.6 | 14.9 | 15.9 | 11.1 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 6.0 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 15.8 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 4.1 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 6.9 | 2.4 | 17.1 | 16.6 | 9.1 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 5.2 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 8.3 | 2.6 | 18.7 | 19.6 | 11.4 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 5.3 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 11.1 | 8.1 | 7.1 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 6.0 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 15.8 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 4.1 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 6.4 | 5.5 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 10.3 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 5.2 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 6.2 | 3.7 | 13.2 | 13.9 | 9.5 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 3.6 |
| Centurio Aya | 11.1 | 6.7 | 19.9 | 22.5 | 16.7 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 11.9 | 4.6 | 22.7 | 26.5 | 18.6 | 5.9 | 9.9 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 8.9 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the MTVQA (Multilingual Text-heavy Visual Question Answering) task. It shows the performance of various large vision-language models across different languages, broken down by language group (tier), reflecting the models’ abilities to answer questions about images with text-heavy content. The results are expressed as average scores, indicating the accuracy of each model’s answers. The table helps to analyze how well these models perform on this specific task, considering varying degrees of language resource availability.
read the caption
Table 24: MTVQA
| en | avg. | bn | de | id | ko | pt | ru | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 59.7 | 37.2 | 4.9 | 47.8 | 33.2 | 38.2 | 47.1 | 42.1 | 47.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 54.1 | 34.1 | 2.6 | 44.6 | 34.3 | 36.3 | 43.8 | 36.4 | 41.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 52.0 | 37.4 | 5.7 | 45.6 | 38.7 | 40.4 | 45.2 | 43.4 | 42.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 54.8 | 40.6 | 22.7 | 46.5 | 42.1 | 39.8 | 46.0 | 43.6 | 43.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 57.8 | 45.3 | 27.4 | 50.3 | 46.0 | 46.4 | 48.6 | 49.5 | 48.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 56.6 | 45.1 | 27.0 | 51.4 | 44.8 | 44.9 | 50.8 | 48.2 | 48.7 |
| Llama 3 - English | 61.9 | 39.2 | 13.2 | 49.0 | 35.6 | 39.1 | 44.9 | 44.1 | 48.4 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 49.3 | 33.8 | 5.9 | 43.8 | 38.0 | 32.4 | 41.7 | 37.3 | 37.4 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 60.6 | 51.0 | 46.7 | 54.1 | 51.2 | 49.4 | 53.4 | 51.2 | 51.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 48.4 | 40.3 | 28.2 | 43.9 | 41.1 | 40.6 | 43.0 | 42.8 | 42.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 51.8 | 42.2 | 27.6 | 46.3 | 43.0 | 42.2 | 45.7 | 44.8 | 45.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 53.8 | 42.9 | 29.1 | 47.6 | 43.4 | 42.2 | 46.6 | 45.9 | 45.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 56.6 | 45.1 | 27.0 | 51.4 | 44.8 | 44.9 | 50.8 | 48.2 | 48.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 58.6 | 45.8 | 26.4 | 52.4 | 44.4 | 45.4 | 51.9 | 49.9 | 50.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 58.5 | 42.1 | 14.2 | 53.0 | 39.8 | 43.3 | 51.4 | 45.7 | 47.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 54.9 | 45.0 | 40.5 | 46.4 | 45.7 | 42.5 | 46.5 | 46.2 | 47.4 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 60.6 | 51.0 | 46.7 | 54.1 | 51.2 | 49.4 | 53.4 | 51.2 | 51.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 61.9 | 51.4 | 42.5 | 56.2 | 51.7 | 50.1 | 54.6 | 52.5 | 52.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 56.6 | 45.1 | 27.0 | 51.4 | 44.8 | 44.9 | 50.8 | 48.2 | 48.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 58.0 | 46.1 | 29.5 | 52.8 | 46.1 | 44.5 | 51.7 | 49.5 | 48.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 58.3 | 47.6 | 35.4 | 52.8 | 48.7 | 45.5 | 52.5 | 49.6 | 48.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 58.3 | 47.0 | 37.6 | 52.6 | 46.8 | 44.1 | 51.5 | 48.1 | 48.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 60.6 | 51.0 | 46.7 | 54.1 | 51.2 | 49.4 | 53.4 | 51.2 | 51.3 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 61.1 | 55.1 | 52.8 | 56.6 | 56.0 | 53.9 | 56.0 | 55.4 | 55.0 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 61.6 | 53.0 | 50.4 | 54.9 | 53.6 | 52.4 | 53.0 | 53.1 | 53.4 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 56.5 | 47.5 | 43.9 | 51.6 | 47.6 | 44.2 | 50.1 | 47.5 | 47.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 60.6 | 51.0 | 46.7 | 54.1 | 51.2 | 49.4 | 53.4 | 51.2 | 51.3 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 60.3 | 51.9 | 44.2 | 54.8 | 53.1 | 51.3 | 54.3 | 53.2 | 52.8 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 60.5 | 52.5 | 45.2 | 54.6 | 53.8 | 51.7 | 54.7 | 53.9 | 53.4 |
Centurio Aya | 59.1 | 53.2 | 43.4 | 56.9 | 54.4 | 53.6 | 56.2 | 54.0 | 54.3 |
Centurio Qwen | 60.6 | 54.8 | 49.9 | 57.0 | 54.9 | 53.5 | 57.2 | 55.8 | 55.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the xGQA (cross-lingual visual question answering) task, comparing the performance of various large vision-language models (LVLMs). The models are evaluated across multiple languages, with the scores reflecting their accuracy in answering questions about images. Different training setups are compared, including variations in the number of languages included in training and different proportions of English versus non-English data. This allows analysis of the tradeoffs between multilingual performance and the cost of obtaining multilingual training data. The table helps quantify the impact of various multilingual training strategies on the model’s ability to understand and correctly respond to the questions across different languages.
read the caption
Table 25: xGQA
🔼 This table presents the results of the XM3600 image captioning task, comparing the performance of various models across multiple languages. The rows represent different model configurations and training setups, while the columns correspond to individual languages, with English denoted as ’en’ and multilingual results as ‘mul’. Metrics include the CIDEr score (a metric for evaluating image caption quality) and language fidelity. This table allows us to analyze how different training approaches affect multilingual performance on image captioning, showing scores for each language and the average across all languages.
read the caption
Table 26: XM3600
| ar | bn | cs | da | de | el | en | es | fa | fi | fil | fr | he | hi | hr | hu | id | it | ja | ko | mi | nl | no | pl | pt | quz | ro | ru | sv | sw | te | th | tr | uk | vi | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - L100 | 93.8 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 91.8 | 100.0 | 88.3 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.8 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 97.7 | 76.2 | 100.0 | 95.3 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.4 | 100.0 | 97.7 | 0.2 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 98.6 | 98.2 | 93.2 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 92.6 | 100.0 | 96.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 | 94.7 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 98.4 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.8 | 79.1 | 100.0 | 88.5 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 97.3 | 100.0 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 27.5 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 99.0 | 63.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 96.9 | 100.0 | 93.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 | 92.2 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 97.9 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.0 | 77.9 | 100.0 | 91.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 95.9 | 100.0 | 75.2 | 100.0 | 52.1 | 37.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 84.4 | 82.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 96.5 | 100.0 | 95.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 | 96.5 | 96.1 | 99.2 | 78.3 | 100.0 | 98.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 98.6 | 89.8 | 100.0 | 98.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 95.7 | 100.0 | 71.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 12.7 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 84.6 | 67.2 | 99.0 | 100.0 | 30.9 | 100.0 | 94.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 | 98.2 | 97.3 | 78.7 | 87.5 | 100.0 | 50.2 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 2.3 | 76.4 | 49.4 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 99.2 | 73.6 | 99.2 | 95.1 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 1.6 | 99.8 | 92.0 | 96.5 | 100.0 | 0.2 | 96.3 | 100.0 | 98.6 | 36.1 | 62.5 | 90.2 | 94.9 | 91.6 | 39.8 | 96.7 |
🔼 This table presents the language fidelity results for the XM3600 dataset, focusing on the ability of different language models to produce outputs in the correct target language. The results are broken down by language tier and model configuration, providing a detailed view of language-specific performance.
read the caption
Table 27: XM3600 language fidelity (§1(b))
| en | avg. | ar | es | fr | ru | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 59.6 | 55.0 | 52.3 | 54.9 | 57.6 | 55.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 59.9 | 51.8 | 49.7 | 51.3 | 55.2 | 51.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 58.9 | 48.3 | 47.7 | 47.1 | 51.2 | 47.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 58.6 | 50.5 | 46.6 | 51.3 | 52.6 | 51.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 58.5 | 53.6 | 50.7 | 54.7 | 55.1 | 54.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 59.6 | 53.3 | 49.9 | 53.7 | 56.8 | 52.6 |
| Llama 3 - English | 46.1 | 36.3 | 33.4 | 37.0 | 36.5 | 38.2 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 45.4 | 37.5 | 36.6 | 36.1 | 38.7 | 38.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 59.7 | 54.8 | 53.0 | 54.7 | 56.3 | 55.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 55.2 | 48.2 | 42.2 | 50.6 | 51.1 | 48.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 58.3 | 53.4 | 50.5 | 54.3 | 55.7 | 53.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 58.2 | 48.4 | 43.5 | 50.3 | 52.7 | 47.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 59.6 | 53.3 | 49.9 | 53.7 | 56.8 | 52.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 61.9 | 54.5 | 50.3 | 56.2 | 57.5 | 54.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 60.0 | 50.5 | 43.6 | 53.8 | 55.1 | 49.5 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 60.8 | 55.3 | 56.3 | 52.6 | 55.0 | 57.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 59.7 | 54.8 | 53.0 | 54.7 | 56.3 | 55.4 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 57.8 | 51.1 | 48.9 | 52.3 | 52.1 | 51.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 59.6 | 53.3 | 49.9 | 53.7 | 56.8 | 52.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 54.3 | 45.4 | 40.1 | 47.8 | 49.4 | 44.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 58.9 | 52.5 | 49.0 | 53.8 | 54.6 | 52.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 56.8 | 49.7 | 46.8 | 49.6 | 53.9 | 48.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 59.7 | 54.8 | 53.0 | 54.7 | 56.3 | 55.4 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 61.7 | 59.4 | 58.8 | 59.0 | 60.0 | 59.7 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 60.3 | 57.3 | 56.5 | 56.5 | 58.3 | 57.8 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 59.9 | 55.0 | 53.1 | 54.6 | 57.1 | 55.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 59.7 | 54.8 | 53.0 | 54.7 | 56.3 | 55.4 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 57.8 | 52.6 | 55.7 | 47.5 | 52.5 | 54.8 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 58.2 | 54.7 | 54.7 | 54.0 | 56.4 | 53.5 |
| Centurio Aya | 65.0 | 62.4 | 61.7 | 61.0 | 64.3 | 62.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 75.4 | 70.2 | 68.8 | 70.9 | 70.5 | 70.8 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the XVNLI (Cross-lingual Visual Natural Language Inference) task across various multilingual vision-language models. XVNLI assesses a model’s ability to determine the relationship (entailment, contradiction, or neutral) between a given textual hypothesis and a pair of images. The table compares performance across different models and language distributions during training, focusing on English and other languages. Metrics used are likely accuracy scores and may also include standard deviations for each language or language group.
read the caption
Table 28: XVNLI
| en | avg. | ar | fr | hi | id | ja | pt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 38.4 | 36.2 | 36.2 | 41.9 | 29.9 | 35.4 | 34.2 | 39.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 36.7 | 36.2 | 31.5 | 38.9 | 31.6 | 37.0 | 34.9 | 43.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 37.0 | 33.9 | 33.2 | 39.9 | 29.2 | 32.3 | 31.2 | 37.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 37.3 | 35.8 | 32.5 | 39.3 | 32.3 | 37.0 | 36.8 | 37.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 37.6 | 35.1 | 32.2 | 40.3 | 32.6 | 34.7 | 32.3 | 38.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 36.6 | 32.0 | 28.5 | 35.9 | 27.8 | 32.0 | 31.2 | 36.7 |
| Llama 3 - English | 33.2 | 32.4 | 30.9 | 34.2 | 30.6 | 32.7 | 30.5 | 35.7 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 33.4 | 32.4 | 34.9 | 36.6 | 28.9 | 31.3 | 30.9 | 31.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 33.0 | 31.7 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 34.0 | 31.6 | 27.9 | 30.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 37.3 | 34.1 | 32.5 | 40.3 | 30.9 | 31.3 | 31.6 | 37.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 36.1 | 30.9 | 27.5 | 33.9 | 28.2 | 28.6 | 32.7 | 34.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 34.4 | 31.9 | 28.5 | 35.9 | 29.2 | 30.3 | 33.5 | 34.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 36.6 | 32.0 | 28.5 | 35.9 | 27.8 | 32.0 | 31.2 | 36.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 36.2 | 33.2 | 31.9 | 38.9 | 29.2 | 32.7 | 29.0 | 37.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 37.1 | 31.9 | 30.5 | 35.6 | 25.8 | 31.0 | 33.8 | 34.7 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 32.6 | 30.0 | 26.8 | 31.5 | 26.8 | 31.6 | 32.0 | 31.3 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 33.0 | 31.7 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 34.0 | 31.6 | 27.9 | 30.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 32.7 | 33.5 | 30.5 | 35.9 | 30.9 | 35.4 | 31.2 | 37.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 36.6 | 32.0 | 28.5 | 35.9 | 27.8 | 32.0 | 31.2 | 36.7 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 33.4 | 30.2 | 28.5 | 32.9 | 28.9 | 30.0 | 27.5 | 33.3 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 35.0 | 33.4 | 30.9 | 39.3 | 33.7 | 31.0 | 30.5 | 35.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 36.0 | 31.3 | 26.5 | 35.9 | 29.2 | 32.0 | 28.3 | 36.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 33.0 | 31.7 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 34.0 | 31.6 | 27.9 | 30.6 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 38.6 | 35.2 | 33.9 | 34.2 | 34.0 | 35.0 | 36.1 | 38.0 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 36.9 | 36.1 | 34.6 | 36.2 | 36.8 | 36.7 | 36.1 | 36.0 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 32.8 | 32.0 | 32.5 | 30.9 | 33.0 | 30.6 | 32.7 | 32.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 33.0 | 31.7 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 34.0 | 31.6 | 27.9 | 30.6 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 39.8 | 39.7 | 38.6 | 40.3 | 34.4 | 40.7 | 38.7 | 45.5 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 36.8 | 35.4 | 34.9 | 35.2 | 37.5 | 36.4 | 34.6 | 33.7 |
Centurio Aya | 37.6 | 37.2 | 36.2 | 38.9 | 38.8 | 39.7 | 34.2 | 35.4 |
Centurio Qwen | 46.4 | 43.0 | 39.6 | 45.0 | 41.6 | 44.1 | 43.5 | 44.1 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the xMMMU (cross-lingual, multi-modal, multiple-choice visual question answering) task. It compares the performance of various large vision-language models (LVLMs) across different language tiers, including English and several multilingual models with varied English data composition in their training. The evaluation metrics likely includes accuracy scores for each language tier. It allows for analysis of how many languages can be included in model training, optimal language distributions in pre-training and instruction tuning, and strategies to enhance multilingual text understanding. The table likely shows the impact of various training strategies on performance across different languages.
read the caption
Table 29: xMMMU
| en | avg. | avg. Latin | avg. other | ar | de | hi | id | it | ko | ru | th | zh | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 65.8 | 55.8 | 62.3 | 51.5 | 50.2 | 63.5 | 58.5 | 61.4 | 64.0 | 49.0 | 52.1 | 49.1 | 49.8 | 60.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 75.2 | 60.2 | 70.9 | 53.1 | 50.2 | 70.8 | 65.4 | 71.8 | 71.6 | 49.8 | 54.1 | 51.0 | 48.0 | 69.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 74.2 | 60.8 | 71.4 | 53.7 | 52.2 | 71.5 | 65.5 | 72.8 | 73.1 | 51.1 | 53.9 | 49.6 | 49.6 | 68.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 70.4 | 58.7 | 67.7 | 52.8 | 51.6 | 66.9 | 61.0 | 69.6 | 67.2 | 50.0 | 53.6 | 48.9 | 51.4 | 67.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 68.4 | 56.2 | 64.2 | 50.8 | 49.5 | 64.5 | 58.4 | 65.4 | 64.9 | 50.0 | 50.5 | 48.8 | 47.9 | 62.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 69.6 | 58.0 | 67.2 | 51.9 | 49.9 | 68.0 | 62.4 | 69.0 | 67.9 | 48.6 | 52.5 | 49.6 | 48.4 | 64.1 |
| Llama 3 - English | 72.0 | 60.5 | 69.6 | 54.4 | 53.5 | 69.9 | 67.2 | 71.1 | 70.9 | 48.9 | 57.5 | 50.1 | 49.4 | 66.5 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 73.4 | 62.2 | 72.5 | 55.4 | 54.5 | 72.2 | 67.1 | 74.4 | 71.5 | 50.5 | 56.6 | 51.6 | 51.9 | 72.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 72.0 | 58.4 | 67.9 | 52.1 | 51.6 | 69.6 | 62.0 | 65.9 | 70.4 | 49.9 | 52.0 | 48.8 | 48.4 | 65.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 58.4 | 52.6 | 55.7 | 50.5 | 50.2 | 55.2 | 53.5 | 57.5 | 56.4 | 49.6 | 50.9 | 48.2 | 50.5 | 53.5 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 56.9 | 51.6 | 54.9 | 49.4 | 48.5 | 54.8 | 49.6 | 55.1 | 56.8 | 50.5 | 48.2 | 49.6 | 50.0 | 52.9 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 60.4 | 54.0 | 58.8 | 50.8 | 51.8 | 58.9 | 54.5 | 58.1 | 60.0 | 50.0 | 51.1 | 48.4 | 49.2 | 58.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 69.6 | 58.0 | 67.2 | 51.9 | 49.9 | 68.0 | 62.4 | 69.0 | 67.9 | 48.6 | 52.5 | 49.6 | 48.4 | 64.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 74.5 | 61.2 | 71.6 | 54.2 | 53.2 | 71.2 | 63.8 | 74.0 | 70.5 | 50.5 | 54.2 | 51.9 | 51.8 | 70.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 71.6 | 59.4 | 69.2 | 52.9 | 51.0 | 70.2 | 60.5 | 69.4 | 71.2 | 49.6 | 54.1 | 50.4 | 51.8 | 66.1 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 65.9 | 56.6 | 62.6 | 52.6 | 51.5 | 62.1 | 59.5 | 62.6 | 65.8 | 50.8 | 54.5 | 50.4 | 48.8 | 59.9 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 72.0 | 58.4 | 67.9 | 52.1 | 51.6 | 69.6 | 62.0 | 65.9 | 70.4 | 49.9 | 52.0 | 48.8 | 48.4 | 65.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 73.1 | 59.4 | 68.4 | 53.3 | 51.0 | 67.4 | 65.8 | 71.0 | 69.0 | 50.6 | 52.6 | 49.9 | 50.1 | 66.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 69.6 | 58.0 | 67.2 | 51.9 | 49.9 | 68.0 | 62.4 | 69.0 | 67.9 | 48.6 | 52.5 | 49.6 | 48.4 | 64.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 79.5 | 63.3 | 74.8 | 55.6 | 52.8 | 75.8 | 68.5 | 76.2 | 76.5 | 50.8 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 51.0 | 70.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 76.1 | 62.4 | 73.0 | 55.3 | 52.4 | 72.2 | 69.6 | 73.6 | 73.8 | 49.2 | 59.9 | 50.0 | 50.6 | 72.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 78.1 | 64.5 | 74.5 | 57.7 | 57.0 | 74.0 | 72.8 | 76.8 | 75.0 | 52.8 | 62.2 | 51.4 | 50.2 | 72.4 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 72.0 | 58.4 | 67.9 | 52.1 | 51.6 | 69.6 | 62.0 | 65.9 | 70.4 | 49.9 | 52.0 | 48.8 | 48.4 | 65.6 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 76.9 | 65.1 | 74.4 | 58.9 | 55.0 | 74.8 | 73.0 | 75.5 | 74.4 | 53.4 | 65.9 | 52.5 | 53.8 | 72.9 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 79.9 | 65.2 | 77.4 | 57.0 | 52.6 | 77.6 | 73.4 | 78.1 | 78.2 | 51.0 | 64.0 | 49.1 | 51.8 | 75.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR English | 78.4 | 64.6 | 74.7 | 57.9 | 59.1 | 77.1 | 70.9 | 73.6 | 74.5 | 50.6 | 66.5 | 51.1 | 49.0 | 73.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 50 | 81.2 | 66.7 | 76.7 | 60.0 | 61.4 | 78.6 | 72.1 | 76.0 | 77.1 | 51.5 | 71.5 | 52.1 | 51.6 | 75.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 1 | 81.0 | 69.8 | 78.3 | 64.1 | 66.8 | 78.0 | 76.8 | 78.5 | 79.1 | 56.9 | 73.2 | 58.6 | 52.4 | 77.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR Latin-down | 78.9 | 65.4 | 74.2 | 59.5 | 57.8 | 75.5 | 67.6 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 56.4 | 67.8 | 55.0 | 52.5 | 71.1 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 50 (frozen) | 76.1 | 62.1 | 70.8 | 56.3 | 59.2 | 73.2 | 63.2 | 66.2 | 76.1 | 50.0 | 68.0 | 47.8 | 49.8 | 67.8 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 59.9 | 53.5 | 57.1 | 51.1 | 49.6 | 59.1 | 56.5 | 56.8 | 58.9 | 49.9 | 51.0 | 50.6 | 49.2 | 53.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 72.0 | 58.4 | 67.9 | 52.1 | 51.6 | 69.6 | 62.0 | 65.9 | 70.4 | 49.9 | 52.0 | 48.8 | 48.4 | 65.6 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 82.8 | 62.5 | 75.1 | 54.0 | 51.5 | 76.4 | 66.5 | 76.5 | 76.5 | 50.1 | 55.2 | 51.0 | 49.8 | 71.1 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 79.1 | 63.5 | 75.2 | 55.7 | 53.9 | 77.2 | 71.4 | 75.6 | 75.0 | 50.6 | 56.0 | 51.1 | 51.0 | 73.1 |
| modelname Aya | 83.1 | 74.2 | 80.9 | 69.7 | 75.9 | 82.1 | 80.1 | 81.4 | 80.6 | 68.8 | 73.5 | 66.5 | 53.4 | 79.5 |
| modelname Qwen | 84.8 | 76.1 | 82.7 | 71.8 | 76.9 | 83.5 | 82.4 | 83.8 | 83.1 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 64.4 | 58.9 | 80.2 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the SMPQA Grounding task, a novel benchmark for evaluating multilingual OCR capabilities in images. The task assesses a model’s ability to correctly identify if a given textual label in a prompt corresponds to a specific section (bar or pie chart slice) in an image. The table systematically evaluates various multilingual language models’ performance across different languages and training strategies. The rows represent different experimental configurations including the use of various language models, different numbers of languages trained on, and data augmentation approaches such as varying English/multilingual data ratios and including synthetic OCR data. The columns represent the accuracy score for each language tested. This provides insight into the impact of multilingual training and data composition on multilingual image text understanding.
read the caption
Table 30: SMPQA Ground
| Model | en | avg. | avg. Latin | avg. other | ar | de | hi | id | it | ko | ru | th | zh | zu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi 3.5 - English | 36.2 | 5.0 | 12.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 17.4 | 0.0 | 12.6 | 15.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5 50 | 36.4 | 5.4 | 13.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.2 | 0.0 | 13.2 | 16.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-4 50 | 35.0 | 5.8 | 14.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 14.6 | 16.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-3 50 | 34.6 | 5.8 | 14.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 16.0 | 0.0 | 16.6 | 20.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - T5-2 50 | 35.8 | 5.8 | 14.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 18.0 | 0.0 | 14.8 | 19.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 33.4 | 5.2 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 17.4 | 0.0 | 14.0 | 14.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 5.2 |
| Llama 3 - English | 41.0 | 8.5 | 21.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.4 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 23.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 14.8 |
| Llama 3 - T5 50 | 41.4 | 8.2 | 20.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 25.2 | 0.0 | 21.8 | 23.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 11.2 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 39.2 | 7.3 | 18.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 18.8 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 10.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 1 | 22.0 | 4.0 | 10.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.0 | 0.0 | 9.0 | 14.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 10 | 24.6 | 4.1 | 10.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.6 | 0.0 | 10.0 | 14.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 24 | 26.0 | 3.8 | 9.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 12.2 | 0.0 | 8.4 | 12.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 4.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 33.4 | 5.2 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 17.4 | 0.0 | 14.0 | 14.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 5.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 75 | 38.4 | 6.0 | 15.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.0 | 0.0 | 14.8 | 18.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 90 | 39.8 | 6.5 | 16.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.0 | 0.0 | 17.0 | 21.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 10 | 32.0 | 6.3 | 15.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 17.8 | 0.0 | 15.8 | 19.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 9.6 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 39.2 | 7.3 | 18.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 18.8 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 10.8 |
| Llama 3 - L100 90 | 40.0 | 7.5 | 18.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.2 | 0.0 | 21.0 | 20.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 12.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - L100 50 | 33.4 | 5.2 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 17.4 | 0.0 | 14.0 | 14.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 5.2 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 100 | 44.0 | 9.9 | 24.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 31.4 | 0.0 | 25.6 | 26.8 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 14.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 50 | 41.8 | 9.4 | 23.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 27.8 | 0.0 | 24.4 | 25.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 15.0 |
| Phi 3.5 - PT 1 | 42.2 | 9.5 | 23.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 27.2 | 0.0 | 24.4 | 29.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 14.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 39.2 | 7.3 | 18.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 18.8 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 10.8 |
| Llama 3 - PT 1 | 48.4 | 11.4 | 27.9 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 29.6 | 0.2 | 30.6 | 30.6 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 20.6 |
| Llama 3 - PT 100 | 48.8 | 10.5 | 25.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 28.8 | 2.6 | 26.2 | 28.4 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 16.6 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR English | 55.8 | 18.3 | 39.9 | 3.9 | 5.2 | 38.6 | 2.4 | 43.2 | 41.6 | 0.0 | 15.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 36.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 50 | 53.8 | 21.0 | 41.8 | 7.1 | 14.4 | 42.2 | 6.4 | 45.8 | 42.6 | 0.2 | 21.2 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 36.4 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 1 | 54.8 | 22.2 | 43.5 | 8.0 | 17.2 | 43.8 | 6.2 | 46.4 | 42.8 | 1.2 | 21.4 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 40.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR Latin-down | 54.6 | 22.4 | 41.0 | 9.9 | 20.2 | 41.6 | 7.0 | 42.6 | 43.0 | 2.8 | 25.6 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 36.8 |
| Phi 3.5 - OCR 50 (frozen) | 47.2 | 15.7 | 34.1 | 3.5 | 5.2 | 36.4 | 3.8 | 37.2 | 33.0 | 0.0 | 11.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 29.6 |
| Gemma 2 - L100 50 | 28.6 | 3.8 | 9.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 10.4 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 5.0 |
| Llama 3 - L100 50 | 39.2 | 7.3 | 18.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 18.8 | 21.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 10.8 |
| Qwen 2.5 - L100 50 | 48.8 | 10.1 | 25.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 32.0 | 0.0 | 23.8 | 29.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 15.6 |
| Aya-Expanse - L100 50 | 46.6 | 10.2 | 25.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 27.4 | 0.0 | 28.8 | 27.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 18.0 |
| modelname Aya | 60.0 | 30.1 | 49.8 | 17.0 | 29.2 | 50.2 | 17.6 | 52.6 | 51.2 | 11.2 | 38.2 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 45.2 |
| modelname Qwen | 65.2 | 31.7 | 54.3 | 16.6 | 21.4 | 53.2 | 21.4 | 55.4 | 56.6 | 16.2 | 34.8 | 5.2 | 0.6 | 52.2 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the SMPQA-Name task, a new benchmark introduced in the paper to evaluate the multilingual text-in-image understanding capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). The task focuses on the model’s ability to accurately read and identify textual content within images. The table shows the performance of various models, including different configurations of the Centurio model (with varying numbers of training languages and data distributions), across multiple languages. The scores reflect the models’ accuracy in recognizing and identifying text in images.
read the caption
Table 31: SMPQA Name
| en | avg. | af | am | cs | el | es | fa | fi | ha | hr | hu | ja | mi | nl | no | pl | ro | ta | te | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 69.7 | 54.7 | 63.6 | 29.4 | 66.2 | 67.8 | 65.1 | 60.0 | 43.3 | 37.5 | 63.6 | 49.8 | 66.7 | 37.0 | 62.4 | 59.1 | 62.6 | 64.0 | 46.9 | 50.9 | 42.6 |
| Centurio Qwen | 72.7 | 56.2 | 65.3 | 47.4 | 62.2 | 56.7 | 67.0 | 53.6 | 48.8 | 36.7 | 65.4 | 54.1 | 67.6 | 39.1 | 63.7 | 63.6 | 60.4 | 58.5 | 45.2 | 63.4 | 49.5 |
| Parrot | 30.5 | 25.7 | 26.0 | 22.8 | 26.1 | 25.5 | 27.3 | 25.9 | 26.4 | 23.7 | 25.3 | 25.6 | 26.7 | 25.4 | 28.0 | 26.6 | 26.5 | 26.8 | 25.5 | 23.9 | 24.0 |
| PALO 13B | 61.4 | 41.1 | 48.4 | 25.9 | 47.9 | 35.8 | 53.2 | 37.5 | 42.7 | 26.1 | 52.3 | 47.9 | 49.1 | 31.0 | 48.9 | 51.2 | 46.1 | 46.5 | 28.9 | 32.2 | 28.3 |
| PALO 7B | 58.7 | 38.6 | 44.2 | 28.4 | 43.6 | 33.5 | 49.9 | 36.9 | 39.1 | 24.5 | 49.6 | 45.4 | 48.8 | 27.8 | 45.1 | 45.8 | 42.0 | 44.0 | 26.7 | 30.1 | 28.3 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 68.4 | 45.4 | 53.2 | 31.3 | 53.2 | 42.3 | 60.8 | 45.4 | 38.3 | 26.3 | 55.2 | 42.1 | 60.5 | 29.5 | 56.6 | 53.7 | 53.1 | 49.7 | 35.3 | 50.1 | 26.5 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 70.3 | 44.2 | 54.4 | 29.1 | 52.8 | 43.3 | 57.8 | 40.5 | 41.3 | 25.8 | 55.6 | 44.9 | 57.3 | 30.0 | 51.8 | 54.8 | 50.3 | 48.9 | 33.2 | 41.2 | 27.3 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 78.2 | 47.2 | 56.6 | 30.3 | 56.7 | 47.2 | 64.0 | 48.7 | 41.7 | 26.1 | 57.1 | 48.0 | 62.2 | 30.0 | 59.2 | 57.8 | 54.6 | 54.5 | 31.9 | 43.4 | 27.6 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 80.7 | 57.5 | 68.9 | 37.2 | 68.5 | 62.2 | 72.6 | 59.8 | 55.1 | 27.1 | 72.2 | 61.8 | 71.8 | 29.5 | 69.5 | 69.6 | 67.5 | 65.6 | 42.7 | 62.3 | 29.3 |
| Maya | 54.0 | 43.2 | 50.6 | 27.1 | 53.3 | 53.6 | 52.7 | 48.7 | 35.3 | 23.7 | 50.5 | 39.3 | 55.2 | 28.6 | 51.4 | 46.4 | 50.0 | 51.3 | 31.9 | 36.9 | 33.4 |
| Llama-Vision | 75.6 | 50.8 | 65.1 | 30.6 | 61.3 | 42.9 | 65.1 | 49.9 | 51.5 | 31.1 | 60.9 | 65.0 | 46.3 | 32.8 | 61.5 | 61.8 | 55.7 | 57.3 | 42.0 | 51.6 | 31.9 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 63.1 | 36.8 | 40.9 | 28.7 | 41.0 | 34.7 | 52.7 | 33.5 | 34.9 | 27.1 | 40.5 | 36.8 | 45.9 | 28.2 | 43.6 | 44.4 | 38.5 | 39.8 | 30.9 | 28.1 | 28.1 |
| Pixtral 12B | 71.0 | 54.2 | 62.3 | 34.3 | 61.6 | 58.3 | 66.1 | 57.3 | 52.0 | 27.7 | 67.1 | 60.4 | 64.8 | 31.9 | 58.6 | 62.1 | 59.8 | 59.0 | 56.7 | 64.5 | 25.0 |
| Pangea | 70.3 | 52.1 | 61.4 | 34.3 | 59.6 | 54.2 | 64.4 | 54.9 | 45.4 | 27.9 | 63.0 | 49.8 | 65.5 | 29.6 | 61.0 | 64.1 | 59.5 | 60.6 | 42.4 | 62.7 | 29.3 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 72.6 | 47.4 | 56.0 | 29.9 | 55.1 | 46.6 | 62.1 | 48.5 | 41.8 | 22.9 | 59.5 | 44.9 | 62.9 | 29.0 | 57.8 | 55.2 | 54.7 | 52.7 | 34.5 | 53.9 | 33.4 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the BIN-MC (Babel-ImageNet Multiple Choice) task. BIN-MC is a visual question answering task where the goal is to identify the correct label for images from the Babel-ImageNet dataset, which contains translations of ImageNet labels into multiple languages. The table shows the performance of different models, varying in the number of languages included in training and the proportion of English data in the training set. The performance metric is the exact accuracy, showing how well the models predict the correct label for each image, categorized by language tiers (from high-resource to low-resource) and aggregated as multilingual average. The results are analyzed based on different training configurations, including various mixes of English and multilingual data and pre-training approaches. This allows researchers to examine the influence of training language distribution and the effect of pre-training on multilingual capabilities.
read the caption
Table 32: BIN-MC
| en | avg. | af | zh | it | pt | th | vi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 53.0 | 41.2 | 52.8 | 51.4 | 47.7 | 27.4 | 27.8 | 40.3 |
| Centurio Qwen | 61.2 | 46.9 | 50.9 | 55.6 | 49.0 | 31.9 | 29.6 | 64.1 |
| Parrot | 46.6 | 36.2 | 38.0 | 37.8 | 36.8 | 25.9 | 23.5 | 55.1 |
| PALO 13B | 45.2 | 28.3 | 33.1 | 31.3 | 36.5 | 19.3 | 20.2 | 29.2 |
| PALO 7B | 41.0 | 29.1 | 34.4 | 31.5 | 32.7 | 21.8 | 21.1 | 33.4 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 63.2 | 50.3 | 46.0 | 60.9 | 50.3 | 34.9 | 39.1 | 70.4 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 67.0 | 53.3 | 57.7 | 61.7 | 53.2 | 33.0 | 39.1 | 75.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 47.9 | 40.5 | 38.0 | 51.6 | 36.4 | 36.2 | 26.1 | 54.9 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 56.1 | 49.7 | 50.9 | 58.6 | 46.8 | 34.7 | 38.3 | 69.0 |
| Maya | 49.2 | 36.3 | 48.5 | 46.4 | 36.6 | 25.9 | 20.0 | 40.3 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 56.3 | 40.7 | 51.5 | 54.4 | 44.1 | 25.2 | 24.3 | 44.4 |
| Pixtral 12B | 49.4 | 33.7 | 39.9 | 53.6 | 34.4 | 19.5 | 7.0 | 47.7 |
| Pangea | 58.0 | 45.5 | 50.3 | 58.6 | 49.0 | 32.2 | 27.8 | 55.3 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 55.0 | 48.2 | 44.2 | 54.6 | 44.3 | 36.9 | 38.3 | 70.8 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the M3Exam task, a multiple-choice visual question answering task, across various language models. The results are broken down by language tier (T1-T5), showcasing performance on English and multilingual data. The models’ performances are measured and compared using accuracy scores and it includes the results for different training setups including varying the number of training languages and the ratio of English to multilingual data.
read the caption
Table 33: M3Exam
| en | avg. | am | ber | bn | de | fil | ha | hi | ru | sw | th | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 82.5 | 66.8 | 71.7 | 54.2 | 59.3 | 73.3 | 59.2 | 65.0 | 71.2 | 75.8 | 67.5 | 72.5 | 65.5 |
| Centurio Qwen | 87.5 | 73.1 | 77.5 | 49.2 | 62.7 | 80.8 | 78.3 | 76.7 | 72.9 | 85.0 | 70.0 | 81.7 | 69.0 |
| Parrot | 59.2 | 52.9 | 45.0 | 64.2 | 53.4 | 63.3 | 49.2 | 41.7 | 62.7 | 62.5 | 35.8 | 67.5 | 36.2 |
| PALO 13B | 63.3 | 26.2 | 25.0 | 55.0 | 0.8 | 44.2 | 47.5 | 40.0 | 0.0 | 5.8 | 32.5 | 0.0 | 37.1 |
| PALO 7B | 48.3 | 25.6 | 40.8 | 75.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 49.2 | 40.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 39.2 | 0.0 | 37.9 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 72.5 | 49.7 | 43.3 | 50.0 | 40.7 | 62.5 | 56.7 | 41.7 | 42.4 | 63.3 | 35.8 | 74.2 | 36.2 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 87.5 | 51.6 | 43.3 | 50.0 | 41.5 | 64.2 | 49.2 | 41.7 | 59.3 | 75.8 | 36.7 | 68.3 | 37.1 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 61.7 | 50.5 | 44.2 | 50.0 | 43.2 | 65.0 | 53.3 | 41.7 | 61.0 | 52.5 | 38.3 | 67.5 | 38.8 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 60.0 | 52.9 | 48.3 | 50.0 | 46.6 | 60.0 | 50.0 | 46.7 | 48.3 | 63.3 | 58.3 | 60.8 | 49.1 |
| Maya | 46.7 | 42.3 | 43.3 | 48.3 | 33.9 | 50.8 | 51.7 | 40.8 | 42.4 | 45.8 | 34.2 | 38.3 | 35.3 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 81.7 | 50.3 | 45.8 | 49.2 | 56.8 | 73.3 | 54.2 | 41.7 | 56.8 | 85.8 | 38.3 | 15.0 | 36.2 |
| Pixtral 12B | 55.8 | 47.7 | 51.7 | 32.5 | 47.5 | 63.3 | 51.7 | 44.2 | 16.1 | 54.2 | 65.8 | 53.3 | 44.0 |
| Pangea | 69.2 | 58.9 | 45.8 | 90.0 | 53.4 | 61.7 | 55.0 | 41.7 | 60.2 | 74.2 | 54.2 | 75.8 | 36.2 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 52.5 | 49.1 | 45.0 | 55.8 | 49.2 | 45.8 | 48.3 | 40.8 | 44.1 | 59.2 | 48.3 | 65.8 | 37.9 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of various Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on the Visually Grounded Reasoning (VGR) task. The models are evaluated across multiple languages, and the results show the accuracy of each model in predicting whether a given textual hypothesis is true or false based on a pair of images. The table allows for a comparative analysis of the models’ performance on this specific task, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in understanding and reasoning with visual and linguistic information across different languages.
read the caption
Table 34: VGR
| Model | en | avg. | am | ber | bn | de | fil | ha | hi | ru | sw | th | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 12.5 | 20.7 | 18.3 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 11.7 | 24.2 | 29.2 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 29.2 | 19.5 | |
| Centurio Qwen | 28.3 | 27.0 | 18.3 | 20.0 | 33.3 | 32.5 | 29.2 | 22.5 | 25.0 | 22.5 | 30.4 | 30.0 | 33.1 | |
| Parrot | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| PALO 13B | 2.5 | 4.9 | 6.7 | 5.0 | 6.7 | 5.0 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 4.2 | |
| PALO 7B | 5.8 | 6.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 5.8 | 6.7 | 4.2 | 9.8 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 5.1 | |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 24.2 | 21.0 | 18.3 | 26.7 | 17.5 | 20.8 | 20.0 | 23.3 | 22.3 | 20.0 | 23.2 | 20.0 | 18.6 | |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 57.5 | 29.0 | 25.0 | 22.5 | 25.8 | 38.3 | 36.7 | 25.8 | 41.1 | 35.8 | 15.2 | 30.0 | 22.9 | |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 22.5 | 20.4 | 17.5 | 20.0 | 13.3 | 26.7 | 25.0 | 24.2 | 20.5 | 16.7 | 21.4 | 15.8 | 23.7 | |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 5.8 | 13.2 | 14.2 | 15.8 | 13.3 | 11.7 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 13.4 | 13.3 | 13.6 | |
| Maya | 20.0 | 20.1 | 20.0 | 25.8 | 19.2 | 20.8 | 15.0 | 25.8 | 17.9 | 23.3 | 21.4 | 15.8 | 16.1 | |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 45.8 | 31.5 | 27.5 | 29.2 | 23.3 | 36.7 | 30.0 | 31.7 | 33.9 | 29.2 | 37.5 | 35.8 | 31.4 | |
| Pixtral 12B | 9.2 | 12.4 | 17.5 | 13.3 | 10.0 | 16.7 | 10.0 | 16.7 | 3.6 | 14.2 | 8.9 | 12.5 | 13.6 | |
| Pangea | 0.0 | 6.7 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 20.8 | 24.2 | 15.8 | 6.2 | 0.8 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 9.2 | 14.6 | 11.7 | 19.2 | 12.5 | 10.8 | 10.0 | 22.5 | 10.7 | 12.5 | 19.6 | 11.7 | 19.5 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of various large vision-language models (LVLMs) on the Visio-Linguistic Outlier Detection (VLOD) task. The VLOD task requires identifying the image that doesn’t fit a given textual description within a set of images. The table shows the performance of different models across various languages, indicating their accuracy in this task. The models include Centurio (two versions), Parrot, PALO (two sizes), InternVL (two sizes), Qwen2-VL (two sizes), Maya, Phi-3.5 Vision, Pixtral, Pangea, and MiniCPM. The results are presented as percentages, likely representing accuracy rates for each model in each language.
read the caption
Table 35: VLOD
| Model | en | avg. | id | sw | ta | tr | zh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Centurio Aya | 85.0 | 77.9 | 79.5 | 70.9 | 73.4 | 83.4 | 82.4 |
Centurio Qwen | 89.6 | 81.7 | 85.0 | 76.8 | 76.0 | 84.2 | 86.7 |
| Parrot | 63.5 | 55.1 | 56.6 | 51.2 | 50.7 | 58.6 | 58.2 |
| PALO 13B | 63.8 | 33.1 | 58.7 | 50.9 | 2.6 | 53.1 | 0.2 |
| PALO 7B | 62.7 | 24.1 | 33.6 | 47.8 | 0.4 | 38.5 | 0.0 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 74.9 | 59.0 | 65.7 | 50.7 | 50.9 | 64.2 | 63.5 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 83.0 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 51.4 | 54.6 | 67.2 | 79.9 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 67.9 | 55.9 | 60.9 | 51.8 | 52.2 | 59.0 | 55.8 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 69.8 | 60.2 | 61.1 | 53.1 | 60.9 | 65.3 | 60.7 |
| Maya | 60.3 | 56.3 | 60.3 | 50.7 | 50.6 | 58.9 | 61.2 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 73.4 | 46.4 | 56.4 | 51.3 | 50.8 | 58.0 | 15.7 |
| Pixtral 12B | 67.7 | 60.7 | 62.5 | 54.4 | 61.8 | 65.5 | 59.1 |
| Pangea | 75.8 | 70.5 | 74.3 | 70.9 | 66.6 | 71.1 | 69.6 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 70.2 | 57.9 | 57.8 | 54.2 | 57.2 | 63.3 | 57.2 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of the performance of Centurio and thirteen other large vision-language models (LVLMs) on the MaRVL (Multicultural Reasoning over Vision and Language) dataset. MaRVL is a benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of models to perform multicultural reasoning tasks, incorporating both visual and linguistic aspects. The table shows the accuracy of each model across various language tiers (T1-T5), providing a detailed breakdown of performance across different linguistic groups. This helps assess how well the models generalize to diverse languages and cultural contexts. The results are presented as percentages and also include a breakdown of performance for English and non-English components. This comprehensive comparison allows for a detailed understanding of each model’s strengths and weaknesses in handling multilingual and multicultural data.
read the caption
Table 36: MaRVL
| en | avg. | fr | hi | he | ro | th | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 55.7 | 49.3 | 45.1 | 58.7 | 62.9 | 51.1 | 46.7 | 31.6 |
| Centurio Qwen | 60.1 | 47.7 | 47.1 | 45.1 | 56.8 | 47.7 | 57.0 | 32.2 |
| Parrot | 28.2 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 3.0 | 10.7 |
| PALO 13B | 51.7 | 33.1 | 42.0 | 17.5 | 53.4 | 34.2 | 20.9 | 30.6 |
| PALO 7B | 54.0 | 22.5 | 39.9 | 9.2 | 30.6 | 16.8 | 12.3 | 26.4 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 46.0 | 42.5 | 45.7 | 37.1 | 38.8 | 31.5 | 51.0 | 50.8 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 45.6 | 38.2 | 51.2 | 27.9 | 24.5 | 35.7 | 36.4 | 53.4 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 53.7 | 26.5 | 40.3 | 10.8 | 9.5 | 15.6 | 38.1 | 44.6 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 54.7 | 31.2 | 38.6 | 18.7 | 13.9 | 37.2 | 42.1 | 36.8 |
| Maya | 55.4 | 17.3 | 19.1 | 13.0 | 21.1 | 18.0 | 11.6 | 20.8 |
| Llama-Vision | 0.0 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 24.8 | 0.0 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 43.6 | 17.9 | 23.5 | 12.1 | 16.3 | 7.8 | 20.9 | 27.0 |
| Pixtral 12B | 59.4 | 43.4 | 46.8 | 31.7 | 54.4 | 44.1 | 44.4 | 39.1 |
| Pangea | 61.4 | 55.0 | 47.4 | 61.0 | 53.7 | 52.9 | 67.2 | 47.9 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 53.4 | 22.3 | 14.3 | 12.1 | 5.1 | 19.5 | 53.6 | 29.3 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of the performance of various Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on the MaXM dataset. MaXM is a multilingual visual question answering dataset, designed to test the models’ ability to understand and answer questions about images in various languages. The table shows the accuracy of each model across different language tiers (T1-T5) and overall (avg), providing a detailed breakdown of performance across a range of multilingual capabilities. The models compared include several popular open-source and closed-source LVLMs, as well as the Centurio model, the focus of the paper.
read the caption
Table 37: MaXM
| avg. | ar | de | fr | it | ja | ko | ru | th | vi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 11.1 | 6.7 | 19.9 | 22.5 | 16.7 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 11.9 | 4.6 | 22.7 | 26.5 | 18.6 | 5.9 | 9.9 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 8.9 |
| Parrot | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 5.2 | 0.9 |
| PALO 13B | 6.3 | 2.6 | 15.6 | 12.1 | 10.4 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 0.0 | 4.2 |
| PALO 7B | 5.8 | 1.8 | 14.3 | 13.3 | 8.3 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 4.1 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 25.1 | 11.2 | 34.4 | 38.4 | 33.5 | 18.4 | 29.0 | 9.8 | 16.5 | 34.6 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 25.0 | 11.5 | 33.8 | 37.4 | 35.3 | 19.7 | 30.3 | 10.4 | 16.5 | 30.4 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 19.0 | 6.1 | 26.8 | 30.9 | 30.7 | 13.5 | 21.1 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 22.4 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 23.2 | 16.9 | 27.3 | 31.7 | 35.2 | 16.1 | 24.6 | 10.8 | 15.6 | 30.7 |
| Maya | 5.3 | 2.8 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 6.6 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| Llama-Vision | 15.2 | 7.4 | 24.0 | 18.7 | 25.3 | 9.4 | 14.5 | 6.1 | 15.2 | 15.8 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 11.1 | 3.3 | 18.2 | 20.2 | 25.2 | 5.6 | 8.8 | 5.4 | 3.0 | 10.5 |
| Pixtral 12B | 14.1 | 4.3 | 25.7 | 27.3 | 25.2 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 7.5 | 5.2 | 16.6 |
| Pangea | 19.3 | 8.3 | 29.5 | 35.2 | 29.2 | 9.3 | 14.5 | 7.4 | 10.8 | 29.2 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 16.1 | 2.3 | 23.9 | 27.5 | 32.7 | 11.7 | 12.7 | 7.3 | 10.0 | 16.5 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the MTVQA (Multilingual Text-heavy Visual Question Answering) task, comparing various multilingual vision-language models. It shows the accuracy of each model across different languages, evaluating their ability to understand and answer questions about images containing text primarily in the language of the question. The results are broken down for different training strategies, including different multilingual data ratios and instruction tuning approaches. This allows analysis of the impact of training strategies on multilingual performance of the model.
read the caption
Table 38: MTVQA
| en | avg. | bn | de | id | ko | pt | ru | zh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parrot | 37.7 | 21.2 | 20.2 | 23.2 | 19.8 | 22.8 | 21.7 | 19.7 | 21.2 |
| PALO 13B | 58.0 | 27.8 | 26.3 | 14.7 | 29.6 | 30.9 | 17.8 | 30.9 | 44.1 |
| PALO 7B | 59.1 | 36.6 | 42.8 | 34.5 | 30.0 | 40.8 | 27.7 | 32.2 | 47.9 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 63.6 | 28.0 | 28.1 | 29.2 | 15.4 | 38.3 | 27.2 | 31.5 | 25.9 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 63.4 | 32.0 | 17.4 | 23.8 | 25.0 | 38.2 | 27.6 | 36.4 | 55.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 60.5 | 38.2 | 18.6 | 43.2 | 32.6 | 39.0 | 39.9 | 44.1 | 50.3 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 62.5 | 49.3 | 37.4 | 51.1 | 48.4 | 50.3 | 51.8 | 52.1 | 54.1 |
| Maya | 58.2 | 49.1 | 40.1 | 53.2 | 49.7 | 47.2 | 52.5 | 50.6 | 50.1 |
| Llama-Vision | 39.3 | 27.6 | 26.0 | 29.2 | 26.8 | 24.9 | 27.9 | 30.7 | 27.9 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 65.2 | 38.0 | 5.0 | 51.9 | 37.3 | 35.6 | 50.6 | 45.9 | 39.5 |
| Pixtral 12B | 59.9 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 14.0 | 0.3 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| Pangea | 64.6 | 60.4 | 59.1 | 61.6 | 60.7 | 58.8 | 62.1 | 60.7 | 59.6 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 57.9 | 45.7 | 33.9 | 49.0 | 46.3 | 42.1 | 51.0 | 48.7 | 48.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the xGQA (cross-lingual visual question answering) task. It shows the performance of various large vision-language models (LVLMs) across different language groups and settings. The models are evaluated on their ability to correctly answer questions about images, assessing their multilingual capabilities. Different training strategies are tested, varying the number of languages included in the training data (English only, 50% English and 50% multilingual, and 100 languages) and training method (instruction-tuning and pre-training). The results are given as accuracy scores (%), allowing for a comparison of how different approaches and configurations affect the models’ performance across languages.
read the caption
Table 39: xGQA
🔼 This table presents a comprehensive evaluation of various multilingual vision-language models on the XM3600 dataset, a large-scale multilingual image captioning benchmark. The results are detailed for multiple language groups and model configurations. Each row represents a different model, with English performance and average multilingual performance reported separately (en & mul). The evaluation considers various languages (represented by ISO codes), showcasing the performance differences between language groups. In addition to overall performance, language fidelity (i.e., how well the model generates text in the target language) is assessed for some models, providing insights into the models’ multilingual capabilities and limitations.
read the caption
Table 40: XM3600
| Model Name | en | avg. | ar | bn | cs | da | de | el | es | fa | fi | fil | fr | he | hi | hr | hu | id | it | ja | ko | mi | nl | no | pl | pt | quz | ro | ru | sv | sw | te | th | tr | uk | vi | zh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 100.0 | 95.7 | 93.6 | 100.0 | 97.7 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 84.6 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 98.8 | 100.0 | 98.8 | 100.0 | 97.3 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 1.8 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 98.8 | 90.6 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 89.6 |
| Centurio Qwen | 99.8 | 95.2 | 95.1 | 100.0 | 98.6 | 93.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.8 | 99.0 | 80.9 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 99.8 | 98.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 95.7 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 3.7 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 98.2 | 86.5 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 100.0 | 86.5 |
| Parrot | 100.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| PALO 13B | 100.0 | 60.1 | 98.6 | 93.9 | 47.1 | 87.5 | 100.0 | 60.7 | 99.6 | 0.0 | 74.0 | 71.5 | 99.8 | 35.4 | 98.2 | 70.1 | 9.0 | 66.4 | 99.2 | 61.5 | 9.8 | 0.0 | 99.8 | 92.2 | 41.2 | 27.5 | 0.0 | 95.5 | 68.2 | 94.9 | 1.6 | 26.4 | 68.0 | 9.4 | 11.3 | 54.7 | 88.9 |
| PALO 7B | 100.0 | 72.0 | 99.6 | 98.8 | 47.5 | 93.4 | 100.0 | 58.2 | 99.8 | 0.0 | 91.8 | 52.7 | 100.0 | 30.7 | 98.8 | 27.0 | 90.8 | 96.9 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 91.6 | 0.0 | 99.4 | 95.1 | 95.5 | 27.0 | 0.0 | 69.1 | 100.0 | 96.9 | 0.0 | 56.8 | 91.6 | 84.4 | 0.0 | 99.6 | 99.8 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 100.0 | 91.0 | 96.7 | 93.9 | 97.1 | 82.8 | 100.0 | 99.0 | 99.8 | 98.8 | 96.1 | 95.3 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 91.4 | 96.1 | 96.9 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 48.2 | 99.6 | 83.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 7.0 | 98.8 | 99.2 | 97.7 | 34.6 | 90.8 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 95.7 | 96.1 | 99.8 | |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 100.0 | 91.1 | 99.4 | 95.3 | 97.7 | 82.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 97.9 | 98.2 | 96.3 | 100.0 | 98.4 | 95.1 | 83.2 | 98.2 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 66.8 | 99.2 | 86.5 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 1.2 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 98.2 | 54.7 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 98.4 | 40.6 | 100.0 | 99.8 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 100.0 | 13.2 | 8.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 9.6 | 12.9 | 0.2 | 5.9 | 58.4 | 0.2 | 10.9 | 10.0 | 4.5 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 0.2 | 12.7 | 3.9 | 19.3 | 18.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 5.3 | 0.0 | 34.0 | 0.0 | 15.4 | 0.0 | 23.6 | 4.5 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 12.7 | 98.8 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 100.0 | 90.0 | 96.5 | 98.2 | 93.9 | 86.1 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 95.7 | 96.3 | 98.2 | 98.2 | 60.2 | 79.1 | 75.4 | 86.9 | 99.0 | 98.8 | 99.0 | 64.5 | 99.2 | 94.1 | 95.7 | 95.3 | 0.2 | 98.2 | 99.4 | 97.9 | 72.1 | 95.1 | 98.8 | 89.8 | 83.2 | 98.2 | 99.0 |
| Maya | 100.0 | 65.7 | 99.0 | 96.1 | 67.6 | 85.5 | 98.6 | 92.0 | 99.8 | 0.2 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 77.0 | 98.4 | 20.7 | 60.7 | 40.6 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 91.4 | 0.0 | 99.8 | 80.1 | 92.0 | 43.9 | 0.0 | 95.7 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 47.9 | 96.3 | 7.2 | 62.5 | 99.8 |
| Llama-Vision | 100.0 | 33.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 68.8 | 95.5 | 7.0 | 52.7 | 0.0 | 35.0 | 80.7 | 88.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 17.0 | 91.0 | 1.6 | 94.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 93.0 | 99.6 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 48.2 | 0.8 | 92.6 | 0.2 | 33.8 | 73.6 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 100.0 | 40.8 | 58.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 85.4 | 99.2 | 16.2 | 99.4 | 0.0 | 15.2 | 30.1 | 99.8 | 14.8 | 4.7 | 25.2 | 56.4 | 31.6 | 99.0 | 58.6 | 9.0 | 1.0 | 93.6 | 89.8 | 27.3 | 63.9 | 0.0 | 56.8 | 0.0 | 85.0 | 2.9 | 13.7 | 3.5 | 38.1 | 0.0 | 51.8 | 37.9 |
| Pixtral 12B | 100.0 | 96.8 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 98.8 | 95.9 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 93.4 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 95.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 9.4 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 95.9 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.8 |
| Pangea | 99.8 | 87.9 | 98.8 | 99.0 | 97.9 | 19.1 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 98.4 | 91.6 | 68.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.2 | 67.8 | 93.6 | 97.9 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 0.8 | 99.6 | 95.7 | 99.6 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 67.0 | 82.4 | 99.8 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 91.0 | 99.8 | 99.0 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 99.8 | 92.3 | 94.7 | 96.5 | 95.5 | 96.3 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.0 | 98.4 | 97.9 | 100.0 | 62.9 | 92.6 | 77.3 | 94.5 | 93.6 | 100.0 | 98.4 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 95.5 | 96.5 | 99.8 | 10.0 | 98.2 | 97.3 | 99.4 | 66.4 | 85.5 | 96.3 | 95.1 | 99.2 | 90.6 | 97.1 |
🔼 This table presents the language fidelity results for the XM3600 dataset. Language fidelity refers to the model’s ability to generate output in the correct target language. The table shows the performance for different language groups (T1-T5, representing various levels of language resource availability) and different model configurations (English-only, multilingual with various English-multilingual ratios, and pre-training configurations). Each cell displays a percentage, indicating the accuracy of language fidelity for that specific model and language group. This table helps analyze how different data compositions and pre-training strategies affect the model’s multilingual capabilities.
read the caption
Table 41: XM3600 Language Fidelity
| en | avg. | ar | es | fr | ru | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 65.0 | 62.4 | 61.7 | 61.0 | 64.3 | 62.7 |
| Centurio Qwen | 75.4 | 70.2 | 68.8 | 70.9 | 70.5 | 70.8 |
| Parrot | 28.7 | 31.4 | 34.0 | 24.3 | 30.0 | 37.4 |
| PALO 13B | 56.6 | 53.6 | 51.8 | 52.7 | 54.9 | 55.0 |
| PALO 7B | 58.0 | 53.4 | 52.5 | 52.3 | 53.7 | 55.1 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 69.0 | 58.7 | 55.7 | 58.8 | 61.4 | 59.0 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 73.5 | 66.4 | 61.8 | 68.0 | 68.4 | 67.3 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 61.9 | 56.2 | 52.9 | 55.3 | 58.6 | 57.9 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 62.1 | 59.6 | 59.2 | 58.9 | 60.0 | 60.3 |
| Maya | 50.1 | 43.9 | 45.3 | 42.7 | 45.8 | 41.8 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 58.9 | 53.3 | 49.7 | 52.7 | 56.4 | 54.3 |
| Pixtral 12B | 60.9 | 52.7 | 36.0 | 57.9 | 59.0 | 58.1 |
| Pangea | 69.0 | 65.2 | 64.5 | 64.3 | 66.3 | 65.7 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 71.9 | 65.4 | 61.1 | 67.5 | 67.0 | 66.1 |
🔼 This table presents a comparison of various multilingual vision-language models (LVLMs) on the Cross-lingual Visual Natural Language Inference (XVNLI) task. The models are evaluated across multiple languages (English, Arabic, Spanish, French, Russian), and the results are expressed as percentages, indicating the model’s accuracy on the task. The table allows for a comparison of the models’ performance in handling diverse languages and offers insight into the effectiveness of different training strategies and model architectures for cross-lingual understanding in a vision-language context.
read the caption
Table 42: XVNLI
| en | avg. | ar | fr | hi | id | ja | pt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 37.6 | 37.2 | 36.2 | 38.9 | 38.8 | 39.7 | 34.2 | 35.4 |
| Centurio Qwen | 46.4 | 43.0 | 39.6 | 45.0 | 41.6 | 44.1 | 43.5 | 44.1 |
| Parrot | 35.3 | 32.4 | 31.9 | 34.9 | 26.1 | 31.3 | 34.9 | 35.4 |
| PALO 13B | 32.4 | 28.9 | 24.2 | 34.9 | 24.2 | 31.6 | 26.4 | 32.3 |
| PALO 7B | 31.8 | 30.9 | 28.2 | 33.6 | 27.3 | 30.6 | 32.3 | 33.3 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 49.2 | 42.7 | 41.6 | 45.6 | 33.7 | 43.4 | 44.2 | 47.8 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 50.7 | 45.2 | 40.3 | 48.7 | 41.2 | 43.1 | 47.6 | 50.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 36.8 | 35.5 | 31.5 | 41.3 | 30.2 | 36.7 | 36.1 | 37.0 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 43.0 | 40.7 | 36.9 | 42.6 | 38.5 | 41.1 | 41.3 | 43.8 |
| Maya | 37.9 | 33.3 | 32.6 | 36.6 | 31.3 | 31.6 | 32.0 | 36.0 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 41.7 | 37.4 | 34.9 | 44.3 | 29.2 | 37.7 | 35.7 | 42.4 |
| Pixtral 12B | 30.3 | 26.2 | 19.1 | 28.5 | 19.2 | 27.3 | 28.6 | 34.7 |
| Pangea | 43.1 | 42.0 | 37.6 | 43.0 | 38.5 | 46.8 | 41.6 | 44.8 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 39.1 | 36.5 | 30.5 | 38.9 | 33.7 | 37.7 | 37.2 | 40.7 |
🔼 This table presents a detailed comparison of various multilingual vision-language models’ performance on the xMMMU (cross-lingual, multi-modal, multiple-choice visual question answering) dataset. It breaks down the accuracy scores (using exact match) achieved by different models across various language groups (T1-T5 tiers representing low to high resource languages), showing the average accuracy across all languages and the performance for each language individually. This allows for a nuanced understanding of each model’s strengths and weaknesses in handling multilingual and multimodal data. The models included represent a mix of architectures and training strategies, enabling an analysis of the influence of factors such as model size, training data composition, and multilingual training techniques.
read the caption
Table 43: xMMMU
🔼 This table presents a comparison of various Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on the CVQA (Cross-lingual Visual Question Answering) task. It shows the performance of each model across multiple languages, highlighting the performance of Centurio, the model introduced in the paper, against other state-of-the-art models. The metrics used likely reflect accuracy, potentially broken down by language.
read the caption
Table 44: CVQA
| en | avg. | avg. Latin | avg. other | ar | de | hi | id | it | ko | ru | th | zh | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 83.1 | 74.2 | 80.9 | 69.7 | 75.9 | 82.1 | 80.1 | 81.4 | 80.6 | 68.8 | 73.5 | 66.5 | 53.4 | 79.5 |
| Centurio Qwen | 84.8 | 76.1 | 82.7 | 71.8 | 76.9 | 83.5 | 82.4 | 83.8 | 83.1 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 64.4 | 58.9 | 80.2 |
| Parrot | 51.0 | 49.9 | 50.5 | 49.5 | 50.4 | 51.6 | 49.6 | 51.0 | 49.8 | 50.4 | 50.5 | 48.2 | 47.8 | 49.5 |
| PALO 13B | 54.0 | 51.5 | 52.7 | 50.7 | 50.9 | 53.2 | 51.2 | 52.5 | 52.8 | 51.0 | 49.5 | 51.0 | 50.7 | 52.1 |
| PALO 7B | 55.5 | 52.8 | 55.4 | 51.0 | 50.4 | 56.9 | 51.0 | 55.0 | 54.1 | 51.6 | 51.1 | 51.4 | 50.2 | 55.8 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 87.0 | 78.3 | 86.9 | 72.6 | 54.9 | 87.6 | 59.8 | 87.0 | 88.2 | 89.4 | 86.4 | 55.1 | 90.4 | 84.8 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 91.0 | 79.2 | 88.7 | 72.8 | 55.8 | 89.8 | 54.9 | 89.1 | 89.1 | 92.5 | 86.9 | 53.1 | 93.6 | 86.9 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 85.0 | 83.5 | 83.4 | 83.5 | 70.6 | 84.4 | 86.5 | 84.1 | 83.5 | 88.1 | 78.8 | 86.4 | 90.4 | 81.8 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 91.2 | 90.9 | 90.1 | 91.4 | 83.4 | 90.5 | 94.8 | 91.0 | 90.8 | 93.8 | 87.5 | 94.1 | 94.9 | 88.2 |
| Maya | 51.4 | 50.9 | 51.6 | 50.4 | 50.4 | 53.4 | 50.1 | 51.5 | 50.0 | 49.9 | 49.5 | 51.1 | 51.6 | 51.6 |
| Llama-Vision | 91.1 | 84.8 | 89.9 | 81.5 | 63.2 | 90.1 | 91.1 | 89.5 | 91.9 | 87.4 | 83.0 | 84.8 | 79.5 | 88.0 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 92.2 | 79.4 | 90.2 | 72.2 | 53.1 | 91.9 | 83.8 | 89.2 | 90.9 | 77.9 | 86.6 | 55.5 | 76.5 | 88.8 |
| Pixtral 12B | 91.1 | 71.0 | 90.5 | 58.0 | 50.4 | 91.5 | 53.6 | 91.1 | 90.9 | 49.5 | 88.2 | 52.9 | 53.4 | 88.4 |
| Pangea | 87.2 | 72.2 | 85.7 | 63.1 | 51.5 | 86.6 | 69.4 | 86.2 | 87.1 | 71.4 | 79.2 | 54.4 | 52.9 | 82.9 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 89.0 | 74.3 | 88.0 | 65.2 | 52.0 | 89.0 | 53.1 | 87.9 | 89.0 | 54.8 | 84.0 | 53.1 | 94.5 | 86.0 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the SMPQA Grounding task, a new benchmark evaluating multilingual OCR capabilities. The results are broken down by language, model, and training strategy. It showcases the performance of several models across multiple languages, highlighting the impact of different training strategies on multilingual text-in-image understanding.
read the caption
Table 45: SMPQA Ground
| en | avg. | avg. Latin | avg. other | ar | de | hi | id | it | ko | ru | th | zh | zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centurio Aya | 60.0 | 30.1 | 49.8 | 17.0 | 29.2 | 50.2 | 17.6 | 52.6 | 51.2 | 11.2 | 38.2 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 45.2 |
| Centurio Qwen | 65.2 | 31.7 | 54.3 | 16.6 | 21.4 | 53.2 | 21.4 | 55.4 | 56.6 | 16.2 | 34.8 | 5.2 | 0.6 | 52.2 |
| Parrot | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| PALO 13B | 25.6 | 4.0 | 9.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 12.0 | 0.0 | 10.2 | 12.4 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0 |
| PALO 7B | 22.4 | 2.7 | 6.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| InternVL 2.5 4B | 77.8 | 47.5 | 67.7 | 34.0 | 0.0 | 71.0 | 0.0 | 69.8 | 69.6 | 69.0 | 54.4 | 0.2 | 80.2 | 60.4 |
| InternVL 2.5 8B | 80.6 | 48.2 | 68.1 | 34.9 | 0.0 | 69.2 | 0.0 | 70.4 | 70.8 | 67.2 | 61.2 | 0.2 | 80.8 | 62.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 2B | 68.8 | 47.4 | 60.0 | 39.0 | 0.2 | 61.2 | 24.8 | 59.4 | 61.2 | 66.0 | 46.8 | 24.0 | 72.0 | 58.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | 85.0 | 64.9 | 76.2 | 57.4 | 1.8 | 80.6 | 58.6 | 75.8 | 79.2 | 77.6 | 70.6 | 43.8 | 92.0 | 69.2 |
| Maya | 14.6 | 1.8 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 8.2 | 0.0 | 3.6 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| Llama-Vision | 58.4 | 22.8 | 46.6 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 55.4 | 2.4 | 38.4 | 37.2 | 8.4 | 13.0 | 6.0 | 11.8 | 55.4 |
| Phi 3.5 Vision | 84.8 | 35.9 | 69.4 | 13.5 | 0.2 | 70.8 | 12.0 | 69.4 | 76.6 | 15.4 | 40.4 | 0.2 | 12.8 | 61.0 |
| Pixtral 12B | 85.0 | 35.9 | 73.3 | 10.9 | 0.0 | 71.8 | 0.0 | 75.4 | 81.6 | 0.4 | 64.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 64.6 |
| Pangea | 72.0 | 23.8 | 54.4 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 58.6 | 0.2 | 57.2 | 64.4 | 0.4 | 19.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 37.4 |
| MiniCPM 2.6 | 80.8 | 39.3 | 67.5 | 20.6 | 0.0 | 67.2 | 0.0 | 69.8 | 71.4 | 1.0 | 38.4 | 0.4 | 83.6 | 61.6 |
🔼 This table presents the results of the SMPQA-Name task, a new benchmark for evaluating multilingual OCR capabilities in images. It shows the performance of various models across different languages, categorized by script type (Latin or other) and resource level. The metrics used are likely accuracy scores, possibly separated for Latin-script and other-script languages, demonstrating each model’s proficiency in reading text from images containing various scripts and language families.
read the caption
Table 46: SMPQA Name
Full paper#