TL;DR#
Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful for text generation, but struggle to produce structured outputs that strictly adhere to a predefined schema. This is problematic in regulated fields like bio-manufacturing where any deviation can violate data integrity. Existing methods such as fine-tuning and prompt engineering have limitations in cost, transparency, and consistency.
To address these issues, the paper introduces ThinkJSON, a reinforcement learning framework for training LLMs to generate schema-adherent outputs. The framework combines synthetic data generation, a distilled reasoning model, and custom reward functions to guide the LLM’s learning process. The results show that ThinkJSON achieves higher schema adherence and lower noise compared to other models. This is a resource-efficient and compliance-aware approach to structured text generation.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This work demonstrates a resource-efficient approach to ensure the quality of AI outputs, with potential applications in other industries with strict regulatory compliance.
Visual Insights#

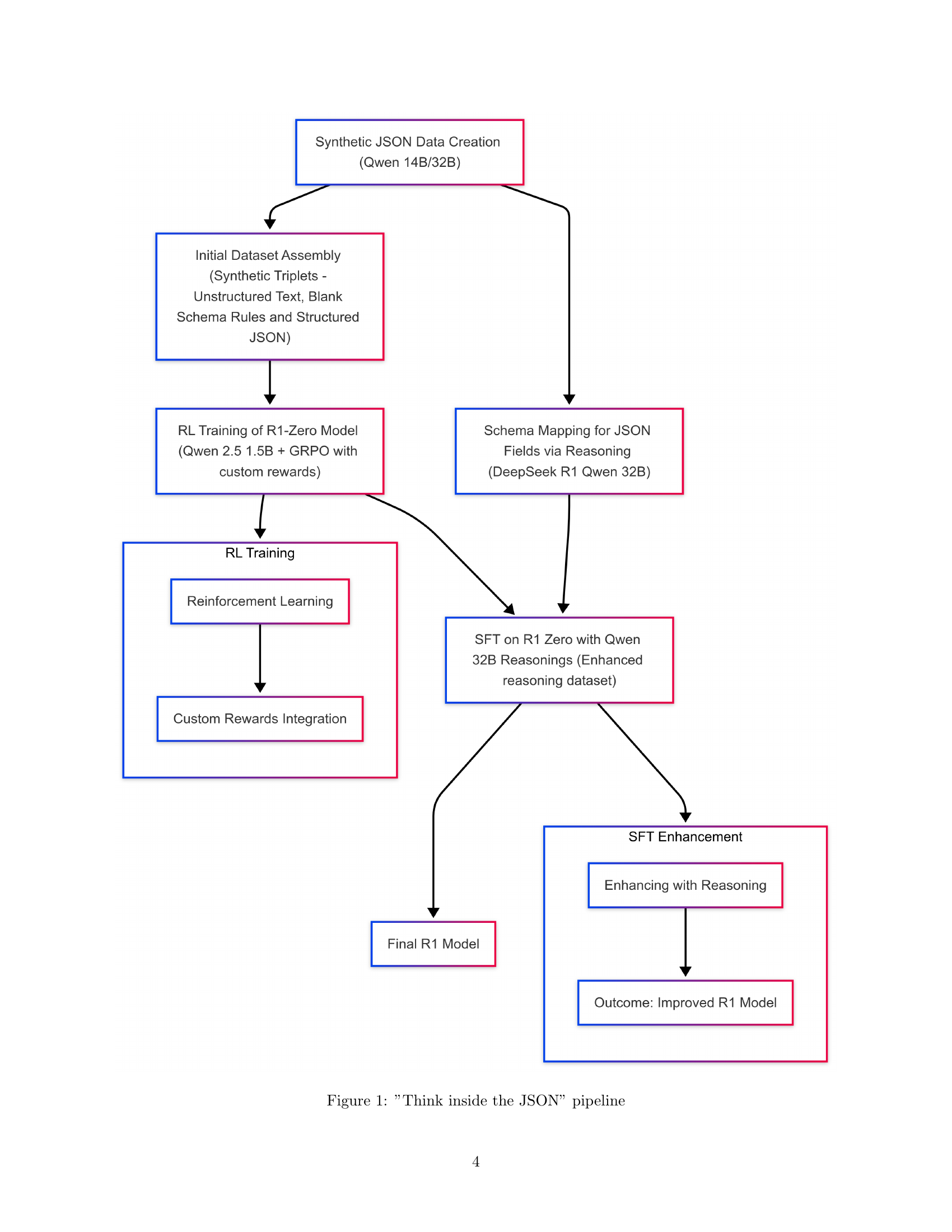
🔼 This figure illustrates the pipeline of the ThinkJSON method. It starts with creating synthetic JSON data using the Qwen 14B/32B model. This data includes triplets of unstructured text, blank JSON schema, and structured JSON. Then, it trains an R1-Zero model using Qwen 2.5 1.5B with the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm and custom rewards. The schema mapping for JSON fields is done via reasoning using DeepSeek R1 Qwen 32B. Next, reinforcement learning is performed on the R1-Zero model, followed by supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with Qwen 32B on an enhanced reasoning dataset. Finally, it results in an improved R1 model.
read the caption
Figure 1: ”Think inside the JSON” pipeline
In-depth insights#
Schema First LLM#
While “Schema First LLM” isn’t explicitly present, the research underscores its implicit value. The paper advocates for strategies ensuring Large Language Models (LLMs) adhere strictly to predefined schemas. This is crucial in sectors like biomanufacturing, where data integrity and regulatory compliance are paramount. The paper emphasizes that generating strictly structured, schema-valid outputs is not a trivial pursuit due to the probabilistic nature of LLMs. The focus should be on guaranteeing reliability in both content and form. The paper introduces a reinforcement learning framework emphasizing the creation of synthetic reasoning data and iterative LLM reasoning. This approach enhances schema adherence while minimizing overhead. The integration of compliance considerations throughout the generation process—rather than relying on post-hoc validation—is a key tenet. By aligning the model with clearly defined schemas, we can ensure consistency in the output.
GRPO+RL = ♥ JSON#
GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization) combined with Reinforcement Learning (RL) aims to enhance JSON generation by LLMs. This approach leverages GRPO’s ability to optimize policies based on group comparisons, promoting schema adherence. RL is used to fine-tune models, guiding them to generate structured data that is consistent and compliant with predefined schemas. The combination potentially addresses the challenge of ensuring LLMs produce accurate and consistent structured outputs. GRPO offers fine-grained control over policy optimization, improving structured outputs. This synergy aims to deliver reliable, schema-adherent AI-driven solutions, meeting stringent standards.
Reasoning Matters#
Reasoning is crucial for enabling LLMs to generate accurate and reliable outputs, especially in structured formats like JSON. By incorporating reasoning, LLMs can better understand the underlying relationships between unstructured text and the target schema. This enhances the LLM’s ability to map the text to the correct schema fields, reducing errors and improving schema adherence. Methods like chain-of-thought prompting and reinforcement learning with reasoning-based rewards help LLMs develop stronger reasoning skills. This, in turn, leads to more consistent and valid structured outputs which are particularly important in regulated industries or applications with strict data integrity requirements.
No Post-Hoc fixes#
Avoiding post-hoc fixes in AI system design is crucial for maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance. The most common way is through integrating compliance checks directly into the generation process. The alternative approach that relies on after-the-fact adjustments is not recommended as it can introduce errors and inconsistencies, especially in regulated industries like bio-manufacturing. The integration approach of schema adherence objectives with iterative reasoning loops is the best choice when compared to prompt-based approaches, as it reduces the need for manual oversight. By validating outputs during the process, ensures precise field mappings and hierarchical consistency which meet strict validation requirements and enable greater efficiency and reliability.
Audit-Ready AI#
Audit-ready AI is crucial, particularly in regulated sectors like biomanufacturing, where transparency and traceability are paramount. It necessitates AI systems that not only perform tasks effectively but also provide clear, verifiable explanations of their decision-making processes. This involves meticulous data lineage, model provenance, and rigorous validation protocols. The AI’s reasoning must be understandable and justifiable to auditors, demonstrating adherence to predefined schemas and compliance standards. Achieving this requires implementing strategies like chain-of-thought reasoning, where the AI explicitly outlines its steps, and constraint-based decoding, ensuring outputs conform to strict formats. Furthermore, robust monitoring and logging mechanisms are essential for tracking AI performance and identifying potential deviations. Essentially, audit-ready AI bridges the gap between complex AI algorithms and regulatory requirements, fostering trust and accountability in AI-driven processes. Key point is to ensure model’s output scores highly on all relevant criteria.
More visual insights#
More on figures

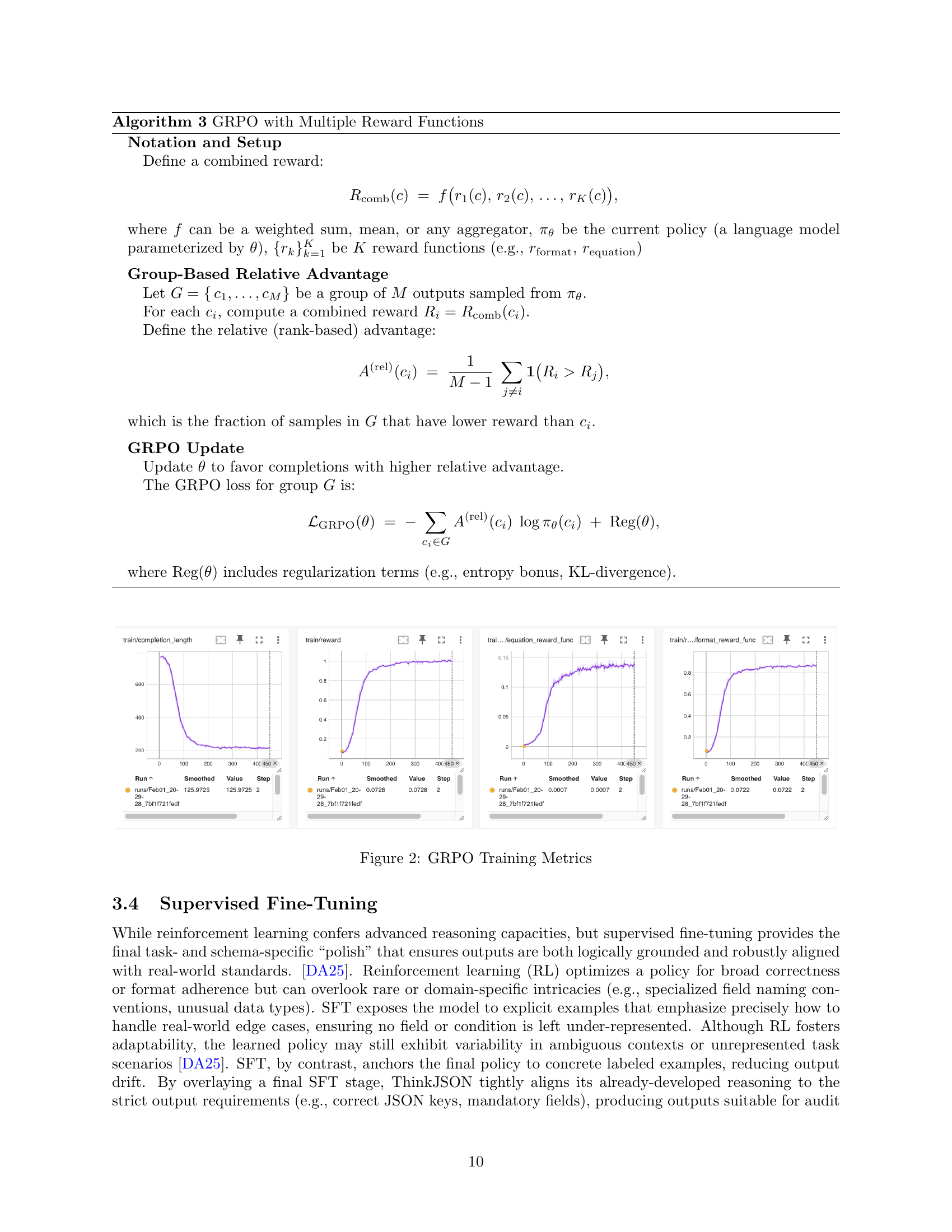
🔼 This figure displays the training metrics for the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm used in the paper. It shows plots of various metrics over training steps, including rewards (equation, format), completion length, and learning rate. These plots illustrate the algorithm’s performance during training and how different reward functions contribute to its optimization. The plots provide insights into the convergence of GRPO towards effective schema adherence.
read the caption
Figure 2: GRPO Training Metrics

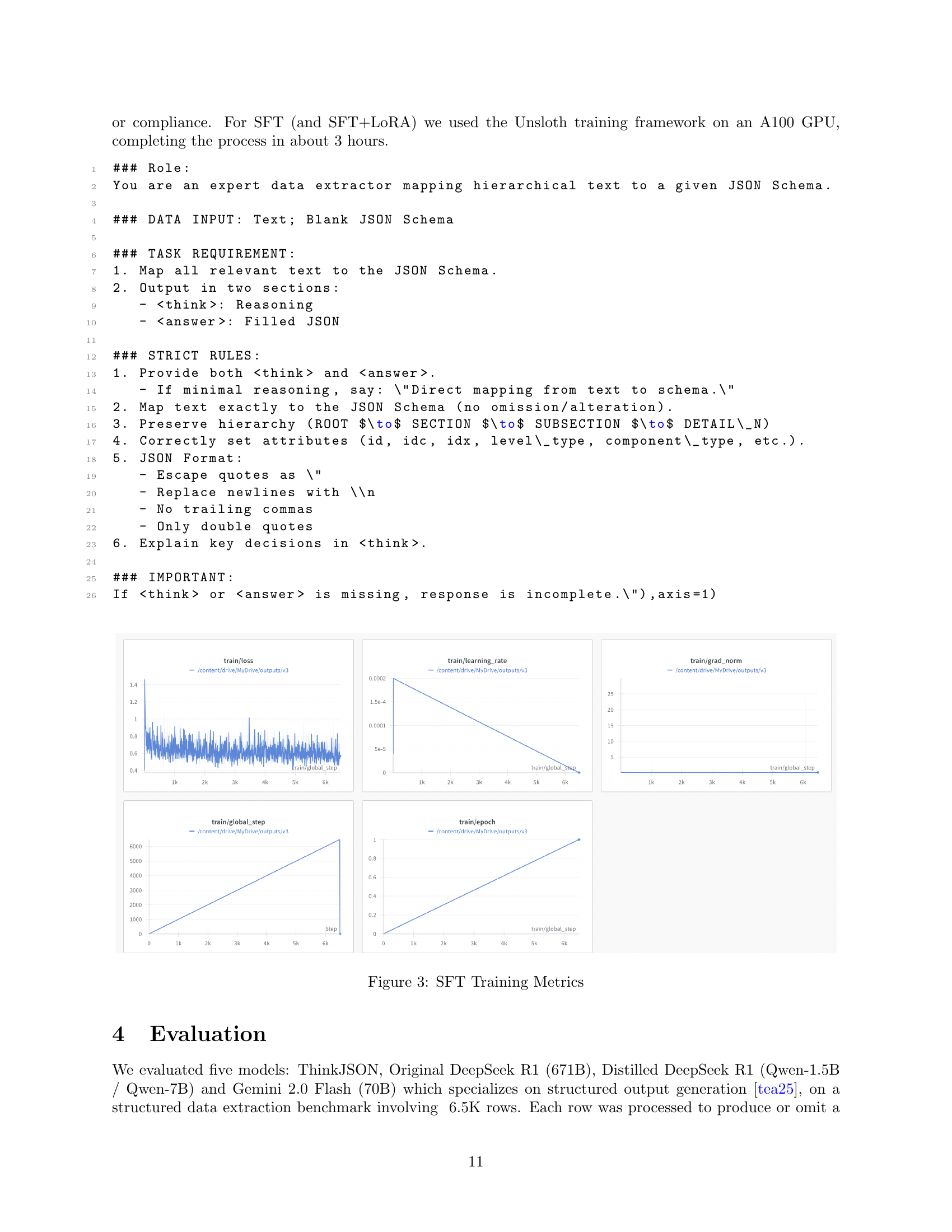
🔼 This figure displays the training metrics for the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) stage of the ThinkJSON model. The four subplots show the progression of various metrics during SFT training: training loss, learning rate, training epoch, and gradient norm. These metrics provide insights into the model’s learning process during SFT, helping to assess its convergence, stability, and overall performance after reinforcement learning.
read the caption
Figure 3: SFT Training Metrics
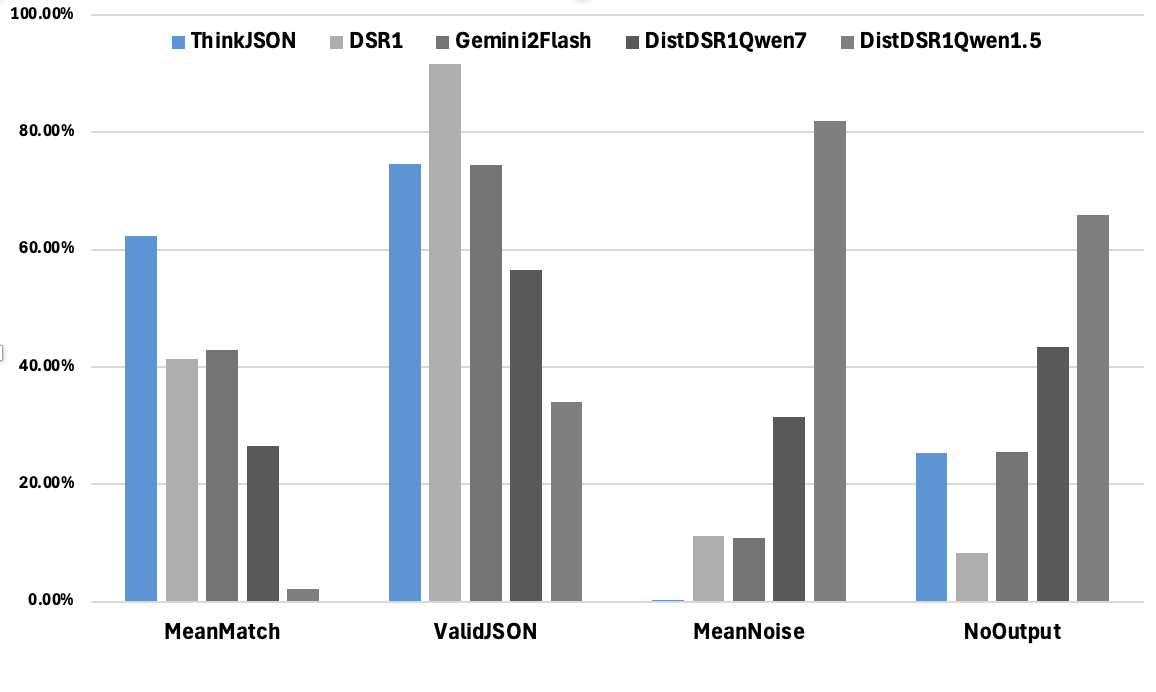
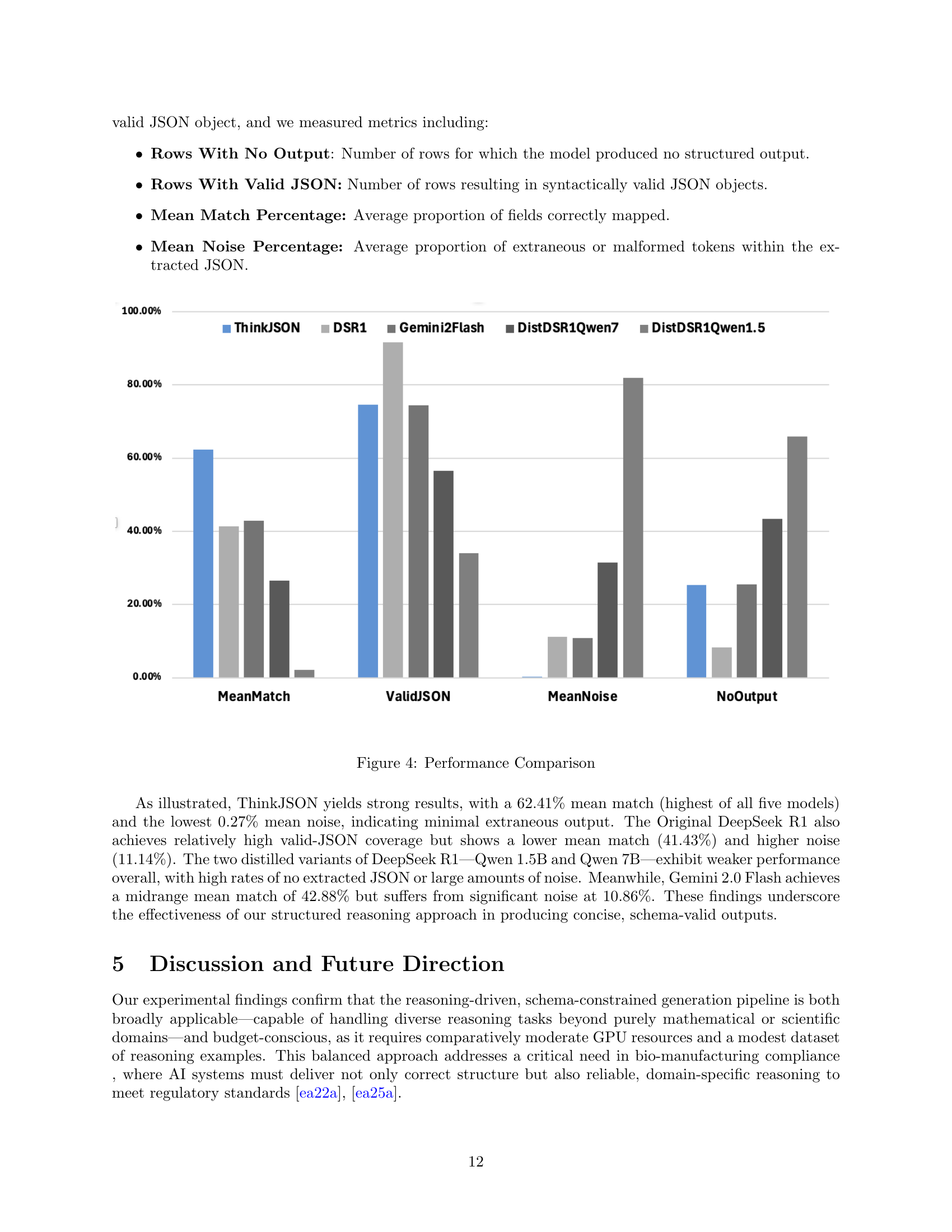
🔼 This figure compares the performance of five different LLMs on a structured data extraction benchmark. The models compared are ThinkJSON (the model proposed in this paper), the original DeepSeek R1, two distilled versions of DeepSeek R1 using Qwen-1.5B and Qwen-7B, and Gemini 2.0 Flash. The benchmark involved 6.5K rows, each aimed at producing a valid JSON object. The metrics used for comparison include: Rows With No Output (number of rows with no structured output), Rows With Valid JSON (number of rows resulting in valid JSON objects), Mean Match Percentage (average proportion of correctly mapped fields), and Mean Noise Percentage (average proportion of extraneous or malformed tokens). The graph visually represents these metrics for each model, allowing for a direct comparison of their effectiveness in structured output generation.
read the caption
Figure 4: Performance Comparison
Full paper#