TL;DR#
The rapid advancement of AI-generated images has created challenges in assessing their quality, requiring consideration of perceptual quality, prompt correspondence, and authenticity. Traditional methods fall short in adequately capturing these dimensions. To address this, the paper introduces a comprehensive framework for evaluating AI-generated image quality that is multimodal, multi-round, and multi-aspect. This approach ensures a more thorough and human-aligned assessment.
The paper proposes M3-AGIQA, which distills image captioning capabilities from online MLLMs into a local model via LoRA fine-tuning. It uses a structured multi-round evaluation mechanism, generating intermediate image descriptions for deeper insights. An xLSTM-based predictor aligns predictions with human judgments. Experiments show state-of-the-art performance and strong generalizability, setting a new benchmark in AGI quality assessment.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important for researchers because it introduces a new benchmark in AI-Generated Image Quality Assessment. By comprehensively addressing quality, correspondence, and authenticity, it offers a robust framework for evaluating AGI models. The method’s superior performance and cross-dataset validation provide a strong foundation for future research and practical applications in enhancing AGI technology.
Visual Insights#
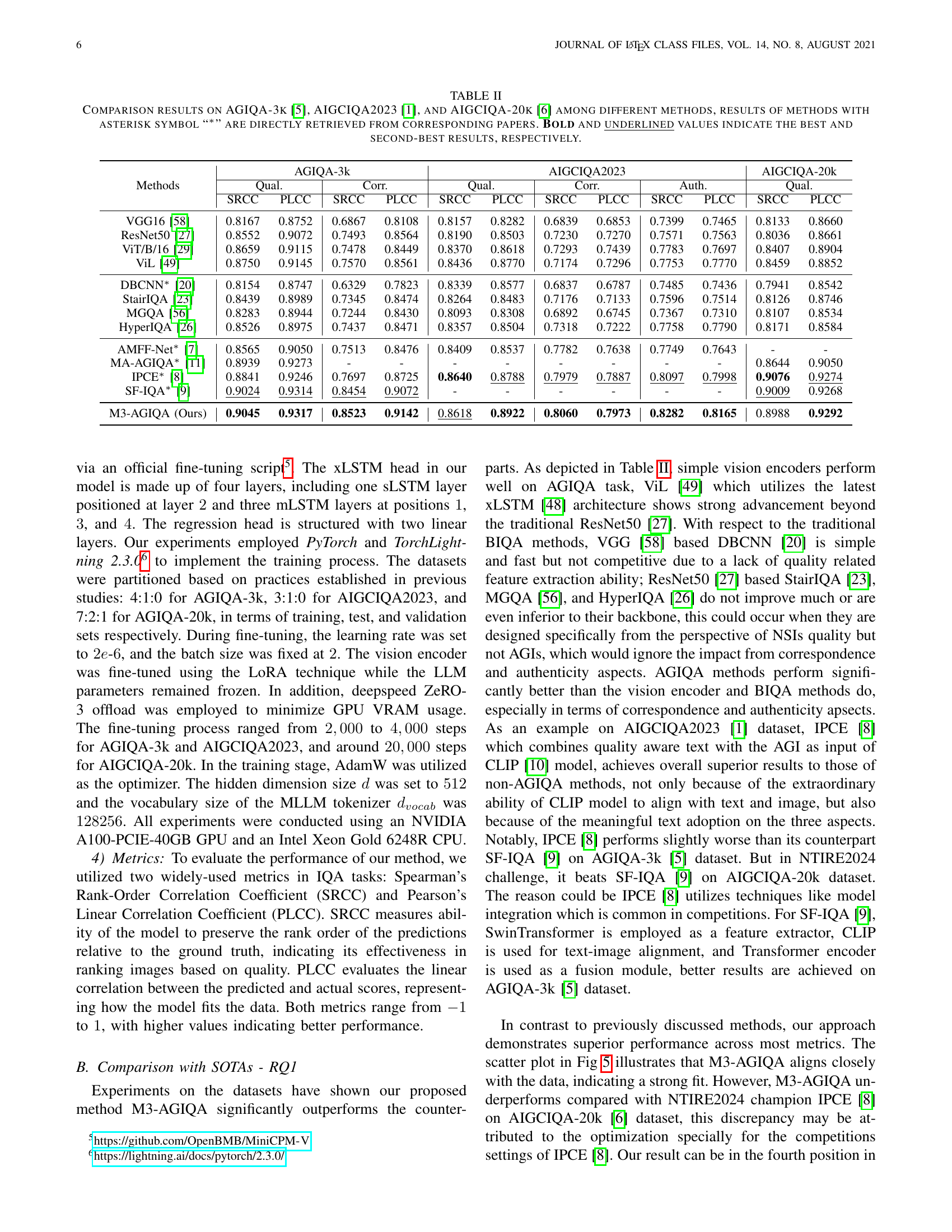
| \topruleStatistics | AGIQA-3k | AIGCIQA2023 | AIGCIQA-20k |
|---|---|---|---|
| \midruleNo. of images | 2,982 | 2,400 | 20,000 |
| No. of T2I models | 6 | 6 | 15 |
| quality MOS | \ding51 | \ding51 | \ding51 |
| correspondence MOS | \ding51 | \ding51 | \ding55 |
| authenticity MOS | \ding55 | \ding51 | \ding55 |
| \bottomrule |
🔼 This table presents a statistical overview of three datasets used in the paper: AGIQA-3k, AIGCIQA2023, and AIGCIQA-20k. For each dataset, it shows the number of images, the number of text-to-image (T2I) models used to generate the images, and indicates whether the dataset includes Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) for quality, correspondence, and authenticity. The presence of a checkmark (✓) signifies the inclusion of MOS for a particular aspect.
read the caption
Table \thetable: Statistics of the datasets.
In-depth insights#
AGIQA Evolution#
The progression of AGIQA is a narrative of increasing complexity, marked by the integration of sophisticated AI techniques. Early AGIQA databases were limited in size and scope, primarily assessing image quality and correspondence. The advent of larger datasets and advanced models has enabled a more nuanced understanding of AGI quality, incorporating aspects like authenticity. Recent efforts utilize deep learning and vision-language pre-trained models, enhancing text-image alignment analysis. Moreover, the evolution sees the rise of multimodal large language models for better AGI assessment.
M3 Framework#
While “M3 Framework” is not explicitly mentioned, I can infer its essence from the paper’s title, “M3-AGIQA: Multimodal, Multi-Round, Multi-Aspect AI-Generated Image Quality Assessment.” Thus, the framework is structured around three key dimensions to assess AI-generated image quality. The framework uses the following methods: Multimodal is leveraging both visual and textual information with MLLMs. Multi-Round involves a structured evaluation through intermediate image descriptions. Multi-Aspect evaluates images across quality, correspondence, and authenticity. It utilizes a XLSTM to predict MOS scores, aligning with human perceptual judgments, a predictor constructed by an xLSTM, and a regression head. This design comprehensively captures AGI quality’s nuances and is validated across datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/strawhatboy/M3-AGIQA.
Zero-shot CoT#
While the provided text doesn’t explicitly mention “Zero-shot CoT”, we can infer its potential role in AI-Generated Image Quality Assessment (AGIQA). Zero-shot learning, in general, refers to the ability of a model to perform a task without any specific training examples for that task. Applied to Chain-of-Thought (CoT), it suggests enabling a Large Language Model (LLM) to reason through a problem (like AGI quality) step-by-step, even without prior exposure to AGIQA-specific examples. In M3-AGIQA, this could manifest in the inference stage, where the LLM, having been fine-tuned on related tasks like image captioning, can leverage its zero-shot CoT capability to analyze an image’s quality, correspondence, and authenticity by generating intermediate reasoning steps. This removes dependence on extensive AGIQA-specific datasets.
xLSTM Insights#
While not explicitly discussed under an “xLSTM Insights” heading, the paper’s use of xLSTM warrants contemplation. XLSTM’s strengths in handling long-range dependencies could be crucial for AGIQA, especially in processing sequential information like image descriptions and conversations. If the model can capture intricate relationships between prompt nuances and visual details, a more human-aligned quality assessment becomes feasible. The decision to replace traditional LSTM with xLSTM emphasizes the need for efficient sequential data processing in AGIQA. Ultimately, a more thorough investigation could show how architecture specifics of xLSTM affects performance and robustness in the AGIQA.
Few Shot AGIQA#
The concept of “Few-Shot AGIQA” is intriguing, suggesting an approach where an AI model can effectively assess the quality of AI-generated images (AGI) with minimal training data. This could involve leveraging meta-learning techniques, transfer learning from related domains (like natural image quality assessment), or the use of sophisticated prompting strategies with large language models (LLMs). The key challenge would be enabling generalization from a very limited set of examples. For instance, the model might be trained on a small dataset of AGI images with corresponding quality scores and then be able to accurately predict the quality of new AGI images generated by different models or with different prompts. This would necessitate a model that is highly adaptable and capable of extracting relevant features from both the image and any associated text prompts. Few-Shot AGIQA would be particularly valuable in scenarios where obtaining large, labeled datasets is expensive or impractical. A successful Few-Shot AGIQA system would represent a significant advancement in the field, enabling rapid and efficient evaluation of AGI quality across diverse contexts.
More visual insights#
More on tables
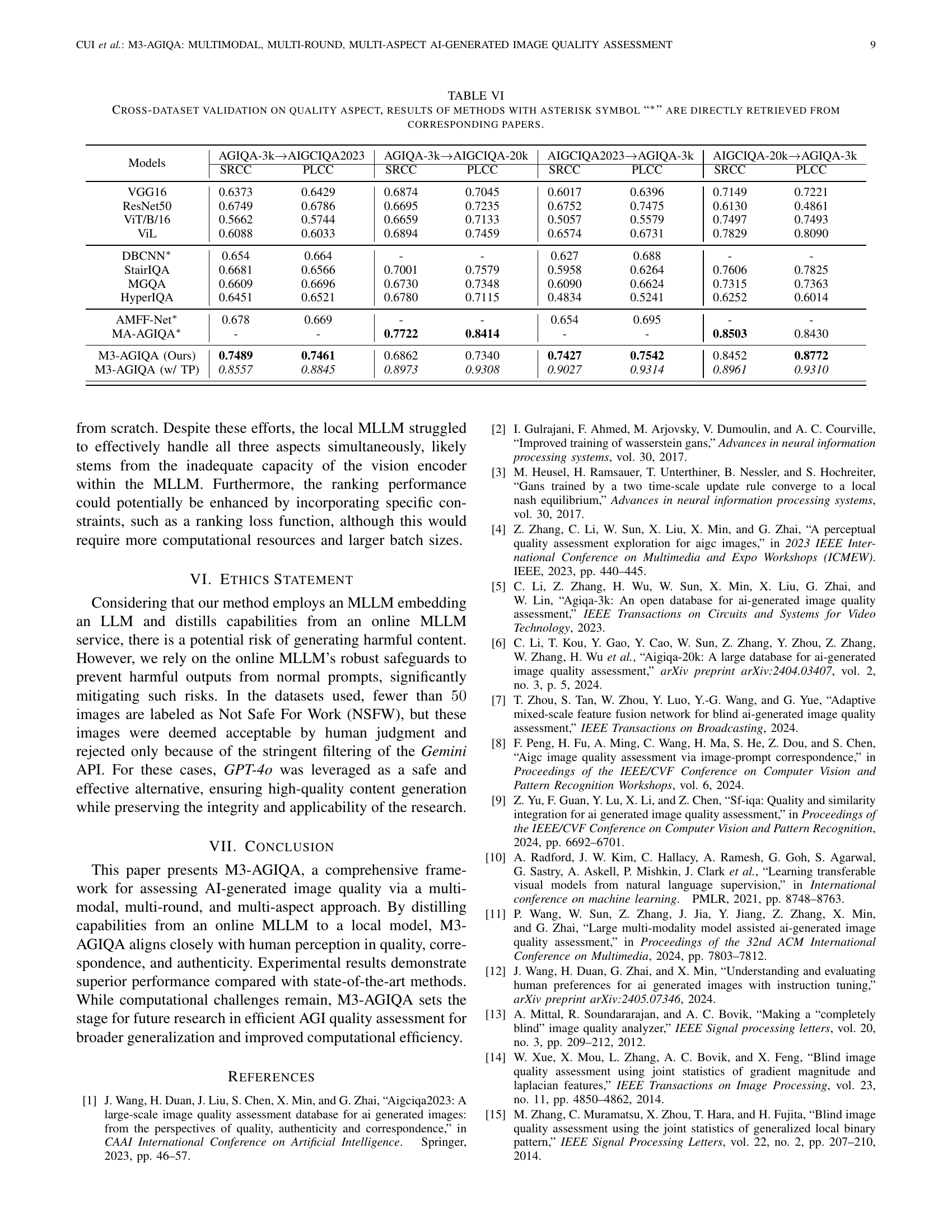
| \toprule\multirow3*Methods | AGIQA-3k | AIGCIQA2023 | AIGCIQA-20k | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qual. | Corr. | Qual. | Corr. | Auth. | Qual. | |||||||
| SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | |
| \midruleVGG16 [simonyan2014very] | 0.8167 | 0.8752 | 0.6867 | 0.8108 | 0.8157 | 0.8282 | 0.6839 | 0.6853 | 0.7399 | 0.7465 | 0.8133 | 0.8660 |
| ResNet50 [he2016deep] | 0.8552 | 0.9072 | 0.7493 | 0.8564 | 0.8190 | 0.8503 | 0.7230 | 0.7270 | 0.7571 | 0.7563 | 0.8036 | 0.8661 |
| ViT/B/16 [dosovitskiy2020image] | 0.8659 | 0.9115 | 0.7478 | 0.8449 | 0.8370 | 0.8618 | 0.7293 | 0.7439 | 0.7783 | 0.7697 | 0.8407 | 0.8904 |
| ViL [alkin2024visionlstm] | 0.8750 | 0.9145 | 0.7570 | 0.8561 | 0.8436 | 0.8770 | 0.7174 | 0.7296 | 0.7753 | 0.7770 | 0.8459 | 0.8852 |
| \midruleDBCNN∗ [zhang2018blind] | 0.8154 | 0.8747 | 0.6329 | 0.7823 | 0.8339 | 0.8577 | 0.6837 | 0.6787 | 0.7485 | 0.7436 | 0.7941 | 0.8542 |
| StairIQA [sun2022blind] | 0.8439 | 0.8989 | 0.7345 | 0.8474 | 0.8264 | 0.8483 | 0.7176 | 0.7133 | 0.7596 | 0.7514 | 0.8126 | 0.8746 |
| MGQA [wang2021multi] | 0.8283 | 0.8944 | 0.7244 | 0.8430 | 0.8093 | 0.8308 | 0.6892 | 0.6745 | 0.7367 | 0.7310 | 0.8107 | 0.8534 |
| HyperIQA [Su_2020_CVPR] | 0.8526 | 0.8975 | 0.7437 | 0.8471 | 0.8357 | 0.8504 | 0.7318 | 0.7222 | 0.7758 | 0.7790 | 0.8171 | 0.8584 |
| \midruleAMFF-Net∗ [zhou2024adaptive] | 0.8565 | 0.9050 | 0.7513 | 0.8476 | 0.8409 | 0.8537 | 0.7782 | 0.7638 | 0.7749 | 0.7643 | - | - |
| MA-AGIQA∗ [wang2024large] | 0.8939 | 0.9273 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.8644 | 0.9050 |
| IPCE∗ [peng2024aigc] | 0.8841 | 0.9246 | 0.7697 | 0.8725 | 0.8640 | 0.8788 | 0.7979 | 0.7887 | 0.8097 | 0.7998 | 0.9076 | 0.9274 |
| SF-IQA∗ [yu2024sf] | 0.9024 | 0.9314 | 0.8454 | 0.9072 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.9009 | 0.9268 |
| \midruleM3-AGIQA (Ours) | 0.9045 | 0.9317 | 0.8523 | 0.9142 | 0.8618 | 0.8922 | 0.8060 | 0.7973 | 0.8282 | 0.8165 | 0.8988 | 0.9292 |
| \bottomrule | ||||||||||||
🔼 This table presents a comparison of different AI-generated image quality assessment (AGIQA) methods across three benchmark datasets: AGIQA-3k, AIGCIQA2023, and AIGCIQA-20k. The performance of each method is evaluated using two metrics: Spearman’s Rank-Order Correlation Coefficient (SRCC) and Pearson’s Linear Correlation Coefficient (PLCC). Both metrics range from -1 to +1, with higher values indicating better performance. The table shows the SRCC and PLCC scores for each method and dataset. Methods marked with an asterisk (*) obtained their results from published papers. The best and second-best results for each metric and dataset are highlighted in bold and underlined, respectively. This allows for a direct comparison of the relative strengths and weaknesses of various AGIQA approaches.
read the caption
Table \thetable: Comparison results on AGIQA-3k [li2023agiqa], AIGCIQA2023 [wang2023aigciqa2023], and AIGCIQA-20k [li2024aigiqa] among different methods, results of methods with asterisk symbol “∗” are directly retrieved from corresponding papers. Bold and underlined values indicate the best and second-best results, respectively.
| \toprule Present Descriptions | Qual. | |||
| Qual. | Corr. | Auth. | SRCC | PLCC |
| \midrule\ding55 | \ding55 | \ding55 | 0.8816 | 0.9193 |
| \ding51 | \ding55 | \ding55 | 0.8989 | 0.9342 |
| \ding51 | \ding51 | \ding55 | 0.9045 | 0.9317 |
| \ding51 | \ding51 | \ding51 | 0.8999 | 0.9321 |
| \bottomrule | ||||
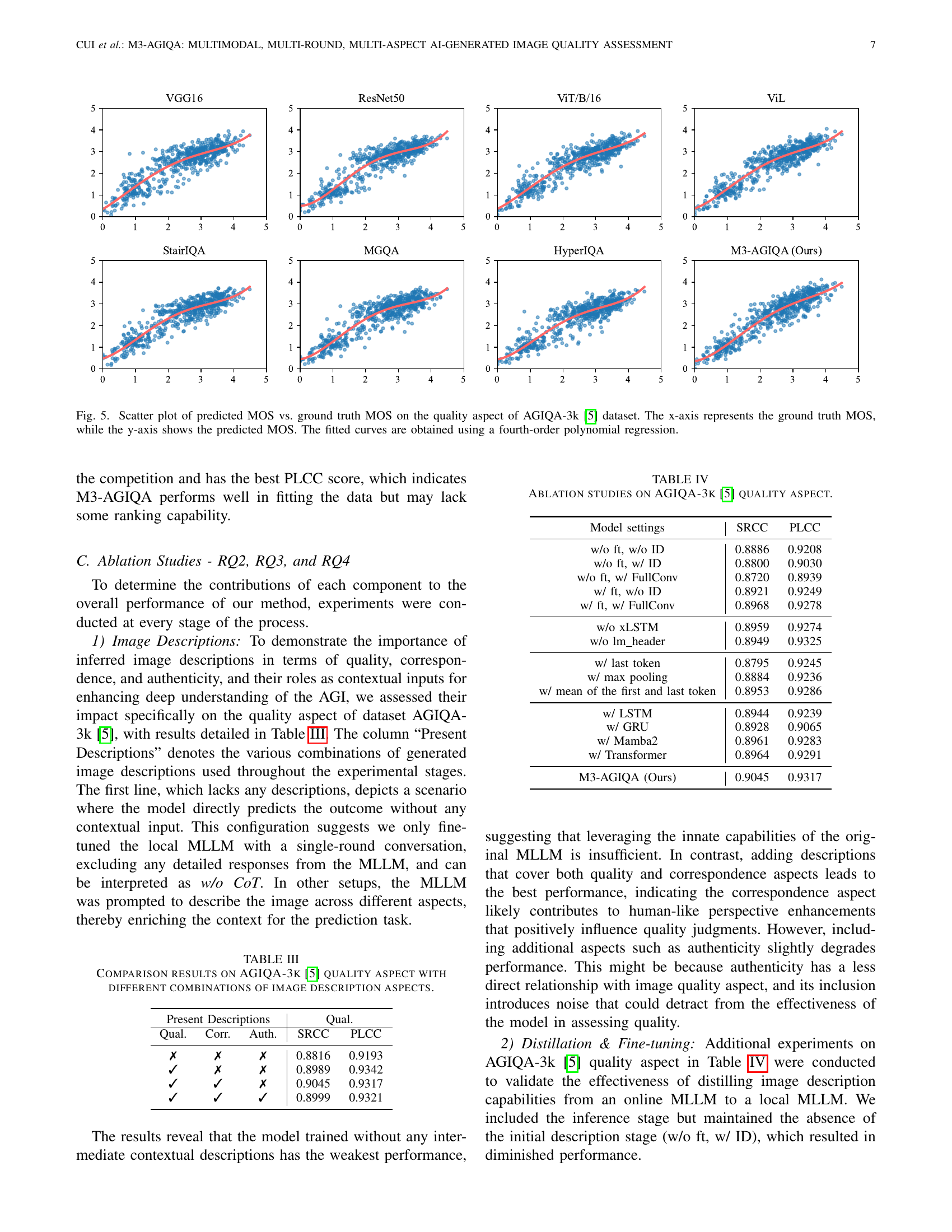
🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study evaluating the impact of different combinations of image description aspects on the performance of the M3-AGIQA model for assessing the quality of AI-generated images. Specifically, it examines how including descriptions of quality, correspondence, and authenticity influences the model’s ability to accurately predict Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) for image quality. The results are shown as Spearman’s Rank-Order Correlation Coefficient (SRCC) and Pearson’s Linear Correlation Coefficient (PLCC) scores, which measure the model’s ranking and linear correlation performance, respectively.
read the caption
Table \thetable: Comparison results on AGIQA-3k [li2023agiqa] quality aspect with different combinations of image description aspects.
Full paper#