TL;DR#
Color constancy methods often struggle when applied to images from different cameras due to variations in their spectral sensitivities. Traditional algorithms rely on assumptions about scene color distributions that don’t always hold true. Learning-based methods can perform better, but often require retraining for each new camera, which is impractical. This paper tackles the issue of generalizing color constancy across different camera sensors.
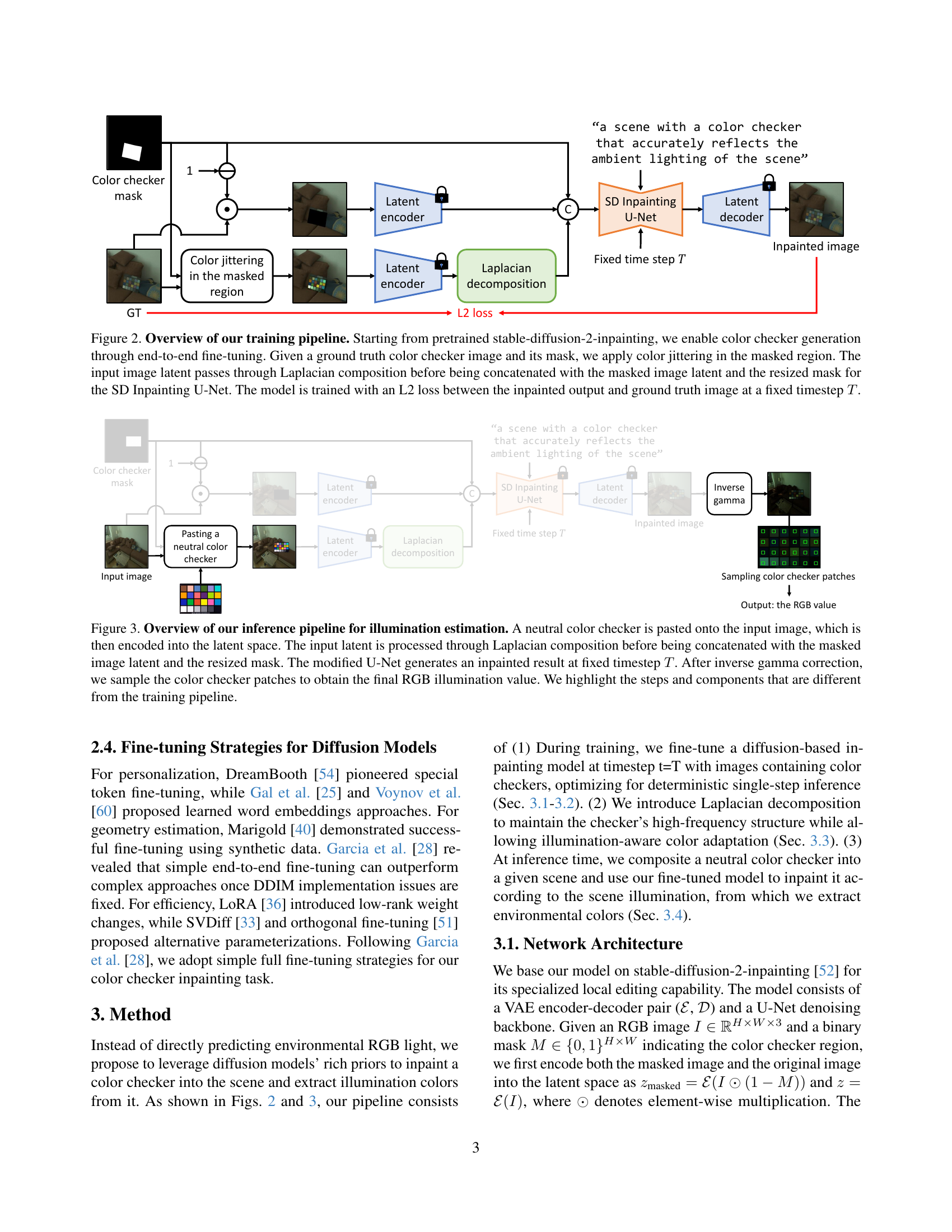
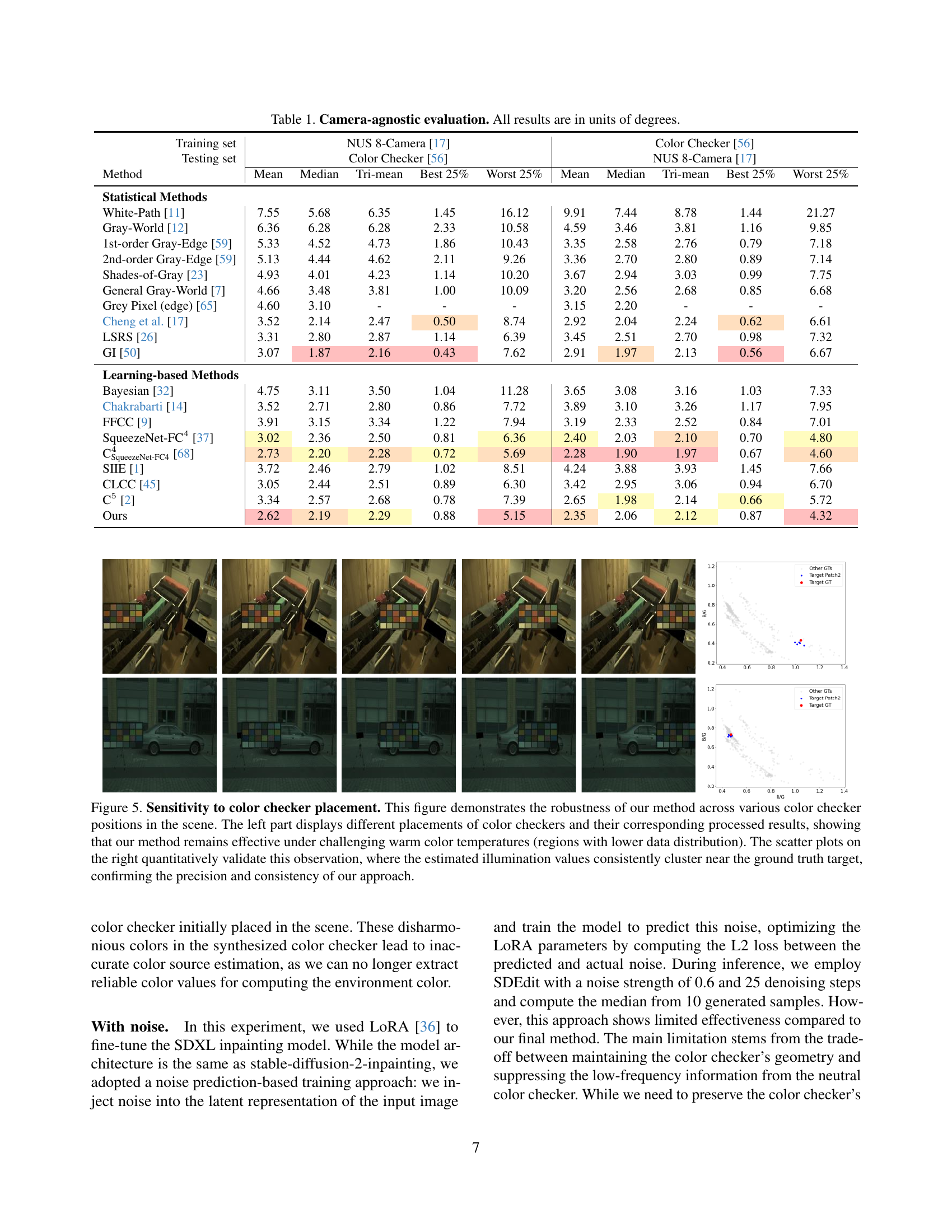
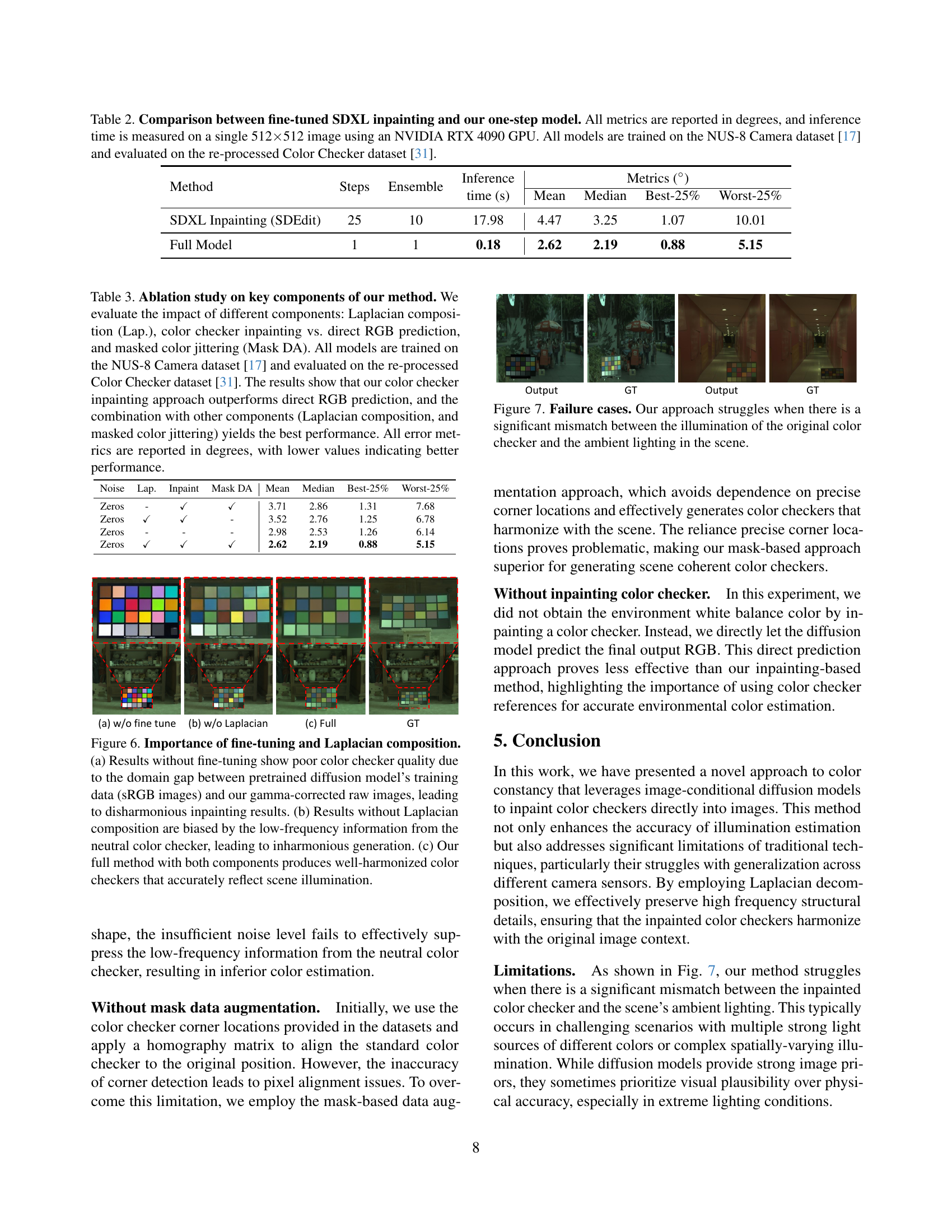
The paper introduces a novel method called GCC that uses diffusion models to inpaint color checkers into images, then uses these checkers to estimate the scene’s illumination. This involves a deterministic inference approach for inpainting, Laplacian composition for checker structure, and a data augmentation strategy for imprecise color checker annotations. GCC is robust in cross-camera scenarios without sensor-specific training.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper introduces a method that uses diffusion models to achieve robust color constancy across diverse cameras without sensor-specific training. It addresses a key challenge in computer vision and opens avenues for real-world applications and further research on generalizable color correction techniques.
Visual Insights#
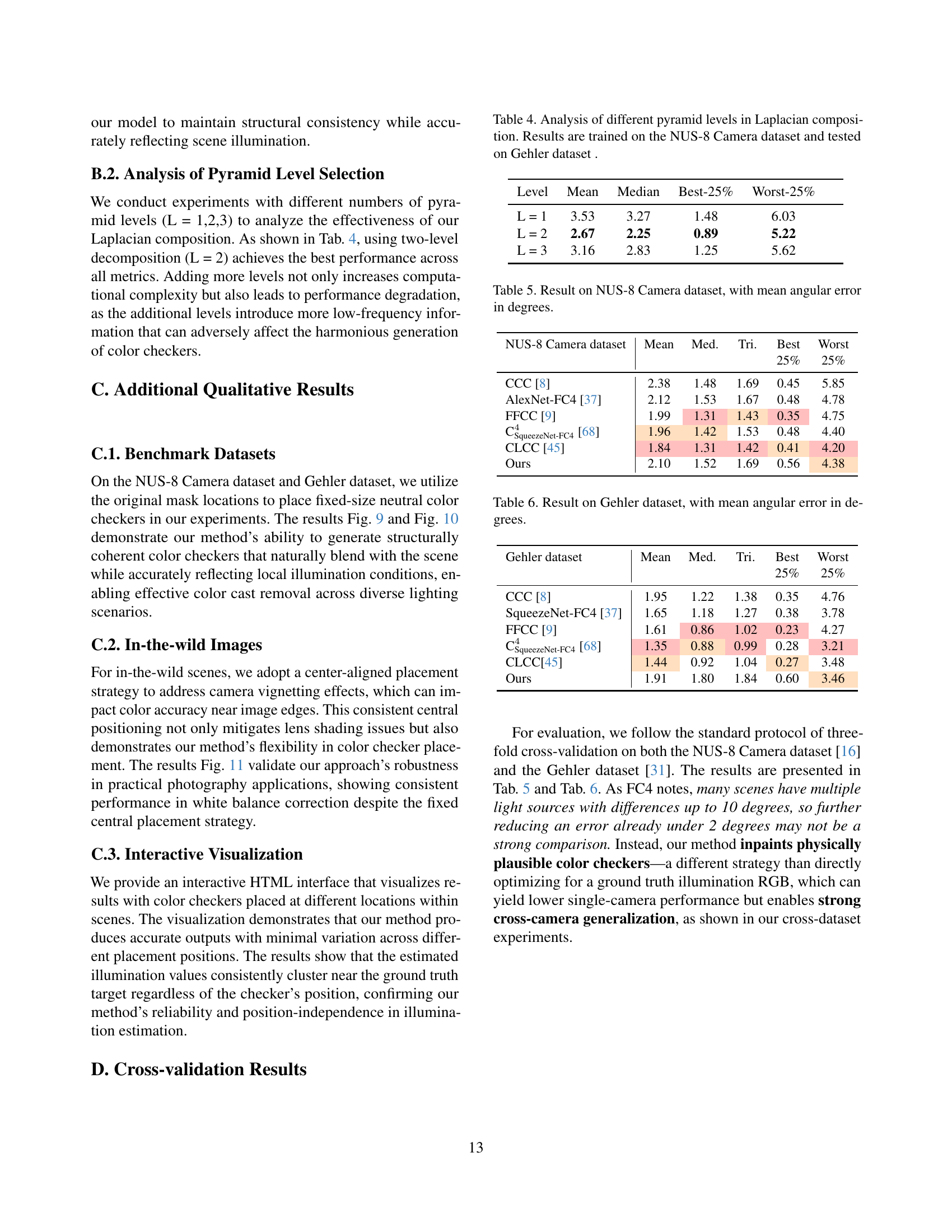
| \topruleLevel | Mean | Median | Best-25% | Worst-25% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \midruleL = 1 | 3.53 | 3.27 | 1.48 | 6.03 | |
| L = 2 | 2.67 | 2.25 | 0.89 | 5.22 | |
| L = 3 | 3.16 | 2.83 | 1.25 | 5.62 | |
| \bottomrule |
🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study evaluating the effect of varying the number of pyramid levels used in the Laplacian decomposition component of the proposed color constancy method. The study specifically examines how the number of levels impacts the performance of the method when trained on the NUS-8 Camera dataset and tested on the Gehler dataset. The table shows the mean, median, best 25%, and worst 25% angular error for each pyramid level configuration (1, 2, and 3 levels). This allows assessment of the trade-off between computational complexity and accuracy.
read the caption
Table \thetable: Analysis of different pyramid levels in Laplacian composition. Results are trained on the NUS-8 Camera dataset and tested on Gehler dataset .
Full paper#