TL;DR#
Traditional portrait animation methods struggle with motion accuracy, rendering quality, and temporal coherence. To address these issues, MagicInfinite is introduced, a novel diffusion Transformer framework that delivers high-fidelity results across diverse characters, facial poses, and speaking scenarios. It enables infinite video generation with temporal coherence using 3D full-attention and a sliding window denoising strategy and supports precise speaker designation in multi-character scenes.
The paper also addresses the challenge of integrating audio and text for realistic animation by proposing a two-stage curriculum learning scheme. It uses region-specific masks and adaptive loss functions to balance global textual control and local audio guidance for speaker-specific animations. The efficiency is enhanced via unified step and CFG distillation techniques, achieving a 20x inference speed boost. MagicInfinite demonstrates superiority in audio-lip synchronization, identity preservation, and motion naturalness.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it introduces MagicInfinite, a new approach to talking head video generation that addresses the limitations of existing methods. It enables high-fidelity, temporally coherent videos with flexible multi-modal control, efficient inference, and superior performance across diverse scenarios. This research has the potential to advance digital entertainment, education, and AI communication by providing a more realistic and engaging way to interact with digital characters.
Visual Insights#

🔼 Figure 1 showcases the capabilities of the MagicInfinite model. It demonstrates the generation of high-quality, realistic animation videos from a single portrait image. The animation is controlled by both text and audio inputs. The figure highlights the model’s ability to maintain temporal coherence and visual fidelity across diverse character styles, head poses, and even varied backgrounds. The examples include realistic humans, stylized anime characters, and full-body figures, demonstrating the versatility of the MagicInfinite approach.
read the caption
Figure 1: Given a portrait image, our model can generate compelling, realistic, and vivid animation videos with control over text and voice, ensuring temporal coherence and perceptual quality even under significant head pose variations and diverse portrait styles.
| IDs | Questions |
| 1 | Which video shows the best match between the character’s lip movements and the audio? |
| 2 | Which video has the character that looks most like the person in the image? |
| 3 | Which video feels the smoothest and least choppy to you? |
| 4 | Which video has character movements that seem most realistic or similar to those in movies and animations? |
| 5 | Which video has scene changes that seem most realistic or similar to those in movies and animations? |
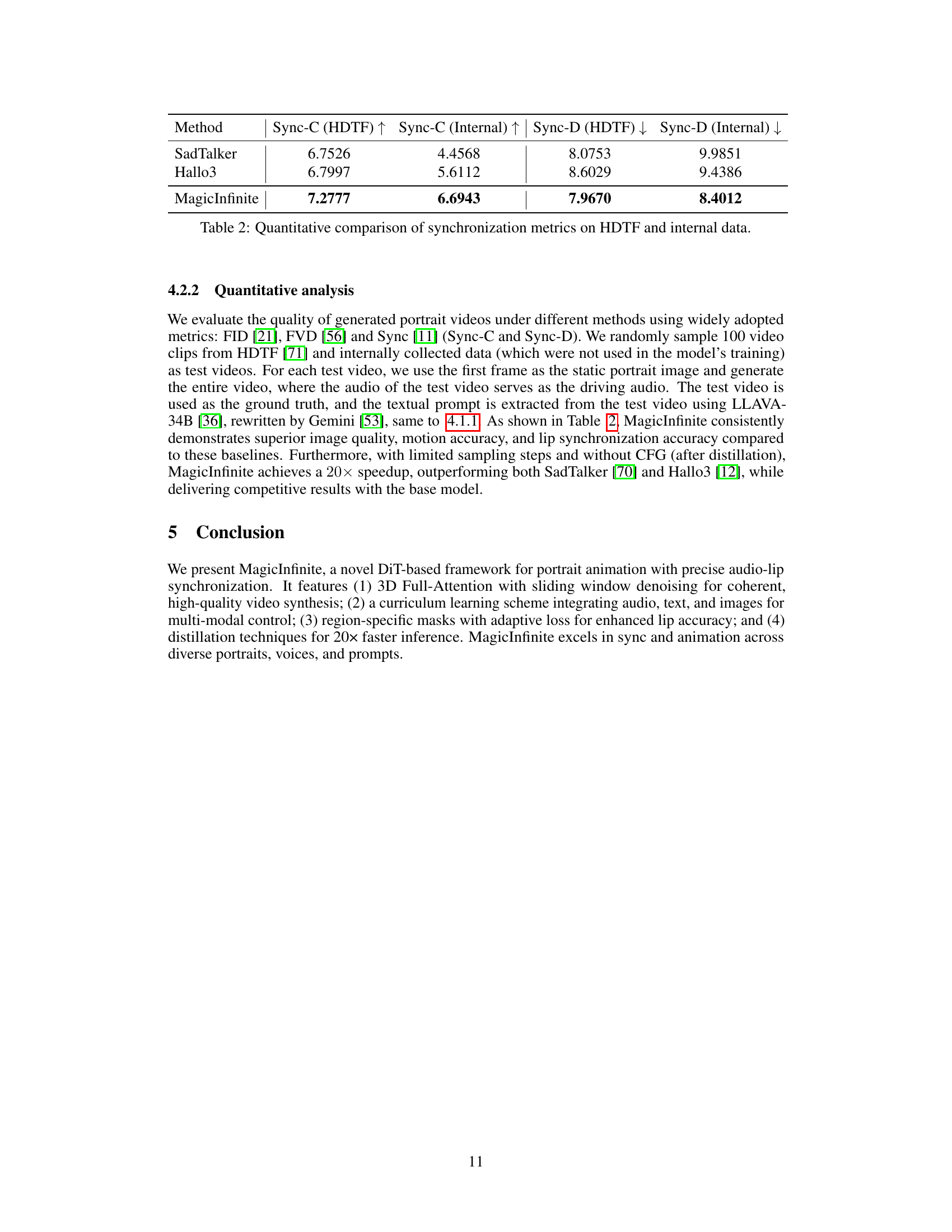
🔼 This table summarizes a user study designed to compare the video quality produced by three different portrait animation models: Hallo3, SadTalker, and MagicInfinite. Participants viewed videos generated by each model for the same input portrait images and audio/text prompts and rated them based on five criteria. These criteria assess the accuracy of lip-sync, the likeness of the generated character to the input image, the smoothness of the animation, the realism of the character movements, and the realism of any scene changes within the videos. The responses were used to evaluate and compare the overall quality of each method.
read the caption
Table 1: The user study comprises a list of five questions. Participants in the user study will answer these questions based on the videos synthesized by Hallo3, SadTalker, and MagicInfinite, as well as the corresponding portrait images.
In-depth insights#
Infinite Avatars#
The concept of “Infinite Avatars” suggests a future where digital representations are limitless in creation and customization. AI-driven tools could generate avatars endlessly, adapting to diverse styles and characteristics. Personalization would reach unprecedented levels, allowing users to embody any persona imaginable. Challenges include maintaining identity consistency and preventing misuse. Scalability and ethical considerations are crucial, demanding robust frameworks for content moderation and responsible AI development.
3D Full-Attention#
3D Full-Attention emerges as a pivotal mechanism to enhance both spatial and temporal coherence in video synthesis. By attending to all tokens across frames, it captures intricate dependencies, crucial for realistic motion. Its integration addresses limitations of prior methods, particularly in complex scenarios like non-frontal faces or high-resolution video, where weak frame correspondence often leads to artifacts. It’s a cornerstone for high-fidelity video generation, ensuring visual quality and temporal consistency, outperforming methods with separate spatial and temporal processing. This approach allows the model to better learn the fine-grained control of audio over lip movements.
Curriculum Learn#
Curriculum learning in the context of talking head generation is a smart training strategy. Starting with simpler tasks like text-to-video generation lets the model grasp the basics without audio interference. The model then gradually incorporates audio, focusing on lip sync with a face region mask and adaptive loss. This ensures the model prioritizes audio cues locally while maintaining global textual control. This two-stage approach prevents the model from overlooking audio nuances. Fine-grained lip movements, are often neglected when training with both text and audio simultaneously due to the text’s stronger influence on overall video content. This curriculum balances text and audio influence, leading to better lip synchronization and more natural-sounding talking heads. This addresses a key challenge in multi-modal talking head generation.
DMD2 Distillation#
DMD2 is presented as a key component for accelerating diffusion model inference. Traditional diffusion models suffer from slow inference speeds due to the iterative sampling process. The paper adopts DMD2 which is validated across image diffusion models to enable accelerated sampling. The approach eliminates MagicInfinite’s reliance on CFG during the step distillation process in DMD2, reducing NFEs. To circumvent GPU memory constraints, LoRA is used to update the parameters of the fake data distribution estimator, for efficient training. DMD2 helps to produce high-quality videos. The framework utilizes a curriculum learning strategy to reduce base loss weight and increase the SDS loss weight for effective learning. It leverages CFG during inference, applying two-fold CFG to timesteps 0.75-1 and three-fold CFG to timesteps 0-0.75. Collaboration of DMD and CFG achieved good results.
Portrait Fidelity#
The paper focuses on generating high-fidelity talking head videos that maintain the subject’s identity. This is addressed through the use of a pre-trained Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to encode the static portrait image, ensuring that the generated video retains the likeness and background context from the initial image. The paper also implements a curriculum learning scheme with a face region mask and adaptive loss function. This approach helps the model prioritize local facial movements and lip synchronization without sacrificing overall portrait fidelity. The user study shows that the majority of the participants agreed that the generated videos by the proposed approach were more realisitic and vivid.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 Figure 2 illustrates the architecture of the MagicInfinite model, a hybrid dual-to-single-stream diffusion model. The process begins with a static portrait image and textual prompt. A Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) encodes this information into tokens. Simultaneously, the audio input is processed by Wav2Vec, and an audio encoder adjusts the sampling rate. A face region mask guides the audio processing to focus on lip synchronization. These tokens (text and audio) are combined and fed into a text-to-video (T2V) model. This model is refined through denoising steps with audio cross-attention incorporated in the final blocks to ensure precise lip synchronization. The output is a high-fidelity, talking-head video.
read the caption
Figure 2: Overview of MagicInfinite. MagicInfinite employs a hybrid dual-to-single-stream denoising network with Audio Cross-Attention in final blocks. MLLM encodes static portrait and text into tokens, concatenated for T2V, refined, and denoised. Wav2Vec encodes audio, resampled by an Audio Encoder, and guided by a Face Region Mask for precise lip sync and adaptive loss.

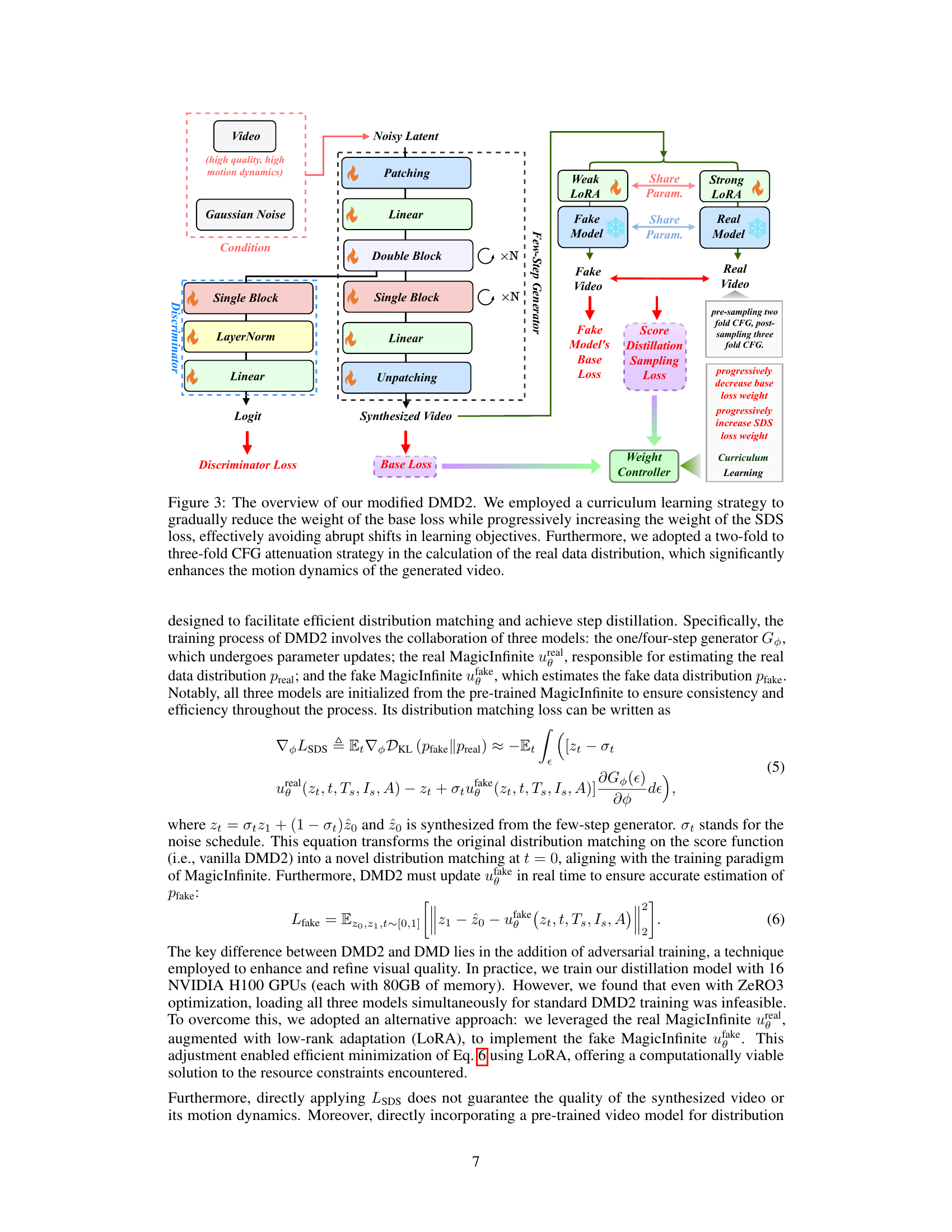
🔼 This figure illustrates the architecture of the modified DMD2 model used for efficient inference. The key improvements are a curriculum learning strategy that smoothly transitions between different loss functions (base loss and SDS loss), preventing instability during training. Additionally, a two-fold to three-fold CFG (classifier-free guidance) attenuation method is used during the calculation of the real data distribution. This refinement significantly improves the motion dynamics and quality of the generated video, enabling more fluid and natural movement.
read the caption
Figure 3: The overview of our modified DMD2. We employed a curriculum learning strategy to gradually reduce the weight of the base loss while progressively increasing the weight of the SDS loss, effectively avoiding abrupt shifts in learning objectives. Furthermore, we adopted a two-fold to three-fold CFG attenuation strategy in the calculation of the real data distribution, which significantly enhances the motion dynamics of the generated video.

🔼 Figure 4 showcases various video generation results from the MagicInfinite model, highlighting its ability to create high-quality and realistic talking avatar videos with diverse character types and styles, including realistic humans and stylized anime characters. The videos demonstrate accurate lip synchronization with the input audio, natural head and facial movements, and coherent background integration, even under significant head pose variations and different lighting conditions. The figure visually emphasizes the model’s capability for precise control over video generation parameters, showcasing its ability to generate compelling and diverse animation across various scenarios.
read the caption
Figure 4: Qualitative experimental results of MagicInfinite
Full paper#