TL;DR#
Current diffusion-based image manipulation methods lack the precision of traditional tools, and struggle with interactive, element-based editing. These methods face challenges in decoupling visual elements, layout control, identity preservation, visual harmony, and data scarcity. Existing benchmarks also don’t comprehensively evaluate element-level manipulations.
This paper introduces BlobCtrl, a unified framework for element-level image generation and editing using a probabilistic blob-based representation. A dual-branch diffusion model and self-supervised training enables flexible manipulation. The authors also present BlobData, a large-scale dataset and BlobBench, a rigorous evaluation benchmark to facilitate future research.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper introduces a novel approach to element-level image manipulation, a crucial area for content creation. By providing a unified framework and open-source dataset, it enables more flexible and precise image editing, and paves the way for future research in visual content creation and manipulation.
Visual Insights#

🔼 BlobCtrl is a framework for element-level image generation and editing. The top row shows the diverse manipulation operations it supports: composing new elements, moving existing ones, resizing, removing, replacing, and combining these actions. The bottom row illustrates the iterative refinement process, demonstrating how BlobCtrl enables precise, fine-grained editing to achieve the desired results.
read the caption
Figure 1: Our proposed BlobCtrl framework enables comprehensive element-level control over both visual appearance and spatial layout, facilitating diverse manipulation operations including compositional generation, spatial transformation, element removal, content replacement and arbitrary combinations thereof (top). Through an iterative refinement process, BlobCtrl allows precise and fine-grained editing capabilities to achieve desired visual outcomes (bottom).
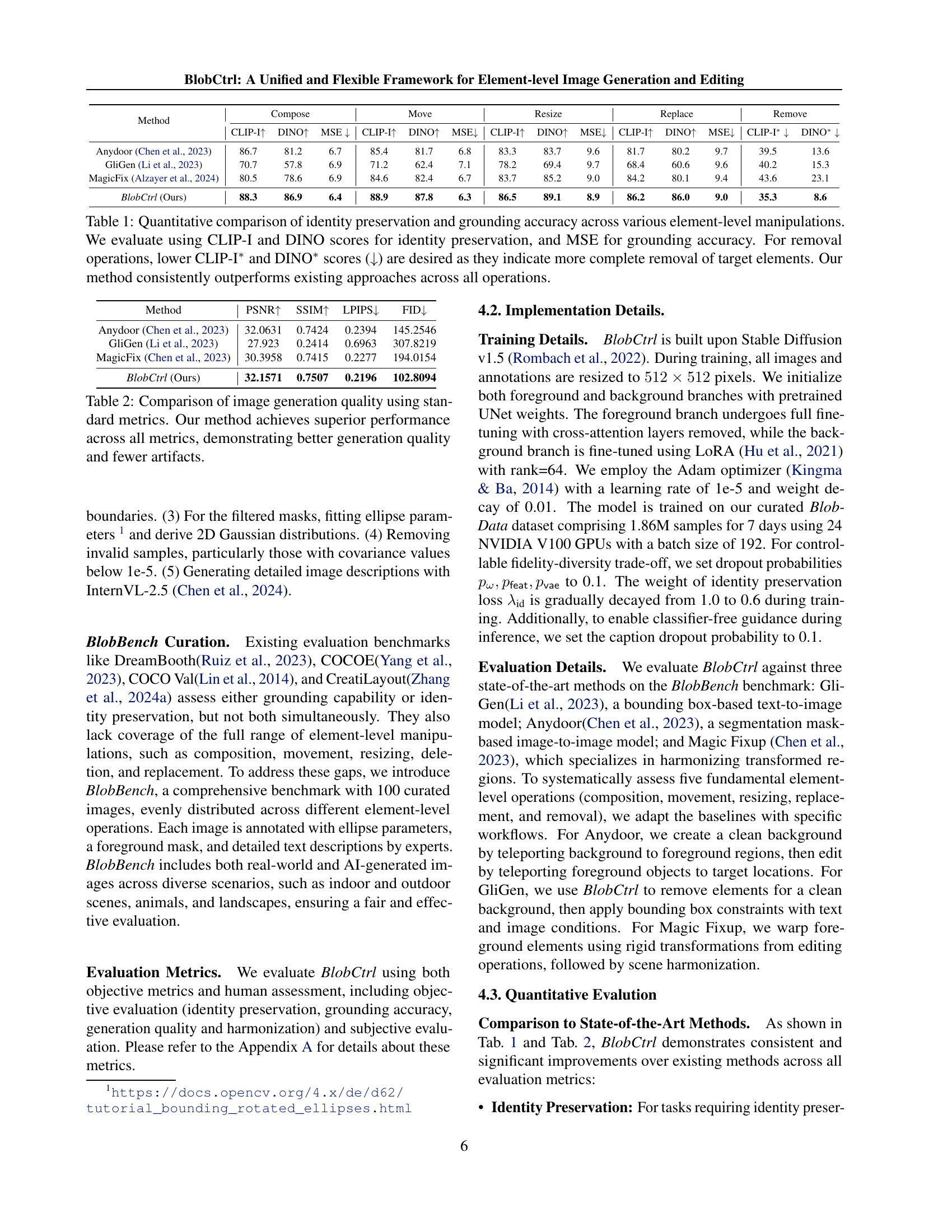
| Method | Compose | Move | Resize | Replace | Remove | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLIP-I | DINO | MSE | CLIP-I | DINO | MSE | CLIP-I | DINO | MSE | CLIP-I | DINO | MSE | CLIP-I | DINO | |
| Anydoor (Chen et al., 2023) | 86.7 | 81.2 | 6.7 | 85.4 | 81.7 | 6.8 | 83.3 | 83.7 | 9.6 | 81.7 | 80.2 | 9.7 | 39.5 | 13.6 |
| GliGen (Li et al., 2023) | 70.7 | 57.8 | 6.9 | 71.2 | 62.4 | 7.1 | 78.2 | 69.4 | 9.7 | 68.4 | 60.6 | 9.6 | 40.2 | 15.3 |
| MagicFix (Alzayer et al., 2024) | 80.5 | 78.6 | 6.9 | 84.6 | 82.4 | 6.7 | 83.7 | 85.2 | 9.0 | 84.2 | 80.1 | 9.4 | 43.6 | 23.1 |
| BlobCtrl (Ours) | 88.3 | 86.9 | 6.4 | 88.9 | 87.8 | 6.3 | 86.5 | 89.1 | 8.9 | 86.2 | 86.0 | 9.0 | 35.3 | 8.6 |
🔼 Table 1 presents a quantitative comparison of different element-level image manipulation methods (compose, move, resize, replace, and remove). The performance of each method is evaluated using three metrics: CLIP-I and DINO scores (higher is better) measure the preservation of the original element’s identity after manipulation, and MSE (lower is better) measures the accuracy of the element’s placement. For removal operations, lower CLIP-I* and DINO* scores are desirable, indicating a more thorough removal. The results show that the proposed BlobCtrl method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across all five manipulation tasks.
read the caption
Table 1: Quantitative comparison of identity preservation and grounding accuracy across various element-level manipulations. We evaluate using CLIP-I and DINO scores for identity preservation, and MSE for grounding accuracy. For removal operations, lower CLIP-I∗ and DINO∗ scores (↓↓\downarrow↓) are desired as they indicate more complete removal of target elements. Our method consistently outperforms existing approaches across all operations.
In-depth insights#
Blob Representation#
Blob representations offer a compelling approach to element-level image manipulation due to their inherent flexibility and control. Unlike segmentation masks that enforce rigid shapes, blobs, particularly when modeled as Gaussians, provide a smooth and continuous representation, enabling harmonious integration and manipulation of visual elements. This allows for precise control over an object’s position, size, and orientation within an image. Blob opacity, derived from the Gaussian distribution, facilitates depth-aware alpha compositing, which effectively addresses occlusion and models relationships between objects. By leveraging blob splatting, visual semantics can be projected into a two-dimensional space, creating spatially-aware features that enhance visual understanding and manipulation.
Dual-Branch Model#
The dual-branch model seems to be a powerful architectural choice for element-level image manipulation, offering a way to disentangle foreground and background processing. By dedicating one branch to preserving the identity and details of foreground elements, and the other to maintaining overall scene context and harmony, it allows for more controlled and coherent image editing. This division of labor is particularly important in tasks where preserving the visual characteristics of specific objects while seamlessly integrating them into a new environment is critical. The success of this approach relies on effective feature fusion between the branches to ensure that the manipulated elements are both visually consistent with the scene and retain their original appearance. Furthermore, random dropout strategies allow for a better balance between apperance fidelity and diversity.
Self-Supervised Train#
Self-supervised training is a clever approach to overcome the scarcity of paired data in element-level image manipulation. Instead of relying on pre-existing datasets, it leverages the idea that any image can be considered the result of a manipulation process. By simulating source and target positions for elements within an image and optimizing for noise prediction, the model learns to fill in elements, inpaint backgrounds, and harmoniously integrate the two. This avoids the need for labor-intensive, perfectly aligned datasets and allows the model to learn from a broader range of images, ultimately boosting its robustness and generalization.This approach effectively leverages readily available data, reduces the reliance on specialized datasets, and ultimately enhances the model’s adaptability to various scenarios.
ID Preserv. Ablation#
An ablation study focusing on Identity Preservation is crucial to understand the contribution of specific components in a model. This helps to determine the most impactful design choices in retaining the original characteristics of the manipulated elements. Removing the ID preservation loss and observing a drop in performance indicates its effectiveness. Analyzing model behavior after removing each component helps to ensure a deeper understanding of the model’s overall capabilities.
Future Work: Depth#
Future research could explore leveraging depth information to enhance element-level image manipulation. Integrating depth estimation or 3D scene reconstruction techniques could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the scene’s geometry, leading to more realistic and consistent manipulations. For example, depth-aware compositing would allow for better handling of occlusions and spatial relationships between elements. Furthermore, incorporating depth information could improve the accuracy of element removal and replacement, ensuring seamless integration of new elements into the scene. Specifically, conditional diffusion model could be experimented.
More visual insights#
More on figures

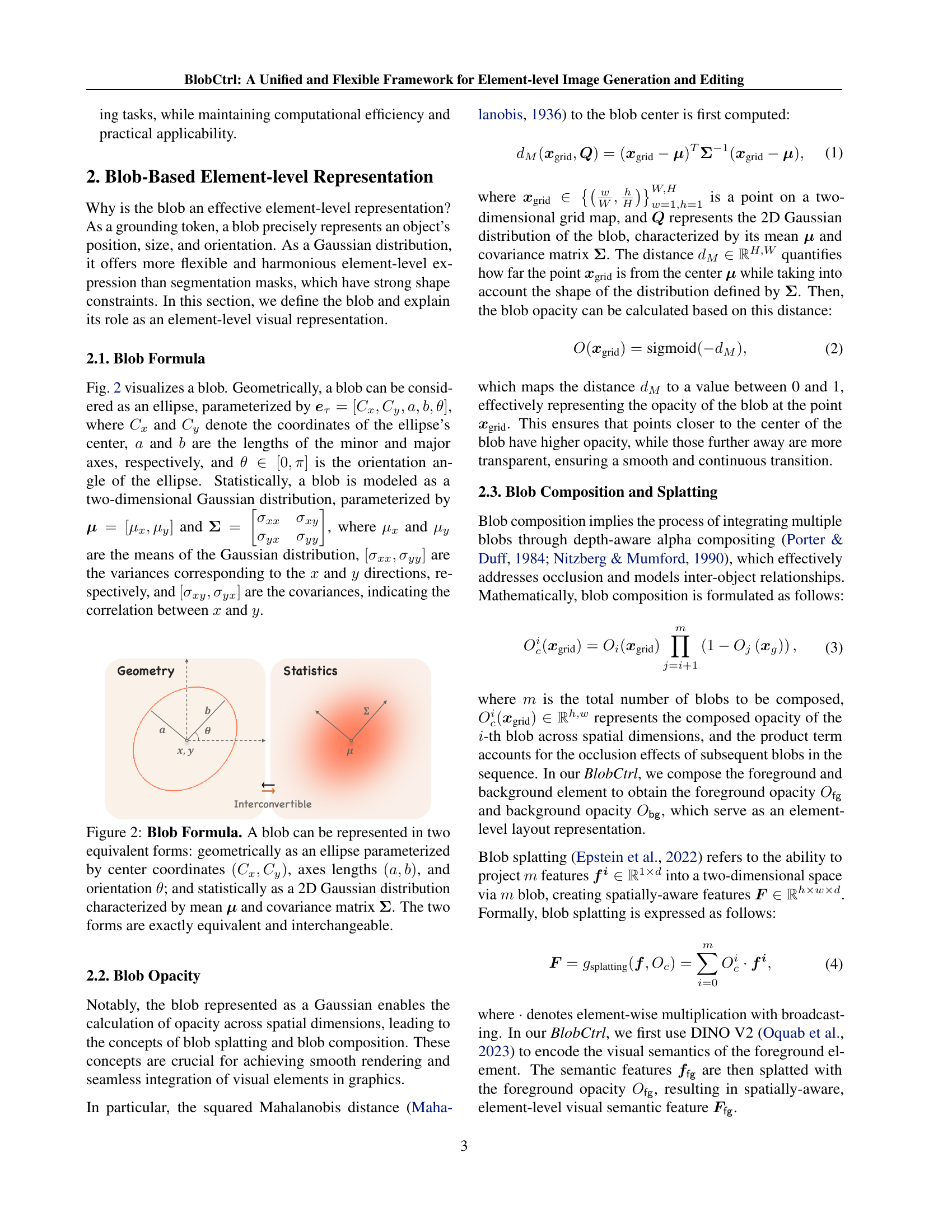
🔼 Figure 2 illustrates the dual representation of a blob, a fundamental element in the BlobCtrl framework. Geometrically, a blob is depicted as an ellipse, defined by its center coordinates (Cx, Cy), the lengths of its minor and major axes (a, b), and its orientation (θ). Simultaneously, it’s statistically modeled as a two-dimensional Gaussian distribution, parameterized by its mean (μ) and covariance matrix (Σ). This dual representation highlights the equivalence and interchangeability between the geometric and statistical interpretations of a blob, illustrating how BlobCtrl seamlessly integrates geometric intuition with statistical rigor in its approach to element-level image manipulation.
read the caption
Figure 2: Blob Formula. A blob can be represented in two equivalent forms: geometrically as an ellipse parameterized by center coordinates (Cx,Cy)subscript𝐶𝑥subscript𝐶𝑦(C_{x},C_{y})( italic_C start_POSTSUBSCRIPT italic_x end_POSTSUBSCRIPT , italic_C start_POSTSUBSCRIPT italic_y end_POSTSUBSCRIPT ), axes lengths (a,b)𝑎𝑏(a,b)( italic_a , italic_b ), and orientation θ𝜃\thetaitalic_θ; and statistically as a 2D Gaussian distribution characterized by mean 𝝁𝝁\bm{\mu}bold_italic_μ and covariance matrix 𝚺𝚺\bm{\Sigma}bold_Σ. The two forms are exactly equivalent and interchangeable.

🔼 BlobCtrl uses a dual-branch diffusion model for element-level image manipulation. The foreground branch focuses on preserving element identity using blob representations, while the background branch maintains scene context and harmonizes the elements. Both branches receive noisy latent inputs and reference conditions. Self-supervised training involves stochastically generating element positions and optimizing for target reconstruction. Feature fusion between branches ensures precise control while maintaining visual coherence.
read the caption
Figure 3: Overview of BlobCtrl. Our framework consists of: (1) A dual-branch architecture with a foreground branch for element identity encoding and a background branch for scene context preservation and harmonization. Both branches use concatenated inputs of noisy latents and reference conditions (Sec. 3.1). (2) A self-supervised training paradigm for element-level manipulation through stochastic position generation and target reconstruction optimization. Through feature fusion between branches, our framework achieves precise control over elements while maintaining visual coherence.

🔼 Figure 4 presents a qualitative comparison of element-level image manipulation results produced by four different methods: BlobCtrl, Anydoor, GliGen, and MagicFix. Each method is evaluated on five fundamental operations: composition, movement, resizing, replacement, and removal. The figure visually demonstrates that while other methods struggle with identity preservation (Anydoor, GliGen), visual harmonization (MagicFix), or both, BlobCtrl consistently achieves superior results. All five operations are shown for each method to illustrate BlobCtrl’s strengths. It’s recommended to zoom in to fully appreciate the details in the source images and the precise element-level manipulations performed.
read the caption
Figure 4: Visual comparison of element-level manipulation capabilities across different methods. We evaluate five fundamental operations: composition, movement, resizing, replacement and removal. Anydoor (Chen et al., 2023) struggles with precise identity preservation, GliGen (Li et al., 2023) fails to maintain any identity information, and Magic Fixup (Chen et al., 2023) produces results with poor visual harmonization. In contrast, BlobCtrl achieves superior results across all operations while maintaining both identity preservation and visual harmony. We recommend zooming in to examine the source images and element-level manipulation instructions in detail.

🔼 Figure 5 illustrates how BlobCtrl’s dual-branch architecture allows for flexible control over the balance between generating diverse outputs and preserving the original appearance of elements. This control is achieved in two ways: adjusting the control timestep interval which influences the level of noise reduction at each step of the diffusion process, and changing the fusion strength (ω) which modulates how much information from the foreground and background branches are combined. Feature dropout mechanisms, further enhancing controllability by randomly dropping features during the training process, are also mentioned, though not visually depicted.
read the caption
Figure 5: Flexible Control. Our dual-branch fusion mechanism enables flexible control over the trade-off between diversity and appearance preservation by adjusting the control timestep interval and fusion strength ω𝜔\omegaitalic_ω. Additionally, the feature dropout mechanisms provide more flexible interfaces for controlling the generation process.

🔼 Figure 6 demonstrates the impact of the Identity Preservation Score Function on model training and performance. The ablation study compares training with and without this function. The left panel shows the lower training loss achieved using the Identity Preservation Score Function, indicating faster convergence. The right panel provides a visualization of the denoising process for scaling a deer image, comparing outputs with and without the function. In the visualization, it’s clear that the Identity Preservation Score Function helps to maintain the foreground element’s identity (the deer) while better integrating it into the background, effectively decoupling foreground and background during element-level manipulation.
read the caption
Figure 6: Ablation of Identity Preservation Score Function. Training loss and denoising visualization for scaling a deer, demonstrating how Identity Preservation Score Function enables faster convergence and effective foreground-background decoupling during element-level manipulation.

🔼 BlobBench is a comprehensive benchmark dataset consisting of 100 images, each annotated with ellipse parameters, foreground masks, and detailed text descriptions. The images cover a wide range of scenarios and element-level operations, including composition, movement, resizing, removal, and replacement. The dataset is designed to provide a thorough evaluation of element-level manipulation capabilities of models.
read the caption
Figure 7: Overview of the BlobBench.
More on tables
| Method | PSNR | SSIM | LPIPS | FID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anydoor (Chen et al., 2023) | 32.0631 | 0.7424 | 0.2394 | 145.2546 |
| GliGen (Li et al., 2023) | 27.923 | 0.2414 | 0.6963 | 307.8219 |
| MagicFix (Chen et al., 2023) | 30.3958 | 0.7415 | 0.2277 | 194.0154 |
| BlobCtrl (Ours) | 32.1571 | 0.7507 | 0.2196 | 102.8094 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of BlobCtrl’s image generation quality against three state-of-the-art methods using standard metrics: PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, and FID. Higher PSNR and SSIM scores indicate better fidelity to the original image, while a lower LPIPS score suggests better perceptual similarity. A lower FID score signifies that the generated images are closer in distribution to real images. The results demonstrate that BlobCtrl significantly outperforms existing methods across all metrics, highlighting its superior image generation quality and reduced artifacts.
read the caption
Table 2: Comparison of image generation quality using standard metrics. Our method achieves superior performance across all metrics, demonstrating better generation quality and fewer artifacts.
| Method | Fidelity | Layout | Harmony |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anydoor (Chen et al., 2023) | 82.5% | 81.7% | 78.1% |
| GliGen (Li et al., 2023) | 51.2% | 68.1% | 80.3% |
| MagicFix (Chen et al., 2023) | 70.2% | 73.1% | 49.4% |
| BlobCtrl (Ours) | 87.2% | 86.5% | 82.1% |
🔼 This table presents the results of a human evaluation comparing the performance of BlobCtrl against three state-of-the-art methods in terms of fidelity, layout, and harmony. Human evaluators rated the generated images on a scale of 1-5 for each of these three aspects, with higher scores indicating better perceptual quality. The results demonstrate that BlobCtrl consistently outperforms existing methods, indicating superior perceptual quality across all evaluation criteria.
read the caption
Table 3: Human evaluation results comparing our method with baselines. Our method achieves consistently higher human preference scores across all metrics, demonstrating superior perceptual quality.
Full paper#