TL;DR#
Generating ultra-high-resolution (4K) images using diffusion models is challenging due to high computational costs. Current models also neglect fine details and textures, and there’s a lack of suitable datasets for training and evaluation. Thus the paper addresses the above issues in this research.
This paper presents a novel framework which is called Diffusion-4K for synthesizing 4K images. It includes Aesthetic-4K which is a high-quality 4K image dataset. To evaluate the fine details, it also introduces GLCM Score and Compression Ratio metrics, combined with existing measures like FID. Furthermore, it introduces a wavelet-based fine-tuning approach for photorealistic image training. As a result, the approach achieves impressive performance and has high text prompt adherence.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper introduces a novel framework, a new benchmark dataset and metrics for 4K image synthesis. It helps push forward high-resolution image generation and opens new research directions. The techniques employed in this paper are highly valuable for other researches in related fields and provides valuable new insights.
Visual Insights#

🔼 This figure showcases example images generated using the Diffusion-4K model. The images highlight the model’s ability to synthesize ultra-high-resolution (4K) images with exceptional detail and realism, emphasizing the fine textures and intricate features that are often lost in lower-resolution image generation methods.
read the caption
Figure 1: Example results synthesized by our Diffusion-4K, emphasizing exceptional fine details in generated 4K images.
| Metric | GLCM Score | Compression Ratio | MUSIQ | MANIQA |
| SRCC | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.36 | 0.20 |
| PLCC | 0.77 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.26 |
🔼 This table presents the correlation coefficients between the proposed metrics (GLCM Score and Compression Ratio) and human evaluations of image quality. It shows the Spearman Rank-order Correlation Coefficient (SRCC) and Pearson Linear Correlation Coefficient (PLCC) calculated by comparing the metric scores with human ratings for the same patches of images. Additionally, it includes correlations with existing image quality assessment metrics (MUSIQ and MANIQA) for comparison.
read the caption
Table 1: Correlation with human evaluation.
In-depth insights#
Aesthetic-4K#
The research introduces Aesthetic-4K, a novel and comprehensive benchmark for evaluating ultra-high-resolution image synthesis, explicitly targeting 4K images. Addressing the gap in publicly available 4K datasets, they curated a dataset with high-quality images and precise captions generated by GPT-4O. Design principles focus on human-centric perceptual cognition, moving beyond holistic measures, emphasizing fine details. Metrics like GLCM Score and Compression Ratio, combined with FID, Aesthetics, and CLIPScore, facilitate a more comprehensive assessment. This benchmark design ensures a direct relation to human decision-making and cognitive abilities. This approach makes sure that generated images are relevant, visually appealing, and faithful to the original prompt. The dataset includes both training (Aesthetic-Train) and evaluation sets (Aesthetic-Eval) with specific resolution and content details.
Wavelet Tuning#
Wavelet tuning can refine image details by emphasizing high-frequency components while preserving overall structure. It decomposes images into low and high-frequency bands, allowing targeted adjustments. The use of wavelet transform enables the model to refine details (high-frequency) while preserving the overall structure (low-frequency). WLF enhances the model’s capacity to generate fine details, also ensures that the changes don’t disrupt the underlying patterns, making the fine-tuning process both efficient and precise.
4K Generation#
The research paper highlights the challenges and advancements in 4K image generation, a domain gaining traction due to its applications in entertainment and industry. It acknowledges that while diffusion models have shown promise, generating high-resolution images like 4K directly is computationally demanding. Therefore, novel methods like Diffusion-4K are crucial for enhancing both efficiency and quality. The study underscores the limitations of existing benchmarks, which often evaluate at lower resolutions, neglecting the fine details that characterize 4K images. Thus, the paper introduces a new benchmark, Aesthetic-4K, designed to comprehensively assess image synthesis quality at ultra-high resolutions, factoring in human perceptual cognition through metrics like GLCM Score and Compression Ratio. The wavelet-based fine-tuning is pivotal to infuse high-frequency details while retaining low-frequency approximation for optimal image synthesis. This approach aims to address the gap in generating photorealistic 4K images, especially when integrated with powerful large-scale diffusion models.
GLCM & Details#
Analyzing GLCM, or Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix, involves deep examination of image texture and its fine details. It serves as a mathematical method of examining how often pairs of pixel with specific values and in a defined spatial relationship occur in an image. GLCM extracts statistical measures that characterize texture, contrast, homogeneity, and correlation. This approach facilitates in-depth analysis, enabling differentiation between textures that might appear similar to human perception. When examining fine details, it allows for in-depth evaluation of the texture and structural characteristics of high-resolution images; the GLCM score and compression ratio serve as significant complements to human perceptual cognition in 4K image synthesis.
Diffusion-4K#
Diffusion-4K is presented as a novel framework designed for direct ultra-high-resolution image synthesis, utilizing latent diffusion models. A key aspect is the Aesthetic-4K Benchmark, addressing the lack of publicly available 4K image synthesis datasets. This benchmark includes a curated, high-quality dataset of ultra-high-resolution images accompanied by precise captions generated by GPT-4O. To evaluate the fine details present in 4K images, new metrics such as GLCM Score and Compression Ratio were introduced, complementing holistic measures like FID and CLIPScore. A wavelet-based fine-tuning approach is proposed to optimize the generation of fine details in the images. Diffusion-4K’s capabilities are validated through experiments, showcasing the effectiveness of the method in synthesizing highly detailed 4K images. Diffusion-4K achieves better image synthesis and text prompt adherence, when used with modern large-scale diffusion models (e.g., SD3-2B and Flux-12B).
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 Figure 2 presents a correlation analysis between the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) Score and the Compression Ratio, metrics designed to evaluate fine details in images, specifically at 4K resolution. The GLCM score measures textural richness by analyzing the spatial distribution of gray levels in local image patches, while the compression ratio assesses the preservation of detail by measuring how well the image compresses using lossy compression (JPEG). The results indicate a strong positive correlation between higher GLCM scores (indicating richer texture) and lower compression ratios (indicating better preservation of fine details), showing strong alignment with human perception of image quality. Human observers tend to rate images with high textural detail and well-preserved fine details more favorably. The analysis is done at the patch level to show the alignment at local feature level.
read the caption
Figure 2: Analysis of GLCM Score↑↑\uparrow↑ / Compression Ratio↓↓\downarrow↓. Our indicators demonstrate strong alignment with human-centric perceptual cognition at the level of local patches.

🔼 This figure displays examples of image-text pairs from the Aesthetic-4K training dataset. The images are high-quality, ultra-high-resolution (4K) images, and the accompanying text captions were generated using GPT-40. This showcases the high standard of the dataset used to train the Diffusion-4K model, emphasizing both visual quality and precise textual descriptions for improved model performance.
read the caption
(a) Image-text samples in training set.

🔼 This figure shows example image-text pairs from the evaluation subset of the Aesthetic-4K dataset. These examples illustrate the high-quality images and precise text prompts characteristic of this dataset, which is specifically designed for evaluating ultra-high-resolution (4K) image synthesis models. The images demonstrate a variety of subjects and visual styles, showcasing the diversity of the dataset.
read the caption
(b) Image-text samples in evaluation set.

🔼 Figure 3 presents examples from the Aesthetic-4K dataset. The dataset contains high-resolution images (4K) paired with detailed captions generated by the GPT-40 language model. These image-caption pairs are carefully selected to represent a high standard of visual aesthetics and showcase fine details. The figure aims to illustrate the quality and precision of the data within the Aesthetic-4K benchmark, which is designed for evaluating and training ultra-high-resolution image synthesis models.
read the caption
Figure 3: Illustration of image-text samples in the Aesthetic-4K dataset, which includes high-quality images and precise text prompts generated by GPT-4o, distinguished by high aesthetics and fine details.

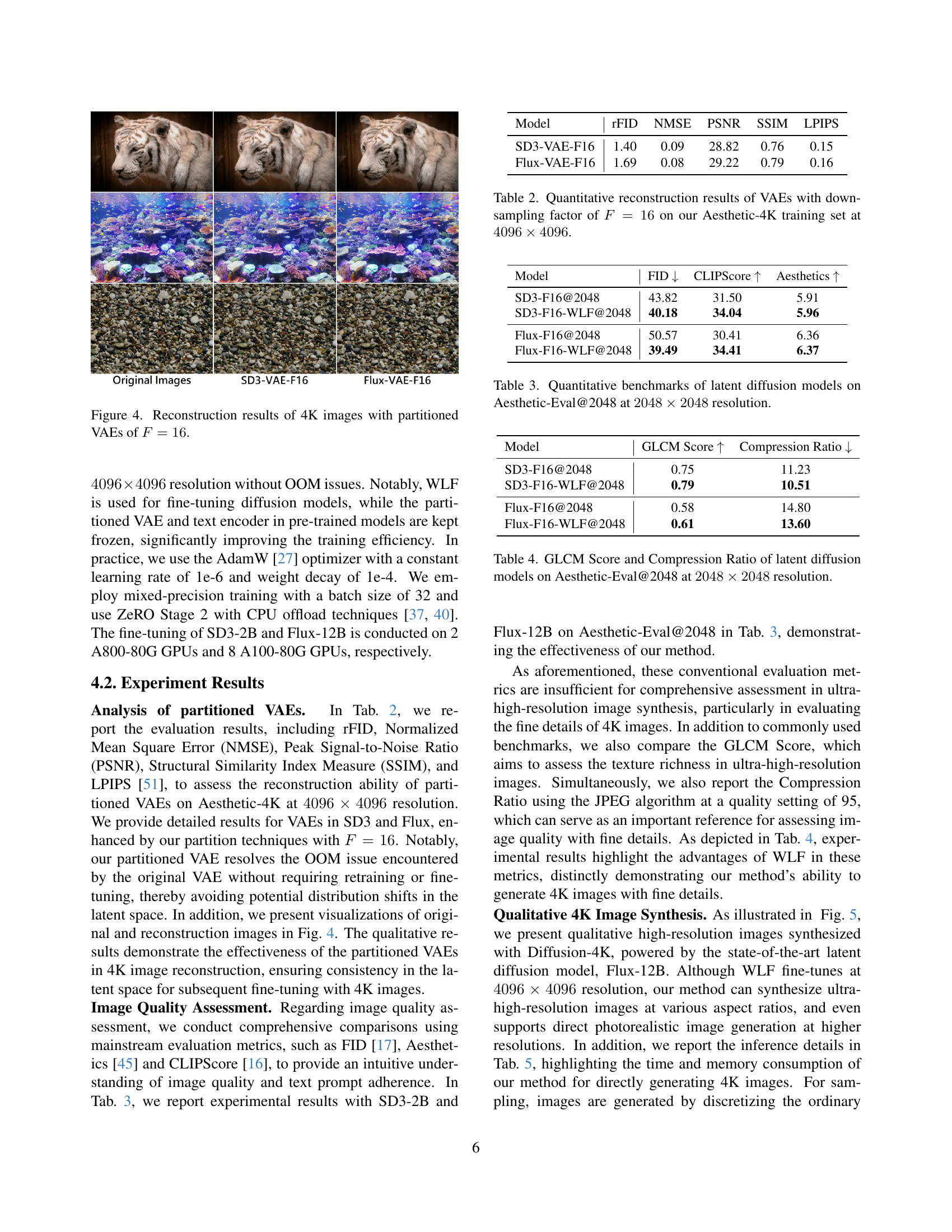
🔼 This figure displays the reconstruction results of 4K images using partitioned Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) with a downsampling factor of F=16. The partitioned VAE approach is a key component of the Diffusion-4K framework, designed to address the computational challenges of handling ultra-high-resolution images. By partitioning the VAE, the model efficiently manages the memory requirements during training and inference. The figure visually demonstrates the quality of reconstruction achieved by the partitioned VAEs, showcasing the effectiveness of this method for ultra-high resolution image processing.
read the caption
Figure 4: Reconstruction results of 4K images with partitioned VAEs of F=16𝐹16F=16italic_F = 16.

🔼 This figure showcases example images generated by the Diffusion-4K model, demonstrating its ability to synthesize high-quality, photorealistic 4K images from various text prompts. The prompts used to generate the images are sourced from the Sora [30] dataset, showcasing the model’s ability to translate text descriptions into detailed and visually appealing images. Each image depicts a diverse range of scenes, subjects, and artistic styles, highlighting the model’s versatility and capacity to generate high-resolution images across multiple categories.
read the caption
Figure 5: Qualitative 4K images synthesis of Diffusion-4K. Prompts are from Sora [30].

🔼 Figure 6 is a bar chart comparing human preferences against those of GPT-40 for various aspects of image quality. The chart displays the percentage of times each model preferred different aspects of four different generated images: Visual Aesthetics, Prompt Adherence, Fine Details, and Human Preference. This allows a comparison to show how well the AI model’s preferences align with human preferences for these image qualities in the context of 4K image generation.
read the caption
Figure 6: Human and GPT-4o preference evaluation.

🔼 This figure compares the image generation results of Diffusion-4K and PixArt-Σ using the same prompts. The left side shows images generated by PixArt-Σ, while the right side displays images from Diffusion-4K. Yellow highlighted patches in the Diffusion-4K images indicate areas with superior fine detail compared to the red-highlighted areas in PixArt-Σ images, demonstrating Diffusion-4K’s improved performance in generating high-resolution images with intricate details.
read the caption
Figure 7: We present comparisons with PixArt-ΣΣ\Sigmaroman_Σ [9] using identical prompts, with images from PixArt-ΣΣ\Sigmaroman_Σ displayed on the left and those synthesized by our Diffusion-4K shown on the right. Our approach demonstrates significant superiority over PixArt-ΣΣ\Sigmaroman_Σ in fine details, as evidenced by the yellow patches vs. the red patches.

🔼 This figure displays a comparison of image generation results between the Diffusion-4K model and the Sana [49] model. Each pair of images shows the same prompt rendered by both models, allowing for a visual assessment of the differences in image quality, detail, and adherence to the prompt. It highlights the relative strengths of Diffusion-4K in producing ultra-high-resolution images with fine details.
read the caption
Figure 8: Comparisons with Sana [49].

🔼 This figure displays an ablation study comparing the performance of the Wavelet-based Fine-tuning (WLF) method. It visually demonstrates the effect of WLF on generating high-resolution images by showing samples of images generated with and without WLF. This allows for a direct comparison and highlights the improvements achieved through the use of WLF in terms of image detail and quality.
read the caption
Figure 9: Ablation study on WLF.

🔼 This figure showcases several high-quality images generated by the Diffusion-4K model. Each image demonstrates the model’s ability to synthesize diverse scenes with high-fidelity details and accurate representation of textures, including nature scenes, cityscapes, animals, and fantasy elements. The images highlight the model’s proficiency in capturing realistic light and shadows, fine textures, and overall photorealism at 4K resolution.
read the caption
Figure 10: High-quality images synthesized by our Diffusion-4k.

🔼 This figure showcases the versatility of Diffusion-4K in generating high-resolution images at various aspect ratios and with different random seeds. The results demonstrate the model’s ability to maintain image quality and coherence across diverse settings, highlighting its robustness and adaptability.
read the caption
Figure 11: Synthesized images with different aspect ratios and random seeds.

🔼 Figure 12 displays examples of images generated by the Diffusion-4K model where the text prompts included intentionally misspelled words. This showcases the model’s ability to generate coherent images even when the input text contains errors, highlighting its robustness and potential for creative applications.
read the caption
Figure 12: Synthesized images with spelled texts.

🔼 This figure shows the distribution of image heights and widths within the Aesthetic-4K dataset. Two histograms are presented, one for height and one for width. Each histogram displays the frequency of images at different height and width values, giving insight into the size and aspect ratio variations present in the dataset. This is important for understanding the characteristics of the dataset and its suitability for training and evaluating ultra-high-resolution image synthesis models.
read the caption
Figure 13: Histograms of image height and width in Aesthetic-4K.
More on tables
| Model | rFID | NMSE | PSNR | SSIM | LPIPS |
| SD3-VAE-F16 | 1.40 | 0.09 | 28.82 | 0.76 | 0.15 |
| Flux-VAE-F16 | 1.69 | 0.08 | 29.22 | 0.79 | 0.16 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of the performance of two different Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) used for image reconstruction. The VAEs, with a downsampling factor of F=16, were evaluated on the Aesthetic-4K dataset at a resolution of 4096x4096 pixels. The evaluation metrics used include the Fréchet Inception Distance (rFID), Normalized Mean Square Error (NMSE), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS). The results show the reconstruction quality achieved by each VAE on the high-resolution images.
read the caption
Table 2: Quantitative reconstruction results of VAEs with down-sampling factor of F=16𝐹16F=16italic_F = 16 on our Aesthetic-4K training set at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096.
| Model | FID | CLIPScore | Aesthetics |
| SD3-F16@2048 | 43.82 | 31.50 | 5.91 |
| SD3-F16-WLF@2048 | 40.18 | 34.04 | 5.96 |
| Flux-F16@2048 | 50.57 | 30.41 | 6.36 |
| Flux-F16-WLF@2048 | 39.49 | 34.41 | 6.37 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of different latent diffusion models’ performance on the Aesthetic-Eval@2048 dataset. The evaluation is conducted at a resolution of 2048x2048 pixels. The metrics used to assess performance are the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID), CLIPScore, and Aesthetics scores. Higher scores for CLIPScore and Aesthetics generally indicate better image quality and alignment with the text prompt.
read the caption
Table 3: Quantitative benchmarks of latent diffusion models on Aesthetic-Eval@2048 at 2048×2048204820482048\times 20482048 × 2048 resolution.
| Model | GLCM Score | Compression Ratio |
| SD3-F16@2048 | 0.75 | 11.23 |
| SD3-F16-WLF@2048 | 0.79 | 10.51 |
| Flux-F16@2048 | 0.58 | 14.80 |
| Flux-F16-WLF@2048 | 0.61 | 13.60 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of different latent diffusion models on the Aesthetic-Eval@2048 benchmark dataset. Specifically, it shows the GLCM (Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix) Score and Compression Ratio achieved by each model for images generated at a resolution of 2048x2048. The GLCM Score measures the richness of texture details in the images, while the Compression Ratio indicates the level of detail preserved after compression. Higher GLCM scores suggest better texture detail, and lower compression ratios indicate more detail preservation. The results help evaluate the models’ ability to generate high-quality images with fine details at the specified resolution.
read the caption
Table 4: GLCM Score and Compression Ratio of latent diffusion models on Aesthetic-Eval@2048 at 2048×2048204820482048\times 20482048 × 2048 resolution.
| Model | Memory | Time (s/step) |
| SD3-F8@4096 | OOM | - |
| SD3-F16-WLF@4096 | 31.3GB | 1.16 |
| SD3-F16-WLF@4096 (CPU offload) | 16.1GB | 1.22 |
| Flux-F8@4096 | OOM | - |
| Flux-F16-WLF@4096 | 50.4 GB | 2.42 |
| Flux-F16-WLF@4096 (CPU offload) | 26.9 GB | 3.16 |
🔼 This table presents a quantitative analysis of the computational resources required for direct image synthesis at an ultra-high resolution of 4096 x 4096 pixels. It shows the memory consumption (in GB) and inference speed (in seconds per step) for different models and configurations. The experiments were conducted using a single NVIDIA A100 GPU with BF16 precision for efficient computation. The results demonstrate the trade-off between model complexity, memory usage, and processing speed during high-resolution image generation.
read the caption
Table 5: Memory consumption and inference speed of direct image synthesis at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096. The result is tested on one A100 GPU with BF16 Precision.
| Captions | Model | CLIPScore | Aesthetics |
| LAION-5B | SD3-F16@4096 | 29.37 | 5.90 |
| GPT-4o | SD3-F16@4096 | 33.12 | 5.97 |
| LAION-5B | Flux-F16@4096 | 29.12 | 6.02 |
| GPT-4o | Flux-F16@4096 | 33.67 | 6.11 |
🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study that investigates the impact of using different image captions on the quality of images generated by two different latent diffusion models (SD3 and Flux). Specifically, it compares the performance of the models when trained with captions generated by GPT-40 (a large language model) versus captions from the LAION-5B dataset. The metrics used to assess image quality are CLIPScore (a measure of how well the generated image matches the text prompt), and Aesthetics (a measure of the aesthetic quality of the image). The experiment is conducted on the Aesthetic-Eval@4096 dataset, which consists of high-resolution (4096x4096) images.
read the caption
Table 6: Ablation study on quality of image captions on Aesthetic-Eval@4096 at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096.
| Model | CLIPScore | Aesthetics |
| SD3-F16@4096 | 33.12 | 5.97 |
| SD3-F16-finetune@4096 | 34.14 | 5.99 |
| SD3-F16-WLF@4096 | 34.40 | 6.07 |
🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study that investigates the impact of the proposed Wavelet-based Fine-tuning (WLF) method on the performance of the Stable Diffusion 3 (SD3) model. The study focuses on the Aesthetic-Eval@4096 dataset, which contains high-resolution (4096x4096) images. The table compares the CLIPScore and Aesthetics scores achieved by three different versions of the SD3 model: the standard SD3 model trained at 4096x4096 resolution, a fine-tuned version of SD3 without WLF, and a fine-tuned version of SD3 with the WLF method. The comparison helps to quantify the improvement in image quality and alignment with text prompts brought by incorporating the WLF method in fine-tuning the SD3 model for 4K image generation.
read the caption
Table 7: Ablation on CLIPScore and Aesthetics of SD3 on Aesthetic-Eval@4096 at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096. SD3-F16-finetune@4096 represents fine-tuning without WLF.
| Model | GLCM Score | Compression Ratio |
| SD3-F16@4096 | 0.73 | 11.97 |
| SD3-F16-finetune@4096 | 0.74 | 11.41 |
| SD3-F16-WLF@4096 | 0.77 | 10.50 |
🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study conducted to evaluate the impact of the Wavelet-based Fine-tuning (WLF) method on the performance of the Stable Diffusion 3 (SD3) model in generating ultra-high-resolution (4096x4096 pixels) images. The study uses the Aesthetic-Eval@4096 dataset for evaluation. The table compares the performance of SD3 fine-tuned with WLF against SD3 fine-tuned without WLF (denoted as SD3-F16-finetune@4096). The comparison is based on two key metrics: the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) Score, which measures the richness of texture details; and the Compression Ratio, which assesses the preservation of image details after compression. Higher GLCM scores indicate richer texture, while lower compression ratios suggest better detail preservation. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the WLF method in enhancing the quality of generated 4K images.
read the caption
Table 8: Ablation on GLCM Score and Compression Ratio of SD3 on Aesthetic-Eval@4096 at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096. SD3-F16-finetune@4096 denotes fine-tuning without WLF.
| Dataset | Median height | Median width | Average height | Average width |
| PixArt-30k | 1615 | 1801 | 2531 | 2656 |
| Aesthetic-Train | 4128 | 4640 | 4578 | 4838 |
| Aesthetic-Eval@2048 | 2983 | 3613 | 3143 | 3746 |
| Aesthetic-Eval@4096 | 4912 | 6449 | 5269 | 6420 |
🔼 This table compares the key characteristics of the Aesthetic-4K dataset and the PixArt-30k dataset, focusing on image dimensions. It shows the median height and width, as well as the average height and width of images in both datasets. This comparison highlights the significant increase in resolution offered by the Aesthetic-4K dataset, demonstrating its suitability for ultra-high-resolution image synthesis research.
read the caption
Table 9: Statistical comparisons of Aesthetic-4K and PixArt-30k.
| Model | SD3-2B-WLF | Flux-12B-WLF |
| Training steps | 20K | 20K |
| Throughput (images/s) | 0.59 | 1.39 |
🔼 This table details the training hyperparameters and performance metrics for two large-scale diffusion models, Stable Diffusion 3 (SD3-2B) and Flux-12B, when fine-tuned using the Wavelet-based Fine-tuning (WLF) method at an ultra-high resolution of 4096x4096 pixels. Specifically, it shows the number of training steps conducted and the training throughput (images processed per second) achieved for each model during the fine-tuning process.
read the caption
Table 10: Training details of SD3-2B and Flux-12B with WLF at 4096×4096409640964096\times 40964096 × 4096.
| Tasks | Prompts |
| Image Caption | {“text”: “Directly describe with brevity and as brief as possible the scene or characters without any introductory phrase like ‘This image shows’, ‘In the scene’, ‘This image depicts’ or similar phrases. Just start describing the scene please.” } |
| Preference Study | {“system”: “As an AI visual assistant, you are analyzing two specific images. When presented with a specific caption, it is required to evaluate visual aesthetics, prompt coherence and fine details.”, “text”: “The caption for the two images is: prompt. Please answer the following questions: 1. Visual Aesthetics: Given the prompt, which image is of higher-quality and aesthetically more pleasing? 2. Prompt Adherence: Which image looks more representative to the text shown above and faithfully follows it? 3. Fine Details: Which image more accurately represents the fine visual details? Focus on clarity, sharpness, and texture. Assess the fidelity of fine elements such as edges, patterns, and nuances in color. The more precise representation of these details is preferred! Ignore other aspects. Please respond me strictly in the following format: 1. Visual Aesthetics: the first image is better or the second image is better. The reason is give your reason here. 2. Prompt Adherence: the first image is better or the second image is better. The reason is give your reason here. 3. Fine Details: the first image is better or the second image is better. The reason is give your reason here. "} |
🔼 This table details the prompts used in a user study to evaluate the performance of the Diffusion-4K model. It outlines the instructions given to participants for describing images (image caption task) and for comparing pairs of images based on visual aesthetics, adherence to the prompt, and the level of fine detail present (preference study task). The prompts are designed to elicit specific responses from participants, focusing on different aspects of image quality. The table shows the separate instructions for the image captioning and preference study tasks and then presents the specific prompts used within the two tasks.
read the caption
Table 11: Designed prompts for image caption and preference study with GPT-4o.
Full paper#