↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Homepage ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Current text-to-image personalization techniques, such as Textual Inversion and DreamBooth, struggle to balance identity preservation and text alignment. Textual Inversion overfits the concept, while DreamBooth overlooks it. This stems from the incorrect learning of embedding alignment.
AttnDreamBooth tackles this by separately learning embedding alignment, attention map, and subject identity across different training stages. It uses a cross-attention map regularization term to improve attention map learning. The results show significant improvements in identity preservation and text alignment compared to baseline methods, enabling high-quality personalized image generation with complex prompts.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is crucial for researchers working on text-to-image personalization because it directly addresses the limitations of existing methods. It offers a novel, three-stage approach that significantly improves both identity preservation and text alignment, which are major challenges in the field. The proposed method and findings open up new avenues for research, including improving training efficiency and exploring other regularization techniques for enhanced personalization results.
Visual Insights#

This figure displays various example prompts and their corresponding generated images using the AttnDreamBooth method. The prompts are complex and combine multiple descriptive elements, demonstrating the model’s ability to create personalized images aligned with detailed textual instructions. Each row shows an example prompt, followed by several generated images showing successful text-image alignment and identity preservation of a learned concept (sloth).
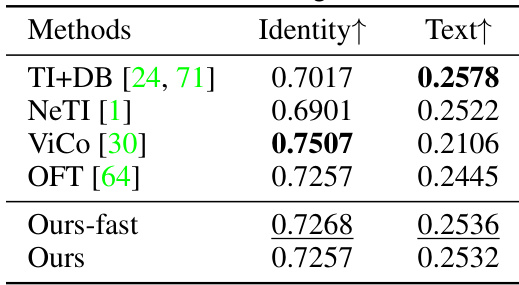
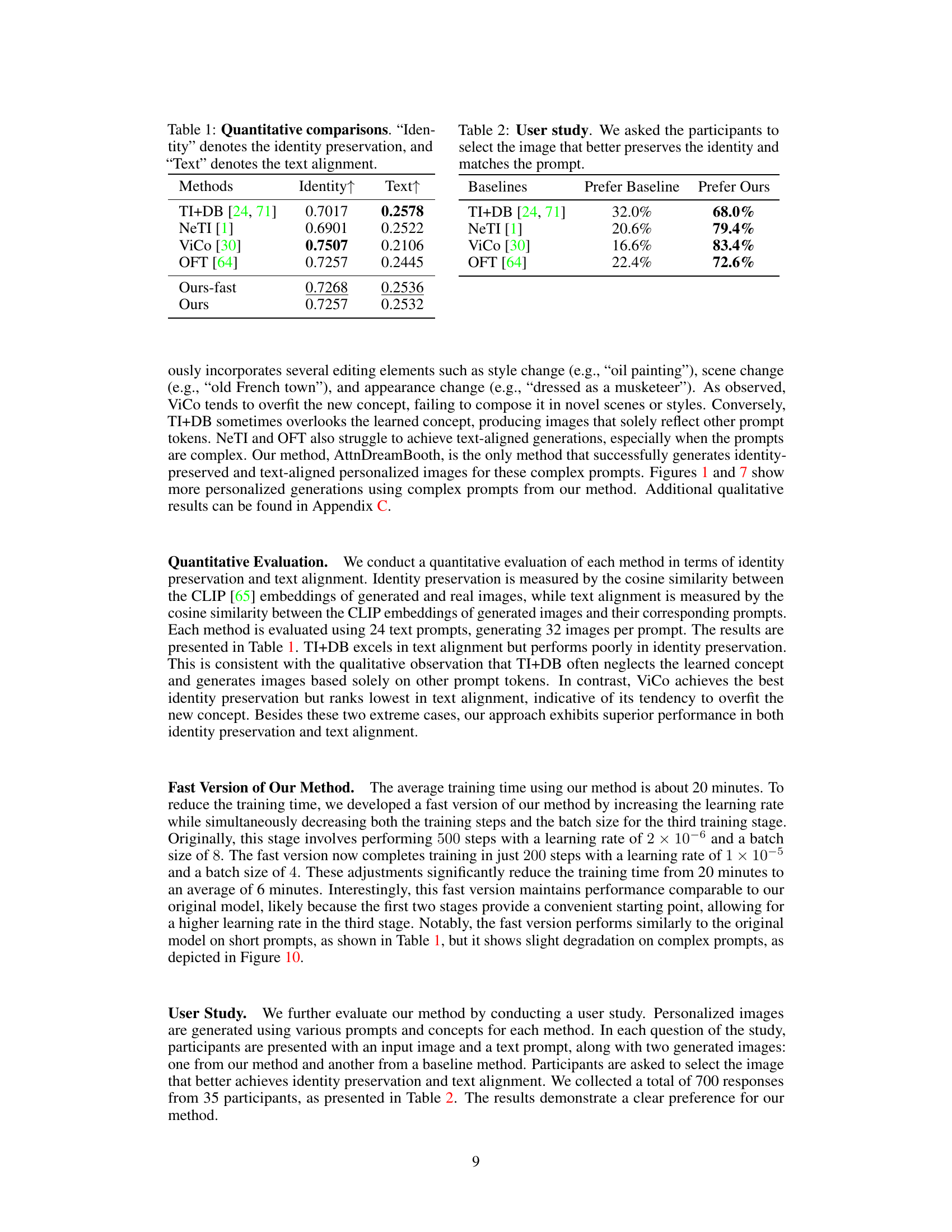
This table presents a quantitative comparison of different methods for text-to-image generation, specifically focusing on identity preservation and text alignment. The methods are compared using two metrics: ‘Identity’, which represents how well the generated image retains the identity of the target concept, and ‘Text’, which measures how well the generated image aligns with the text prompt. Higher values indicate better performance. The table shows that while some methods excel in one area, AttnDreamBooth achieves a balance between both metrics.
In-depth insights#
AttnDreamBooth#
AttnDreamBooth represents a novel approach to personalized text-to-image generation, addressing limitations of existing methods like Textual Inversion and DreamBooth. AttnDreamBooth excels by decoupling the learning process into three stages: first, optimizing embedding alignment to prevent overfitting; second, refining the attention map via cross-attention layer fine-tuning; and third, capturing subject identity by fine-tuning the U-Net. A key innovation is the introduction of cross-attention map regularization, enforcing similarity between the new concept’s attention map and its super-category, thus enhancing text alignment. This multi-stage approach significantly improves identity preservation and text alignment, as demonstrated by qualitative and quantitative evaluations, showcasing its effectiveness even with complex prompts. The approach is further refined by a fast version, significantly reducing training time without major performance loss, making it more practical for real-world applications. Overall, AttnDreamBooth presents a compelling advancement in personalized image synthesis, offering a more balanced and robust solution than its predecessors.
Cross-Attention#
Cross-attention mechanisms are crucial in advanced text-to-image models, enabling the alignment of textual descriptions with visual features. AttnDreamBooth leverages cross-attention by separating its learning into stages: first optimizing textual embedding alignment, then refining the attention map, and finally capturing subject identity. This staged approach addresses limitations of prior methods like Textual Inversion (overfitting) and DreamBooth (overlooking concepts). A key innovation is the introduction of cross-attention map regularization, encouraging similarity between attention maps for the new concept and its super-category. This regularization enhances learning and improves both identity preservation and text alignment in generated images. The effectiveness of cross-attention is demonstrated through qualitative and quantitative evaluations, showing AttnDreamBooth’s superior performance compared to existing techniques in handling complex prompts and achieving accurate text-image correspondence. The results highlight the importance of carefully managing cross-attention for effective personalized text-to-image generation.
Multi-Stage Training#
Multi-stage training in the context of text-to-image generation models is a powerful technique that addresses the limitations of single-stage approaches. By breaking down the training process into distinct phases, each focusing on a specific aspect of the personalization task, multi-stage training improves the alignment between text and image, and preserves the identity of the subject. The typical approach involves an initial stage that focuses on embedding alignment, ensuring that the concept is correctly integrated into the model’s embedding space. A subsequent stage refines the attention map, ensuring that the model correctly focuses on the relevant features of the input image. Finally, the final stage involves fine-tuning the model’s U-Net to accurately capture the subject’s identity. This carefully staged process significantly enhances model performance over single-stage alternatives, allowing for complex prompt generation and improved accuracy. The sequential nature of the stages is crucial, as earlier stages set the foundation for the later stages to build upon. However, careful consideration must be given to the hyperparameters for each stage, including the learning rate and the number of training steps, to avoid issues such as overfitting. Further exploration of optimal stage configurations and regularization techniques is an important area for future research in this field.
Ablation Study#
An ablation study systematically removes components of a model to assess their individual contributions. In the context of the described personalized text-to-image generation model, this would involve training variations where specific modules (e.g., textual embedding optimization, cross-attention map refinement, or U-Net fine-tuning) are disabled. By comparing the performance of these reduced models against the full model, we gain insights into each component’s relative importance for achieving high-quality, text-aligned results. For example, removing the textual embedding optimization stage might lead to poor identity preservation, while removing the U-Net fine-tuning could result in insufficient subject detail. The ablation study’s key strength lies in isolating the impact of individual components, allowing for a precise understanding of the model’s architecture and paving the way for future improvements. A well-executed ablation study strengthens the overall argument by providing evidence for the model’s design choices and highlighting the critical components crucial for its success. Moreover, it provides a path to streamlining the model by identifying potentially redundant or less impactful parts.
Future Work#
Future research directions stemming from this AttnDreamBooth model could involve several key areas. Improving efficiency is paramount; the current three-stage training process, while effective, is time-consuming. Exploring alternative training strategies, perhaps incorporating techniques from other efficient personalization methods or leveraging pre-trained models more effectively, could significantly reduce training time and resource consumption. Another crucial area is enhanced controllability; while AttnDreamBooth improves text alignment, more precise control over various aspects of image generation, such as composition, layout, and style, is highly desirable. This might involve integrating additional conditioning signals or refining the attention mechanisms to achieve finer-grained manipulation. Addressing limitations related to complex prompts is also vital. While the model shows improvements over baselines, handling truly complex and ambiguous prompts remains a challenge; further investigation into prompt engineering and model architecture modifications could address these issues. Finally, extending the approach to video generation presents a compelling future direction, leveraging the strengths of AttnDreamBooth in creating consistent and text-aligned personalized video sequences.
More visual insights#
More on figures

This figure compares the results of Textual Inversion and DreamBooth methods for text-to-image personalization. It shows that Textual Inversion tends to focus excessively on the learned concept, neglecting other aspects of the prompt, while DreamBooth often overlooks the learned concept and prioritizes other elements. This is visualized using cross-attention maps, highlighting the misallocation of attention in Textual Inversion and the lack of attention to the learned concept in DreamBooth.
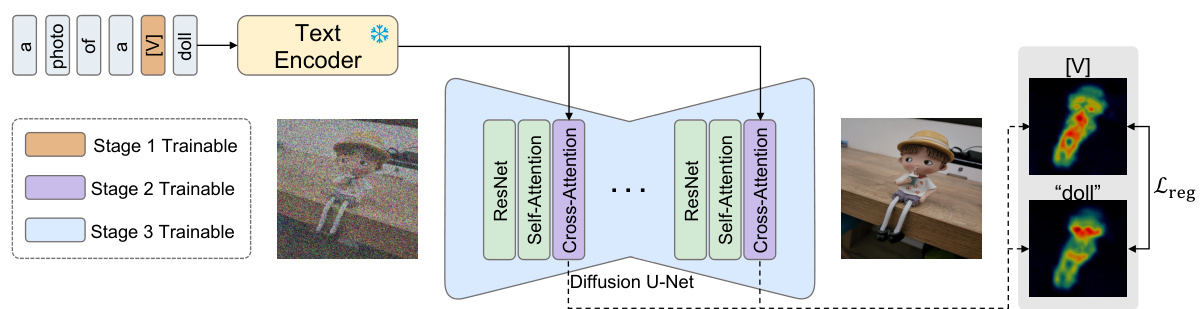
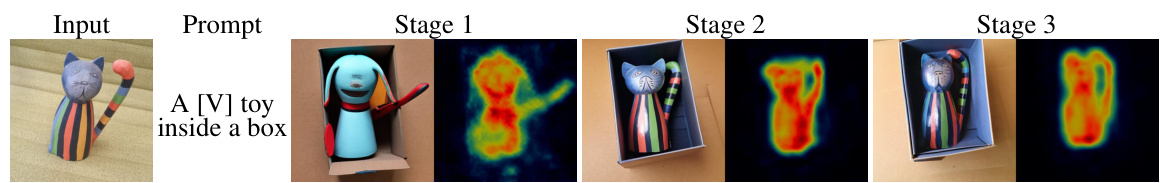
This figure illustrates the AttnDreamBooth method’s three training stages. Stage 1 focuses on aligning the new concept’s textual embedding with existing tokens. Stage 2 refines the attention map by fine-tuning cross-attention layers. Finally, Stage 3 captures the subject’s identity by fine-tuning the entire U-Net. A cross-attention map regularization term is introduced to enhance attention map learning.
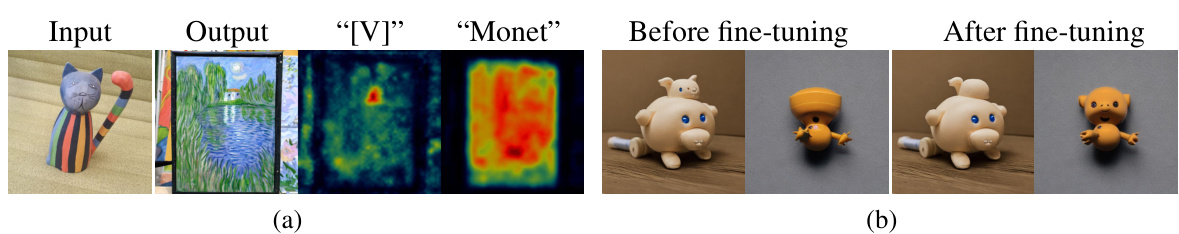
This figure analyzes the limitations of combining Textual Inversion (TI) and DreamBooth (DB), denoted as TI+DB, for text-to-image generation. Column (a) shows that TI+DB fails to incorporate the learned concept when used in a complex prompt, indicating a problem with concept integration. Column (b) demonstrates that the learned textual embedding remains largely unchanged after fine-tuning, suggesting insufficient learning of the embedding alignment for the new concept, which is a key factor in successful text-to-image personalization.
This figure shows the results of the AttnDreamBooth model after each of its three training stages. The images generated are shown alongside heatmaps (attention maps) highlighting which parts of the image correspond to the token [V], representing the new concept being learned. Stage 1 shows a rough alignment of the embedding, with a blurry attention map. Stage 2 demonstrates a refined attention map with improved identity. Stage 3 shows the final result, with an accurate representation of the concept’s identity.

This figure compares the image generation results of AttnDreamBooth against four other state-of-the-art methods (TI+DB, NeTI, ViCo, OFT) across various complex prompts. Each row shows the same prompt with images generated by each method. The images generated by AttnDreamBooth better reflect both the text description and the original concept image compared to other methods, demonstrating its superior performance in both text alignment and identity preservation.

This figure shows several example images generated by the AttnDreamBooth model to demonstrate its ability to generate diverse and high-quality personalized images from complex prompts. The images showcase different subjects (toys, furbies, bears) in various settings and styles, highlighting the model’s capacity for text-aligned personalization.

This figure shows the ablation study results of AttnDreamBooth. It presents a visual comparison of personalized image generation results when different components of the model (textual embedding optimization, cross-attention layer fine-tuning, U-Net fine-tuning, and cross-attention map regularization) are removed. The results demonstrate that all sub-modules are essential to achieve identity preservation and text alignment in personalized image generation.

This figure shows several example images generated by the proposed AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is generated using a complex prompt that combines a description of an object and a particular style or setting. For example, one prompt is ‘as a cowboy draws its tiny revolver in a dusty town showdown, surrounded by cacti and a saloon’. The resulting image shows a sloth dressed as a cowboy. The diversity and fidelity of the generated images illustrate the effectiveness of AttnDreamBooth in handling complex textual descriptions while maintaining consistency with the learned concept.

This figure shows several example images generated by the AttnDreamBooth model, showcasing its ability to generate personalized images based on complex and varied text prompts. Each example shows a subject (a sloth, knight, astronaut, etc.) in a different scenario with a different style specified in the prompt. This demonstrates the model’s capacity for precise control over both the subject and scene, indicating the effectiveness of the proposed method in aligning the textual descriptions with the generated imagery.

This figure showcases the results of AttnDreamBooth, a novel method for text-aligned personalized text-to-image generation. It demonstrates the ability of the method to generate images based on complex prompts that include multiple details and stylistic elements, achieving high fidelity and alignment with the input text. Each image is generated using a different complex prompt. The prompts cover a diverse set of scenarios, including descriptions of the subject as different characters or in different environments. The successful generation of these images highlights the model’s ability to handle complex text inputs and maintain coherence across multiple aspects of the generated images.

This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the proposed AttnDreamBooth method against four other state-of-the-art text-to-image personalization methods. For each of five concepts (sloth, doll, fluffy toy, teapot, toy boat), the figure displays four images generated by AttnDreamBooth and two images each from the four comparison methods (TI+DB, NeTI, ViCo, OFT). The images illustrate the different approaches’ performance in terms of generating images that accurately reflect both the specified concept and the detailed textual descriptions provided in the prompt.

This figure showcases the capabilities of AttnDreamBooth in generating personalized images based on complex and varied text prompts. Each image shows a subject (a sloth) incorporated into different scenarios and artistic styles as directed by the text prompts. The results demonstrate the model’s ability to accurately integrate the user-specified concept (‘a sloth’) into diverse and complex scenes while maintaining textual and visual coherence, showcasing the power of text-aligned personalization.

This figure displays various examples of personalized images generated using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image depicts a specific object (e.g., a sloth, a knight, an astronaut) placed within diverse scenarios and artistic styles as described by complex text prompts. The diversity and detail in the generated images highlight the method’s ability to precisely control the subject’s appearance while adhering to the user’s textual instructions.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method. It shows a variety of images generated from complex prompts, demonstrating the model’s ability to generate personalized images that accurately reflect both the specified concept and the descriptive text provided. Each image shows a different subject (e.g., sloth, knight, astronaut) rendered in a specific style (e.g., cowboy, cyberpunk) and scene according to the text prompt. The figure highlights the method’s capability in preserving the identity of the subject while maintaining text alignment in complex, multi-element prompts.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth model on various complex prompts. Each image demonstrates the ability to generate personalized images while maintaining alignment with the descriptive text. The variety of styles, settings, and attire depicted in the images highlight the model’s versatility in handling complex instructions.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method applied to various complex prompts. Each image shows a personalized generation with a specific object (e.g., sloth, knight, astronaut) integrated into different styles and contexts according to the prompt. It aims to illustrate the model’s ability to generate text-aligned, personalized images while handling intricate and varied textual instructions.

This figure shows several examples of personalized image generation using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image shows a subject (e.g., sloth, knight, astronaut) incorporated into different settings and styles as described by complex text prompts. The figure visually demonstrates the method’s capability to accurately preserve the subject’s identity while aligning with the diverse textual descriptions.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method on various complex prompts, demonstrating its ability to generate text-aligned and personalized images. Each image shows a different prompt, where an object (e.g., a sloth) is presented in a specified style and context (e.g., as a cowboy, as a knight, as a musketeer). The diversity and quality of the generated images highlight the efficacy of the proposed method in handling complex text-to-image generation tasks.

This figure shows several example images generated by the AttnDreamBooth model. Each image shows a personalized object (e.g., sloth, knight, astronaut, etc.) placed in various settings and styles as described in complex text prompts. The figure demonstrates the model’s ability to generate high-quality, text-aligned images of personalized concepts, even with intricate textual descriptions.

This figure showcases the results of AttnDreamBooth, demonstrating its capability to generate high-quality, personalized images based on complex text prompts. It presents various examples of the model’s output, showing different scenarios and styles. Each image depicts a specific subject (a sloth, knight, astronaut, robot, etc.) in different settings and artistic styles, all based on a user-provided textual description. The quality and coherence of the images suggest effective text alignment and subject identity preservation. The figure visually demonstrates the model’s ability to handle complex prompts while maintaining text alignment and identity preservation.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method. It presents several examples of personalized image generation from complex text prompts. Each image shows a different subject (sloth, knight, astronaut, etc.) rendered in a variety of styles and scenarios described in the prompt. The figure visually demonstrates the model’s ability to maintain the identity of the subject while accurately reflecting the details specified in the prompt.

This figure showcases the results of AttnDreamBooth, a novel method for text-aligned personalized text-to-image generation. It presents several example prompts, each combining a concept (e.g., a sloth) with a detailed description of its setting and style (e.g., ‘as a cowboy draws its tiny revolver in a dusty town showdown, surrounded by cacti and a saloon’). The corresponding generated images demonstrate the model’s ability to accurately represent the specified concept within the complex scene and style described in the text prompt, highlighting its strong text alignment capabilities.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method on various complex prompts. Each image shows a different prompt describing a subject (e.g., a sloth, a knight, a robot) in a specific context and style. The diversity of the generated images and their adherence to the textual description highlights the method’s capability in handling nuanced and intricate text-to-image tasks.

This figure shows several example images generated by the proposed AttnDreamBooth method. Each image depicts a personalized concept (e.g., a sloth, a knight, a robot) integrated into a complex scene described by a textual prompt. The figure highlights the method’s ability to accurately represent the personalized concept within the specified scene, demonstrating successful text alignment and identity preservation.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method. It demonstrates the model’s ability to generate images based on complex and nuanced text prompts, incorporating several elements like character costumes, locations, artistic styles, and actions. The success of AttnDreamBooth in aligning the generated image with the detailed prompt is highlighted, showcasing its advantage over previous methods that might overemphasize one aspect of the prompt or ignore others.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method, demonstrating its ability to generate images from complex and detailed text prompts. Each image shows a personalized depiction of a concept (e.g., sloth, knight, astronaut) integrated into diverse scenarios and artistic styles. The figure highlights the model’s capacity for both accurate identity preservation of the learned concept and precise alignment with the textual descriptions provided in the prompts.

This figure shows several examples of personalized images generated using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is accompanied by a complex prompt describing the desired scene and style. The goal of the figure is to demonstrate the ability of AttnDreamBooth to generate images accurately reflecting both the personalized concept and the specific instructions within the prompts. The variety of examples highlights the model’s flexibility in handling nuanced and detailed instructions.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method on various complex prompts. It demonstrates the model’s ability to generate images of a specific concept (e.g., a sloth) while accurately integrating and aligning the concept with detailed descriptions within different scenes and styles (e.g., as a cowboy, knight, musketeer, astronaut, etc.). The images highlight successful text alignment and identity preservation, even in complex scenes and varied artistic styles. This figure visually supports the paper’s central claim of achieving high-quality personalized text-to-image generation with detailed textual control.

This figure shows several example images generated by the AttnDreamBooth model. Each image shows a different subject (sloth, knight, musketeer, astronaut, robot, assassin, Captain America, boatman, automaton) placed in a different setting and style, all based on a complex text prompt. The diversity of the generated images and the accurate representation of the requested elements in each prompt demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed AttnDreamBooth method for text-aligned personalized text-to-image generation.

This figure showcases the results of the AttnDreamBooth method on various complex text prompts. Each image demonstrates the model’s ability to generate images of a specific subject (a sloth, a knight, a musketeer, etc.) placed in various scenes and styles as described in the text prompt, highlighting its ability to maintain subject identity and textual alignment.

This figure showcases several examples of personalized image generation using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image depicts a subject (e.g., a sloth) rendered in a variety of settings and styles, all specified by complex text prompts. The results demonstrate the ability of the method to generate images where the subject’s identity is preserved while adhering accurately to diverse textual descriptions.

This figure shows several examples of personalized images generated using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is accompanied by a complex prompt that describes the scene, style, and subject (a specific toy in this case). The goal is to illustrate the ability of the method to generate images that are both faithful to the user-provided concept (the toy) and consistent with the textual description of the scene, showcasing the method’s capability for text-aligned personalization.

This figure shows several examples of personalized images generated using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is accompanied by a complex text prompt describing the scene and style. The results demonstrate the model’s ability to generate images that accurately reflect both the subject (identity preservation) and the textual descriptions (text alignment), even with intricate and varied prompts.
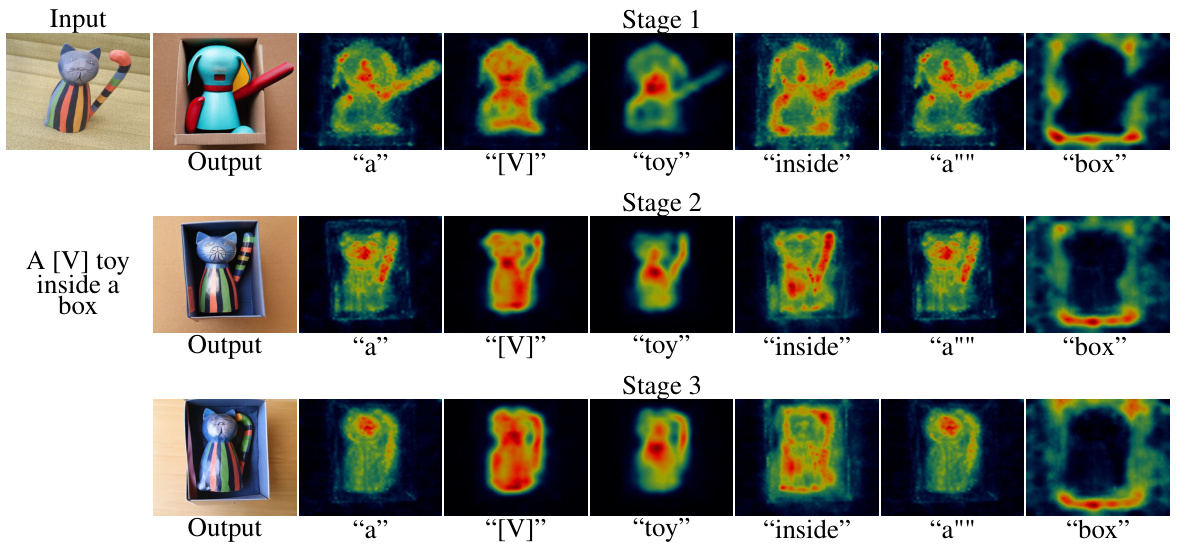
This figure shows the results of the AttnDreamBooth model after each of its three training stages. Each stage focuses on a different aspect of learning: Stage 1 learns embedding alignment (how the new concept relates to existing words); Stage 2 refines the attention map (where the model focuses its attention within the image); and Stage 3 learns the subject identity (ensuring the generated image accurately represents the new concept). The figure includes generated images and their corresponding attention maps to illustrate the model’s progress at each stage. The attention maps visually depict where the model focuses its attention when generating the image.

This figure shows the ablation study results of AttnDreamBooth. It presents a visual comparison of personalized images generated by the model with different components removed. The full model, which includes the textual embedding optimization (Stage 1), cross-attention layer fine-tuning (Stage 2), U-Net fine-tuning (Stage 3), and cross-attention map regularization, is shown alongside variations where each of these components is removed individually. The results demonstrate that all components are crucial for achieving both identity preservation and text alignment in personalized image generation.
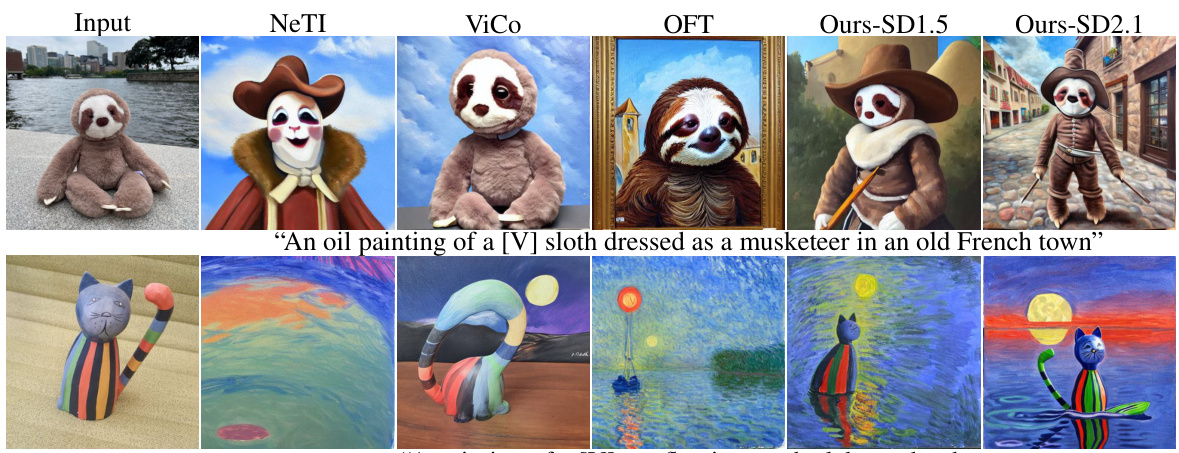

This figure compares the image generation results of AttnDreamBooth against four other state-of-the-art methods for different complex prompts. It shows that AttnDreamBooth significantly outperforms the other methods in terms of both identity preservation (how well the generated image retains the characteristics of the target concept) and text alignment (how well the generated image matches the given text description).

This figure shows several examples of personalized image generation results obtained using the proposed AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is generated from a complex text prompt that combines a description of a scene, an object (the subject), and a style or artistic choice. The examples demonstrate the method’s ability to maintain the identity of the subject while successfully incorporating the other elements of the prompt.

This figure showcases various examples of personalized images generated using the AttnDreamBooth method. Each image is accompanied by a complex text prompt that describes the desired scene, style and subject. The figure demonstrates the model’s ability to generate text-aligned images that accurately reflect the content of the prompt, while maintaining the identity of the personalized subject. This highlights the key advantage of AttnDreamBooth over existing methods, which often struggle to balance identity preservation and text alignment when dealing with complex prompts.
This figure showcases the effectiveness of the AttnDreamBooth method in generating images from complex prompts. It presents various example prompts, each paired with the images generated by the model. The diversity of the prompts illustrates the method’s capability to handle detailed, multifaceted descriptions and generate corresponding visuals.
More on tables
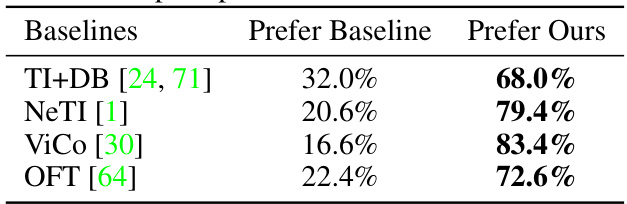
This table presents the results of a user study comparing AttnDreamBooth to four baseline methods (TI+DB, NeTI, ViCo, and OFT). Participants were shown a concept image and a text prompt, along with two generated images: one from AttnDreamBooth and one from a baseline method. They were asked to choose the image that better preserved the identity of the concept and matched the prompt. The table shows the percentage of participants who preferred each method for each baseline method. For example, 68% of participants preferred AttnDreamBooth over TI+DB, while 83.4% preferred AttnDreamBooth over ViCo.

This table lists the 24 prompts used in the quantitative evaluation of the AttnDreamBooth model. These prompts are diverse and cover several aspects, including changes in background, environment, concept color, and artistic style, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of the model’s performance under varying conditions. The prompts are designed to test the model’s ability to maintain text alignment and identity preservation across different scenarios.

This table presents the quantitative results of an ablation study conducted on the AttnDreamBooth model. Each row shows the performance of a variant of the model where one of the components (Stage 1, Stage 2, Stage 3, or the regularization term) has been removed. The results are measured in terms of Identity Preservation and Text Alignment, both represented as an upward-pointing arrow (↑) to denote higher is better. The ‘Full Model’ row provides the performance of the complete model. The study demonstrates the importance of each component to the overall performance of the model. Removing any single component leads to a significant decrease in either Identity Preservation or Text Alignment, or both.
Full paper#