↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Homepage ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used for robot task planning, but their susceptibility to hallucinations and misinterpretations of ambiguous instructions poses a significant challenge. Robots may confidently execute plans that are unsafe or fail to meet user expectations. This issue is especially critical in scenarios involving human-robot interaction where safety is paramount.
To address this problem, the authors propose “introspective planning.” This approach uses a knowledge base containing examples of human-selected safe plans and their corresponding rationales. During task execution, the LLM retrieves relevant examples from this knowledge base, which helps it reason about uncertainties and generate safer plans. The method’s effectiveness was demonstrated via experiments, showcasing improvements in compliance, safety, and confidence estimations.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is crucial for researchers working with LLMs in robotics because it directly addresses the critical issue of LLM unreliability in real-world applications. The proposed introspective planning method offers a practical solution to align robot actions with user intentions, improving safety and reducing the need for constant human intervention. Furthermore, the integration of conformal prediction provides a statistically rigorous framework for uncertainty quantification, which is vital for building trustworthy and robust robotic systems. The new benchmark further contributes to advancing safe and reliable robot manipulation.
Visual Insights#

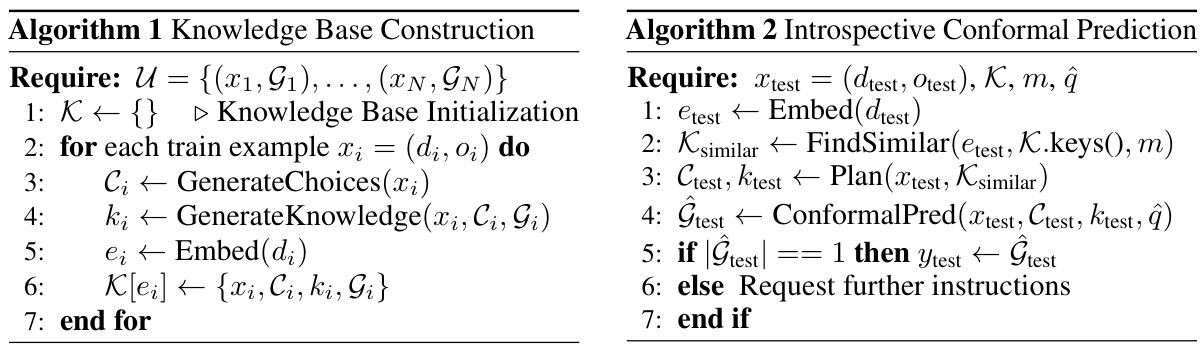
This figure illustrates the two main stages of the introspective planning pipeline. First, a knowledge base is constructed using the LLM to generate examples of human-aligned introspective reasoning based on human-provided instructions and their corresponding valid options. In the deployment phase, when given a new instruction, the LLM generates potential next steps. It then queries the knowledge base to find similar examples and uses these retrieved examples as prompts to refine its predictions, aligning its uncertainty with the inherent ambiguity of the task.
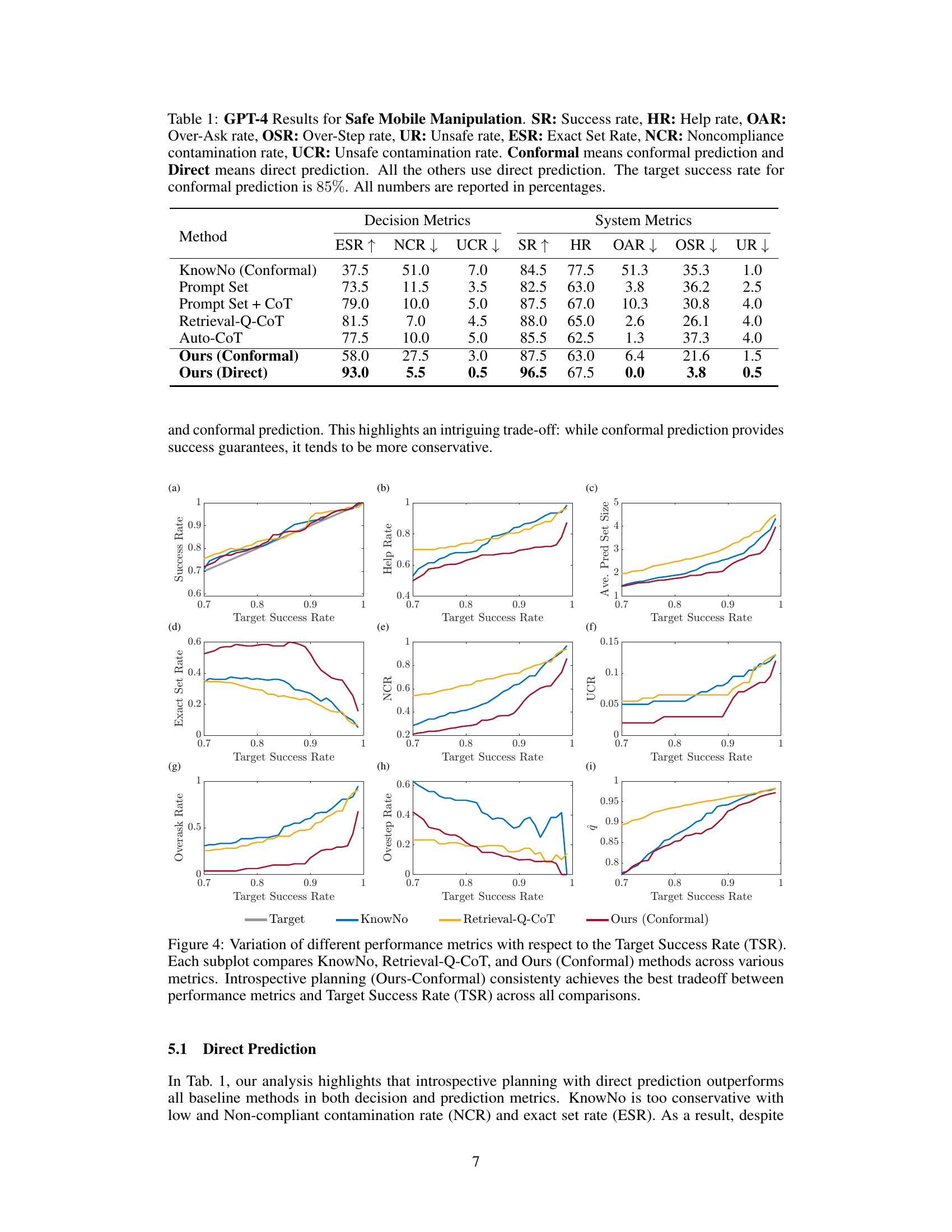
This table presents the results of the Safe Mobile Manipulation experiment using GPT-4, comparing different methods: KnowNo (with conformal prediction), Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, and the proposed method (both with and without conformal prediction). Metrics include success rate (SR), help rate (HR), over-ask rate (OAR), over-step rate (OSR), unsafe rate (UR), exact set rate (ESR), non-compliant contamination rate (NCR), and unsafe contamination rate (UCR). The target success rate for conformal prediction methods was set to 85%. The table highlights the performance differences between using direct prediction versus conformal prediction, showcasing the tradeoff between accuracy and confidence guarantees.
In-depth insights#
Introspective Planning#
The concept of “Introspective Planning” presents a novel approach to aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with robotic tasks. It directly addresses the issue of LLM hallucination and inherent ambiguity in natural language instructions by incorporating a human-aligned knowledge base. This base contains examples of introspective reasoning, acting as post-hoc rationalizations of safe and compliant plans. During deployment, the LLM retrieves relevant examples from this knowledge base to guide its decision-making, effectively reducing uncertainty and improving both safety and compliance. Introspective planning’s integration with conformal prediction further enhances its capabilities by providing tighter confidence bounds and minimizing the need for user clarification. This framework offers a promising solution for building more robust and reliable LLM-powered robotic systems, emphasizing proactive uncertainty assessment and alignment with human intent.
Conformal Prediction#
Conformal prediction is a valuable technique for quantifying uncertainty in machine learning models, especially useful when dealing with complex models like LLMs. It provides a statistically guaranteed level of confidence in predictions by constructing a prediction set rather than a single prediction. This method is particularly effective for robotic applications because it allows robots to express their uncertainty and solicit clarification from users when necessary, leading to safer and more reliable decision making. The approach enhances robustness and safety, especially when dealing with inherent ambiguity in user instructions. Conformal prediction ensures a minimal acceptable success rate, guaranteeing that the correct action is included in the prediction set, minimizing incorrect actions and unnecessary user clarification. Incorporating conformal prediction within an introspective planning framework further refines uncertainty quantification, leading to tighter confidence intervals and more precise predictions.
Mobile Manipulation#
The concept of ‘Mobile Manipulation’ in robotics research represents a significant challenge, demanding the integration of sophisticated control algorithms, perception systems, and planning strategies. Autonomous mobile robots must not only navigate complex and dynamic environments but also dexterously manipulate objects, often in unstructured settings. This requires robust solutions for localization, path planning, obstacle avoidance, and precise manipulation control. Success hinges on the reliable integration of these seemingly disparate functionalities. Research in mobile manipulation often explores advanced techniques in computer vision, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, using these tools to improve object recognition, grasp planning, and task execution. A key focus is the development of algorithms that can handle uncertainty, given the variability of real-world environments and unpredictable object properties. Safe and compliant manipulation is paramount, with safety mechanisms essential to prevent accidents or damage. The integration of human-robot interaction further adds to the complexity, requiring efficient and intuitive interfaces for safe and effective collaboration.
Uncertainty Handling#
This research paper tackles the crucial problem of uncertainty handling in robot planning when using Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs, while powerful, are prone to hallucinations and misinterpretations, especially when dealing with ambiguous natural language instructions. The core idea is introspective planning, which encourages the LLM to introspect on its own uncertainty. The paper proposes a novel method for constructing a knowledge base of introspective reasoning examples, using these to guide the LLM during deployment. A key innovation is integrating conformal prediction, providing statistical guarantees about the accuracy and safety of generated plans while minimizing unnecessary clarification requests. The method also improves plan compliance and safety, demonstrated through evaluations on various tasks, including a newly introduced safe mobile manipulation benchmark. The effectiveness of introspective planning in combination with conformal prediction is a significant contribution, offering improved reliability and robustness in LLM-based robotic systems.
Future Work#
Future research directions stemming from this introspective planning framework could explore several promising avenues. Extending introspective planning to handle multi-label tasks and truly ambiguous situations would significantly enhance the system’s ability to address complex, real-world scenarios. This requires developing sophisticated multi-label conformal prediction methods to provide robust uncertainty quantification. Investigating the trade-offs between direct prediction and conformal prediction more rigorously is crucial. While conformal prediction offers strong statistical guarantees, it can be overly conservative. Finding ways to tighten the confidence bounds while maintaining high accuracy is a key challenge. Exploring different knowledge base construction methods and evaluation metrics is important to optimize the system’s performance and efficiency. Analyzing the influence of different prompt engineering techniques on the LLM’s reasoning and plan generation, and determining the best approaches for various task domains should be explored. Finally, rigorous testing and validation on more diverse and challenging robotic tasks, including those with safety-critical components, will be necessary to fully assess the robustness and generalizability of this method.
More visual insights#
More on figures

This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the proposed introspective planning method against the KnowNo baseline on two examples from the Safe Mobile Manipulation dataset. Both methods utilize conformal prediction with a target success rate of 85%. The left example demonstrates an ambiguous task where KnowNo produces an over-precise prediction set while IntroPlan correctly identifies both valid options. The right example features an ambiguous task where safety is important; KnowNo generates an over-broad prediction set while IntroPlan correctly selects the safe option. This highlights IntroPlan’s superior performance in handling ambiguous situations, particularly when safety is critical, by leveraging introspective reasoning to refine the prediction sets.
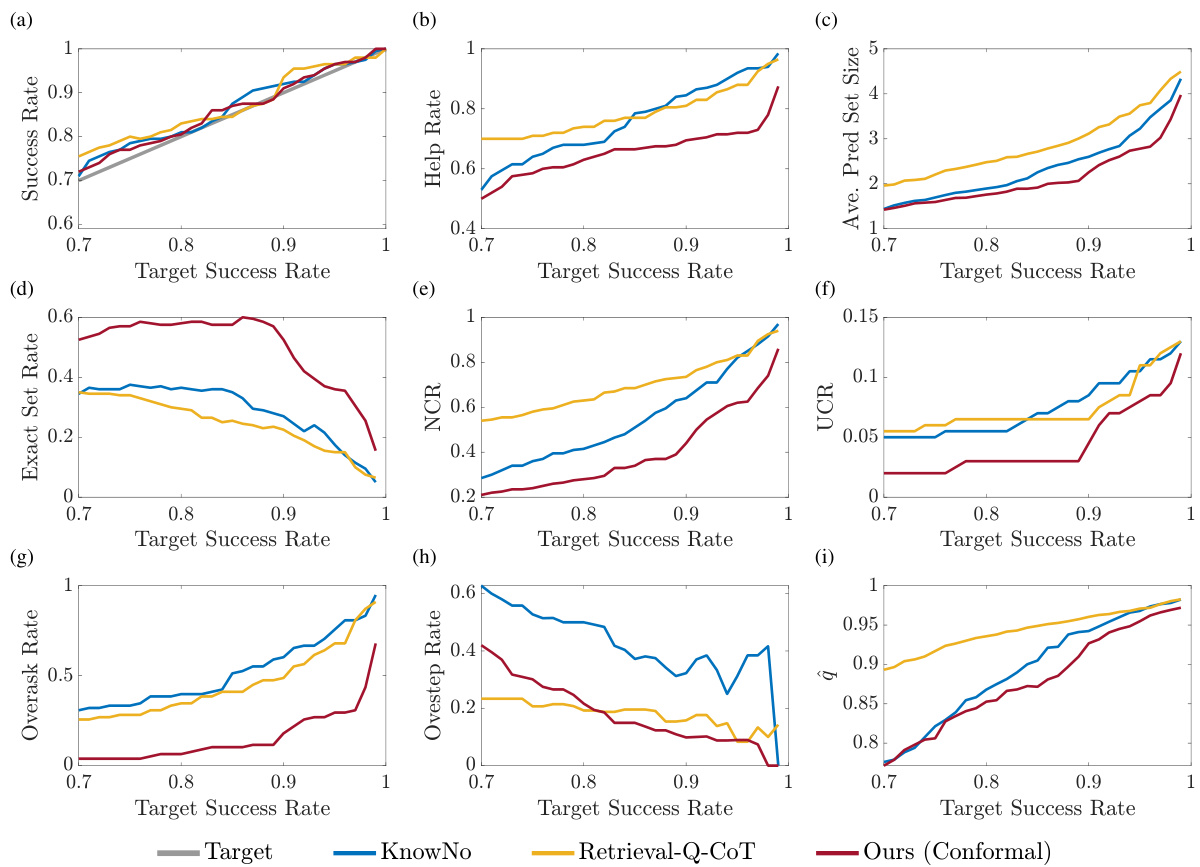
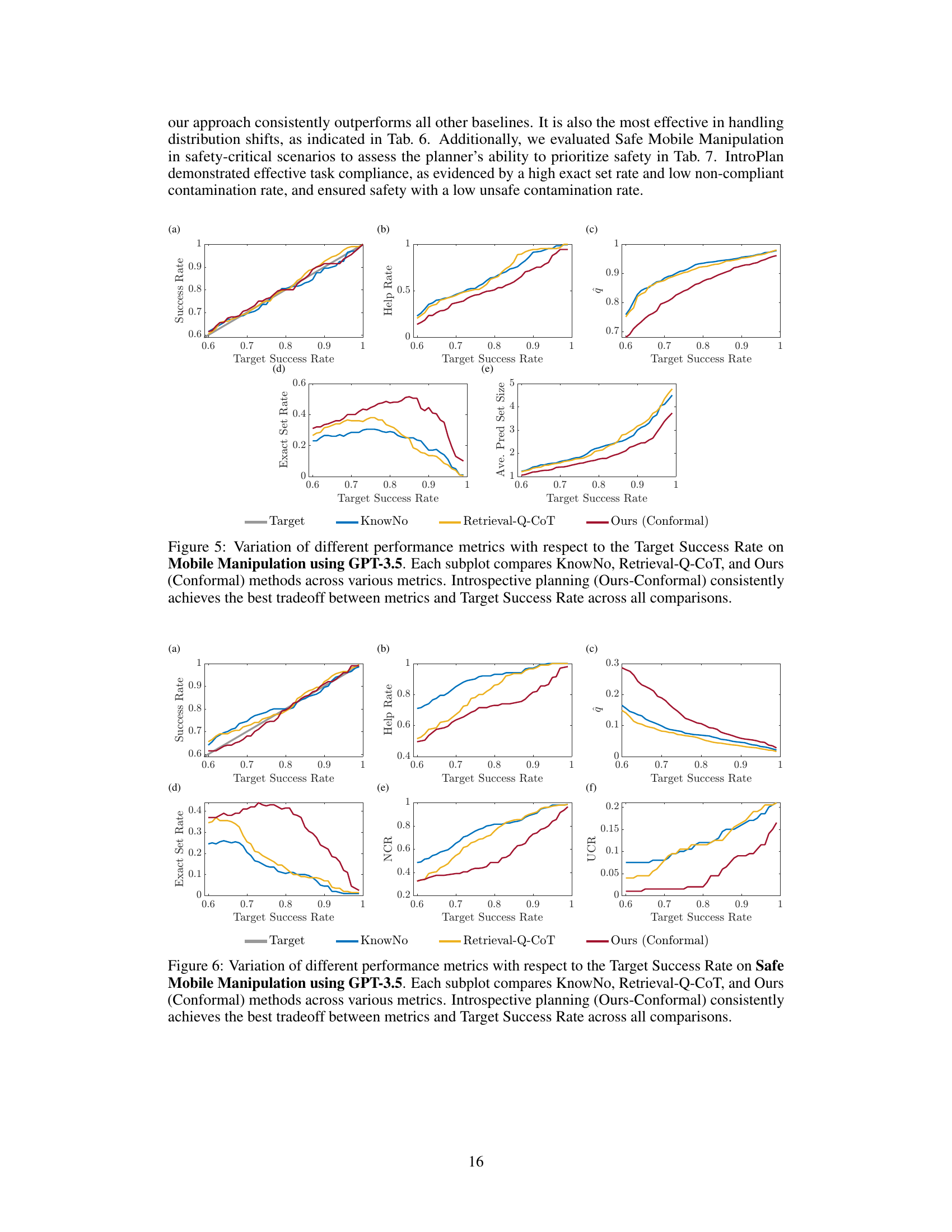
This figure shows the performance comparison between three methods: KnowNo, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and the proposed method (Ours-Conformal) across various metrics with respect to the target success rate. Each subplot presents a different metric (success rate, help rate, average prediction set size, exact set rate, non-compliant contamination rate, unsafe contamination rate, overask rate, overstep rate, and the conformal prediction threshold (ŷ)). The results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently achieves the best balance between performance metrics and the target success rate.

This figure shows a comparison of different performance metrics (Success Rate, Help Rate, Average Prediction Set Size, Exact Set Rate, and the calibrated threshold ŷ) across three different methods (KnowNo, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and Ours (Conformal)) at various target success rates. The ‘Ours (Conformal)’ method, which incorporates introspective planning and conformal prediction, consistently demonstrates the best balance between achieving high success rates and minimizing unnecessary user interaction (Help Rate) while maintaining high prediction accuracy (Exact Set Rate).

This figure compares the performance of three different methods: KnowNo, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and the proposed ‘Ours (Conformal)’ method, across various metrics and target success rates. The ‘Ours (Conformal)’ method consistently shows the best balance between achieving a high target success rate and maintaining good performance on other metrics, highlighting its effectiveness.
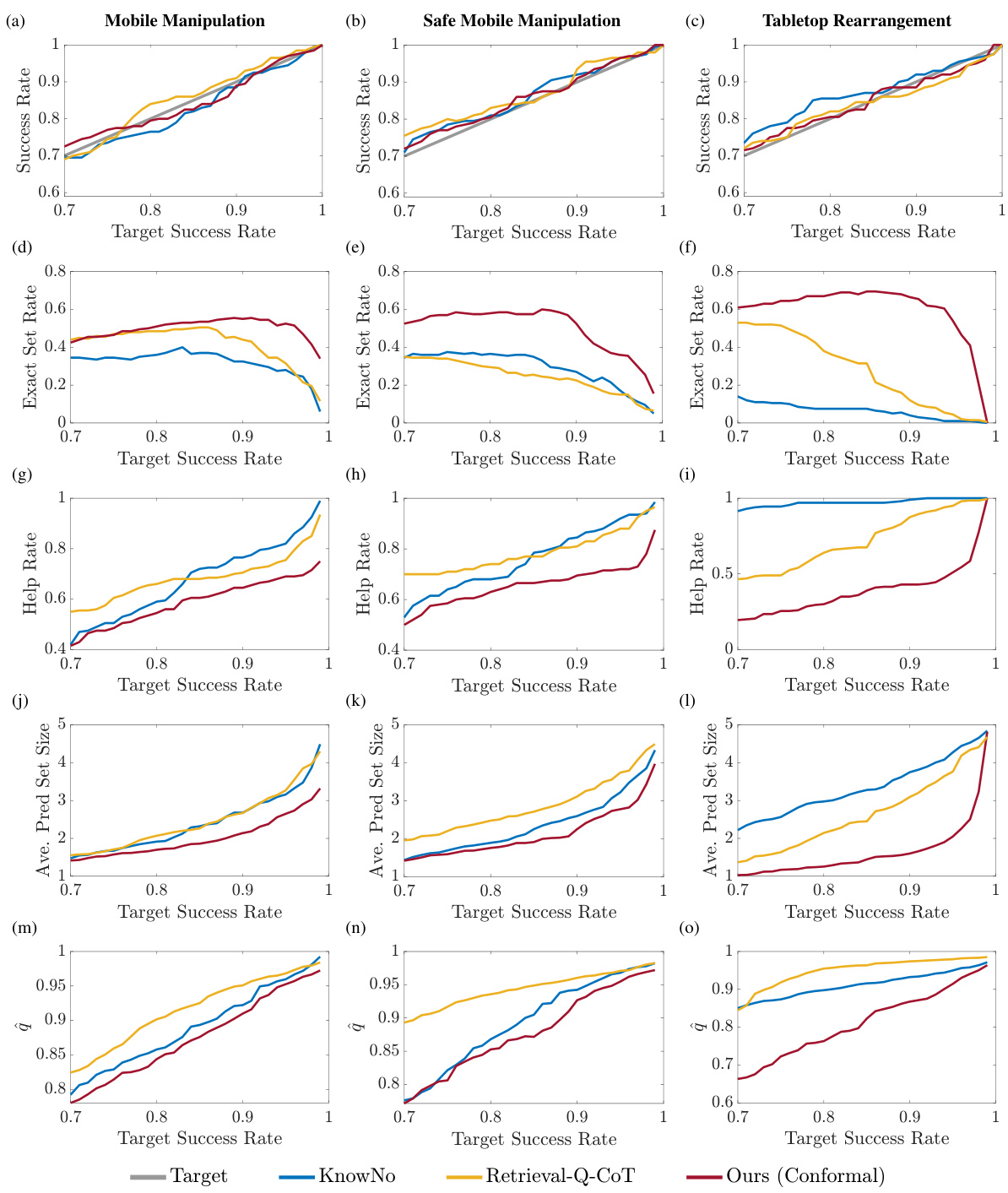
This figure compares the performance of three different planning methods across three different datasets. The y-axis shows different metrics such as success rate, exact set rate, help rate, average prediction set size, and the conformal prediction threshold. The x-axis represents the target success rate. The three methods are KnowNo, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and the proposed method (Ours-Conformal). The figure demonstrates that the proposed method achieves the best tradeoff between various performance metrics and the target success rate.
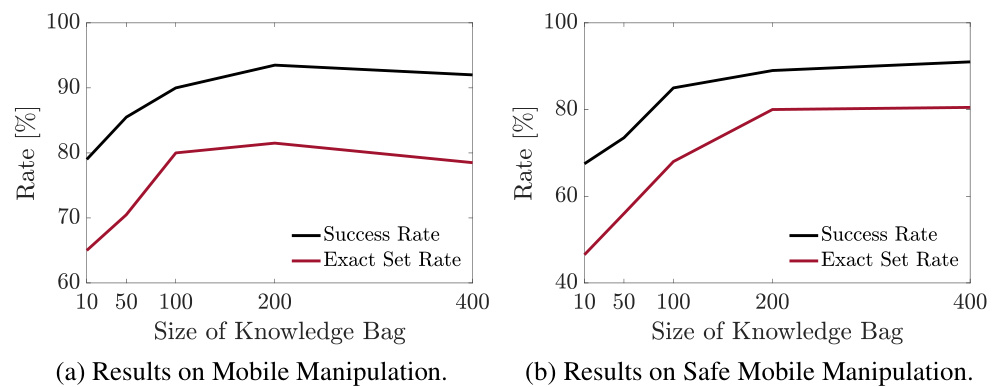
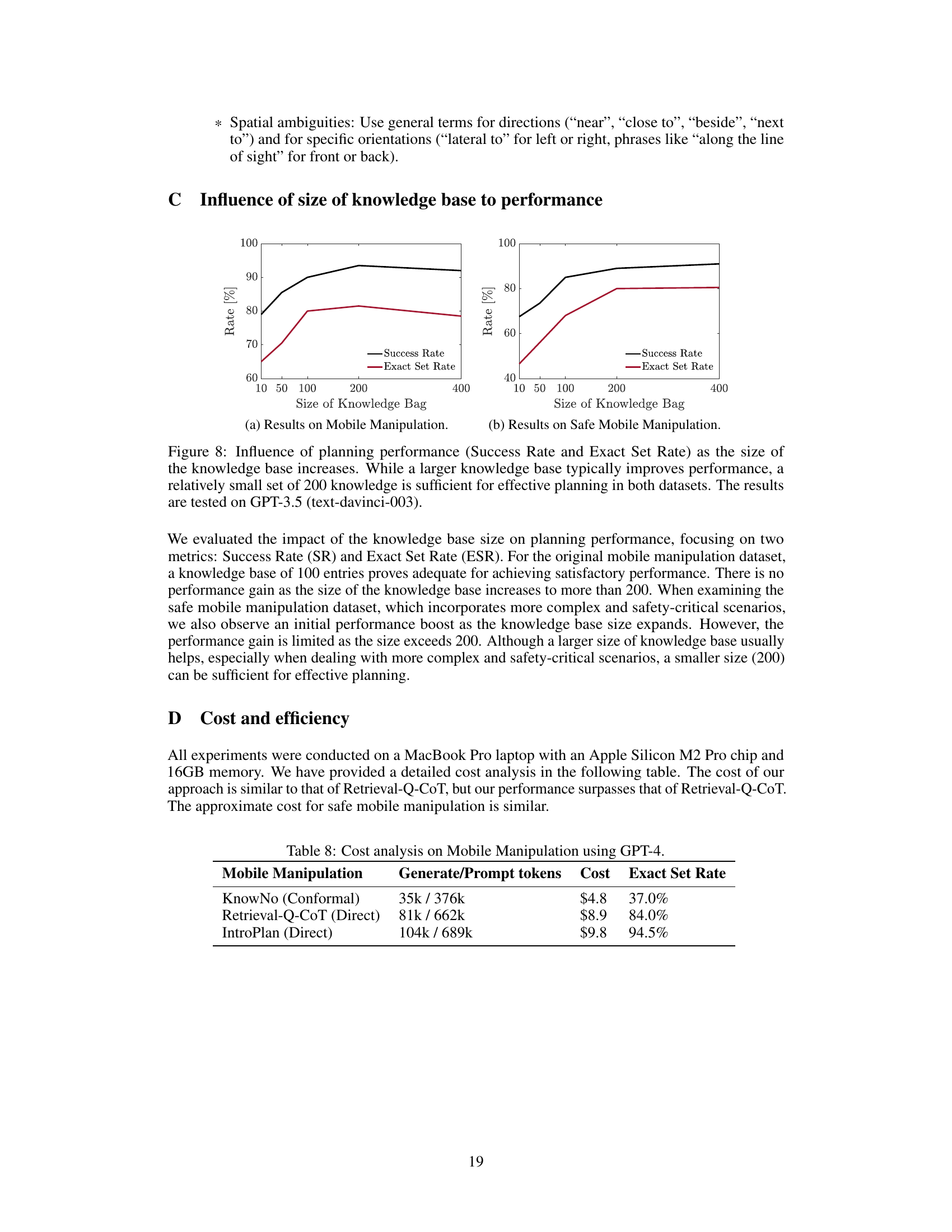
This figure shows the impact of the knowledge base size on the success rate and exact set rate for two mobile manipulation tasks. The left graph shows the results for standard mobile manipulation, while the right shows results for safe mobile manipulation. In both cases, increasing the knowledge base size leads to improved performance up to around 200 entries, after which there are diminishing returns.
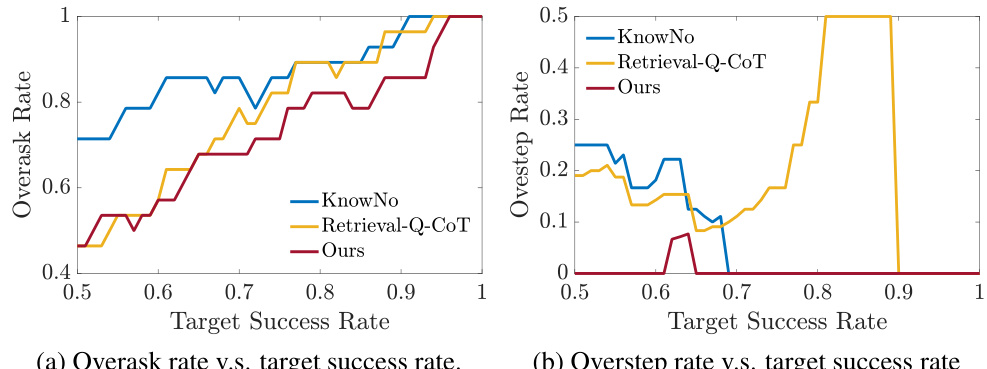
This figure shows the performance comparison of three different methods: KnowNo, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and the proposed introspective planning method (Ours-Conformal) across various metrics, such as Success Rate, Help Rate, Exact Set Rate, etc., with respect to the target success rate. The results indicate that the introspective planning method consistently achieves the best balance between high performance and a reasonable success rate.

This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the proposed Introspective Planning method and the KnowNo baseline on two examples from the Safe Mobile Manipulation dataset. Both methods use conformal prediction with a target success rate of 85%. The figure highlights that Introspective Planning produces more precise prediction sets compared to KnowNo by generating explanations through introspective reasoning before applying conformal prediction. KnowNo, on the other hand, directly predicts valid options using conformal prediction, leading to over-stepping and over-asking in certain scenarios.

This figure illustrates the introspective conformal prediction process. It starts with the LLM generating multiple options for a task. Introspective planning provides rationale for each option. Then, conformal prediction uses likelihood scores from a calibration dataset to determine a threshold (ĝ). Options with scores above this threshold (1-ĝ) are included in the prediction set. This ensures a high probability that the correct option is included, offering a statistically guaranteed confidence level for the robot’s action.
More on tables

This table presents the results of the Safe Mobile Manipulation experiment using GPT-4, comparing different methods (KnowNo, Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, Ours (Conformal), Ours (Direct)). It shows success rate (SR), help rate (HR), over-ask rate (OAR), overstep rate (OSR), unsafe rate (UR), exact set rate (ESR), non-compliant contamination rate (NCR), and unsafe contamination rate (UCR) for each method. The target success rate for the conformal prediction methods was 85%. All values are percentages.
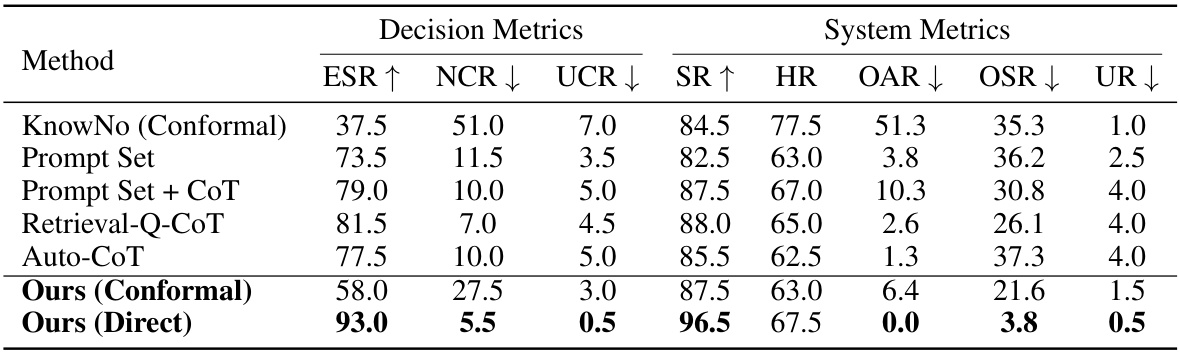
This table presents the performance comparison of different methods on the Safe Mobile Manipulation task using GPT-4. It shows various metrics such as Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Over-Ask Rate (OAR), Over-Step Rate (OSR), Unsafe Rate (UR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Noncompliance Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The methods compared include KnowNo (with conformal prediction), Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, and the proposed method (both with and without conformal prediction). The target success rate for conformal methods was set to 85%. All values are percentages.
This table presents the performance comparison of different methods on the Safe Mobile Manipulation task using GPT-4. The methods are compared using several metrics including Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Over-Ask Rate (OAR), Over-Step Rate (OSR), Unsafe Rate (UR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Noncompliant Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The table highlights the performance of the proposed ‘Ours’ method (both with and without conformal prediction) in comparison to baseline methods such as KnowNo, Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, and Auto-CoT.

This table presents the performance comparison of different methods on the Safe Mobile Manipulation task using GPT-4. The methods are evaluated based on several metrics including Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Over-Ask Rate (OAR), Over-Step Rate (OSR), Unsafe Rate (UR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Non-compliant Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The table highlights the performance of the proposed method (Ours) using both direct and conformal prediction, comparing it to several baselines. The target success rate for the conformal prediction methods is 85%.
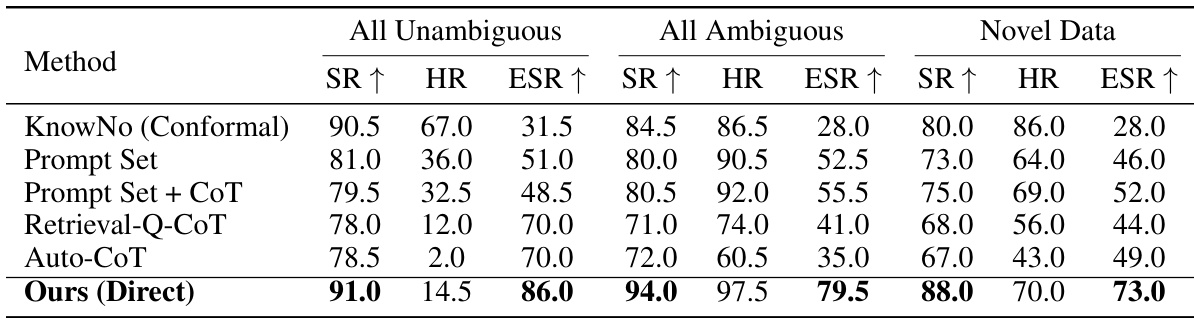
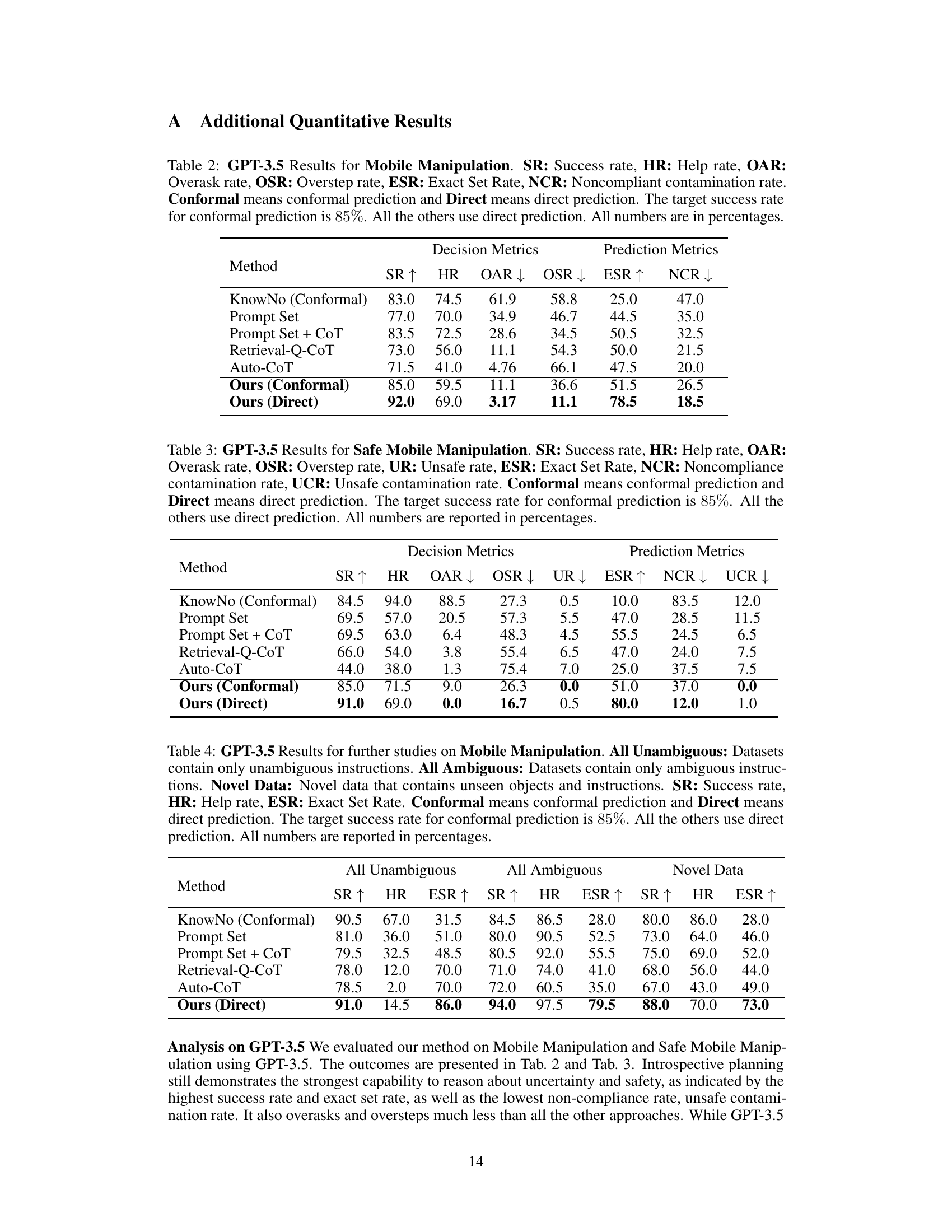
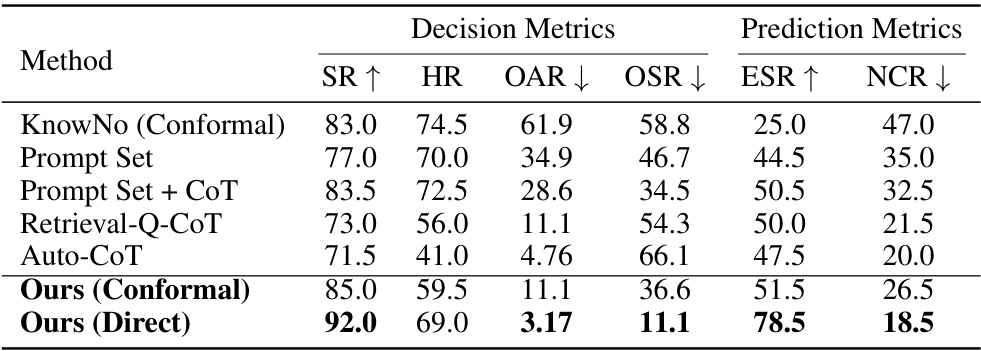
This table presents the results of GPT-3.5 model performance on three different datasets of mobile manipulation tasks: one with only unambiguous instructions, one with only ambiguous instructions, and one with novel, unseen objects and instructions. It compares the success rate (SR), help rate (HR), and exact set rate (ESR) of various methods, including the proposed introspective planning with direct prediction, and baselines like KnowNo using conformal prediction, Prompt Set with or without Chain of Thought, and Retrieval-Q-CoT. The results reveal the model’s ability to handle various levels of ambiguity and generalization to new situations.

This table presents the performance comparison of different methods on the Safe Mobile Manipulation task using GPT-4. It shows various metrics including Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Over-Ask Rate (OAR), Over-Step Rate (OSR), Unsafe Rate (UR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Non-compliant Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The methods compared include KnowNo (with conformal prediction), Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, and the proposed method (Ours) with both conformal and direct prediction. The target success rate for conformal prediction methods is 85%. All values are percentages.
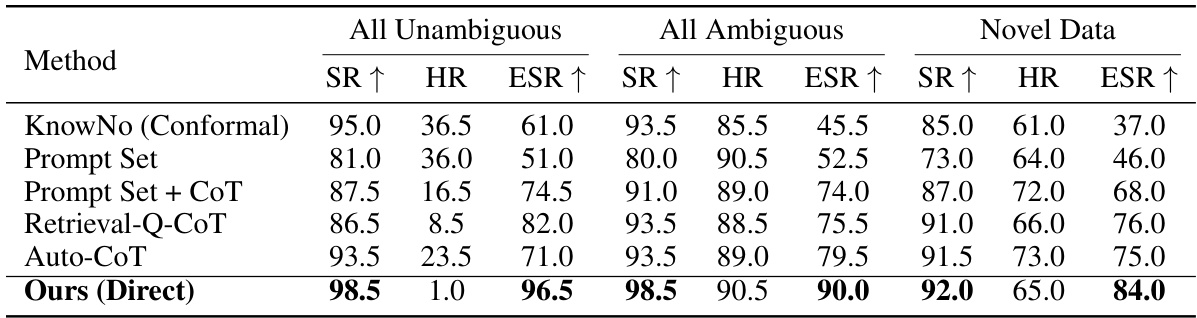
This table presents the results of further studies on mobile manipulation using GPT-4, categorized into three datasets: all unambiguous instructions, all ambiguous instructions, and novel data with unseen objects and instructions. It compares different methods (KnowNo (Conformal), Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, and Ours (Direct)) across success rate (SR), help rate (HR), and exact set rate (ESR). The target success rate for the conformal methods is 85%, while direct prediction methods don’t have a target success rate. All values are percentages.

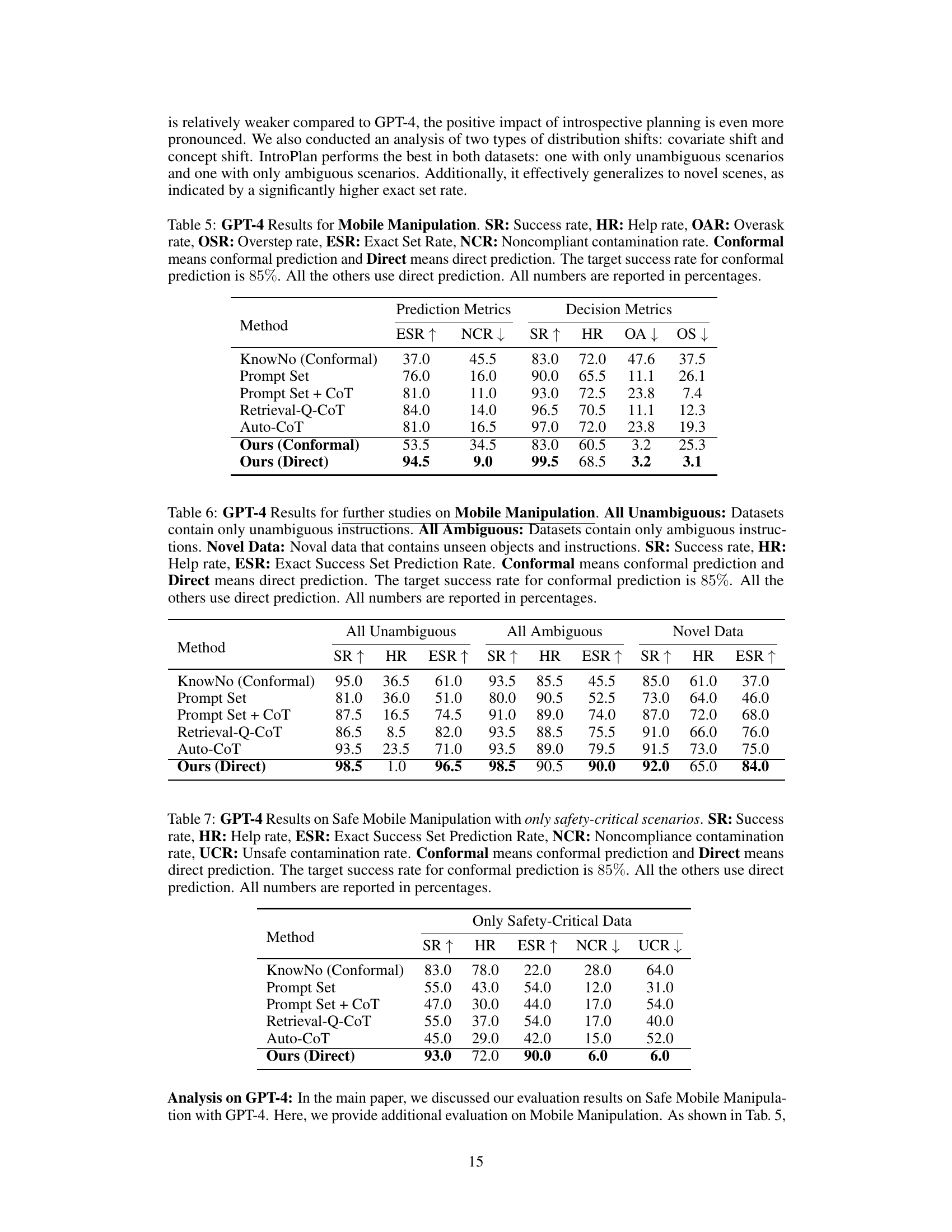
This table presents the results of the experiments using GPT-4 on a dataset focusing on safety-critical scenarios. It compares different methods: KnowNo (using conformal prediction), Prompt Set, Prompt Set + Chain of Thought, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, and the proposed ‘Ours’ method (with both direct and conformal prediction). The metrics evaluated include Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Non-compliant Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The target success rate for the conformal prediction methods is 85%.

This table presents the results of the GPT-4 model for the Safe Mobile Manipulation task. It compares different methods (KnowNo, Prompt Set, Prompt Set + CoT, Retrieval-Q-CoT, Auto-CoT, Ours (Conformal), and Ours (Direct)) across several metrics: Success Rate (SR), Help Rate (HR), Over-Ask Rate (OAR), Over-Step Rate (OSR), Unsafe Rate (UR), Exact Set Rate (ESR), Non-compliance Contamination Rate (NCR), and Unsafe Contamination Rate (UCR). The ‘Conformal’ methods used conformal prediction with a target success rate of 85%, while the others used direct prediction. The table helps assess the effectiveness of each method in terms of accuracy, efficiency, safety, and compliance with user instructions.
Full paper#