TL;DR#
Current text-to-image models struggle to fully utilize advanced LLMs due to misalignment in training objectives and positional biases in decoder-only architectures. This leads to poor prompt following and image quality. This paper identifies and addresses these limitations.
The researchers introduce the LLM-Infused Diffuser, a novel framework to leverage LLMs’ text understanding capabilities. They introduce a linguistic token refiner to mitigate positional biases and a collaborative refiner to fuse multiple LLMs for improved performance. Their LI-DiT model, built on this framework, significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models in various benchmarks, demonstrating superior image quality and alignment with given prompts. This work provides a significant advancement in utilizing LLMs for image generation, improving both the efficiency and effectiveness of current models.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it addresses a critical challenge in text-to-image generation: effectively leveraging the power of large language models (LLMs) for prompt encoding. The proposed LLM-Infused Diffuser framework significantly improves prompt understanding, surpassing state-of-the-art models. This opens new avenues for research into advanced text-to-image models and has immediate practical implications for AI applications.
Visual Insights#

🔼 This figure displays a selection of high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately follow complex and diverse prompts, producing high-quality results across a range of artistic styles and image resolutions. The specific prompts used to generate each image can be found in the appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.
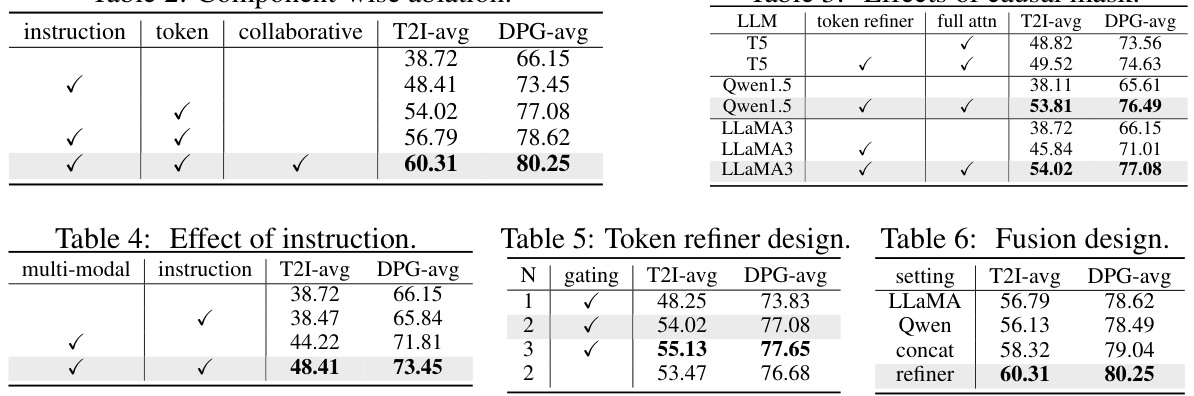
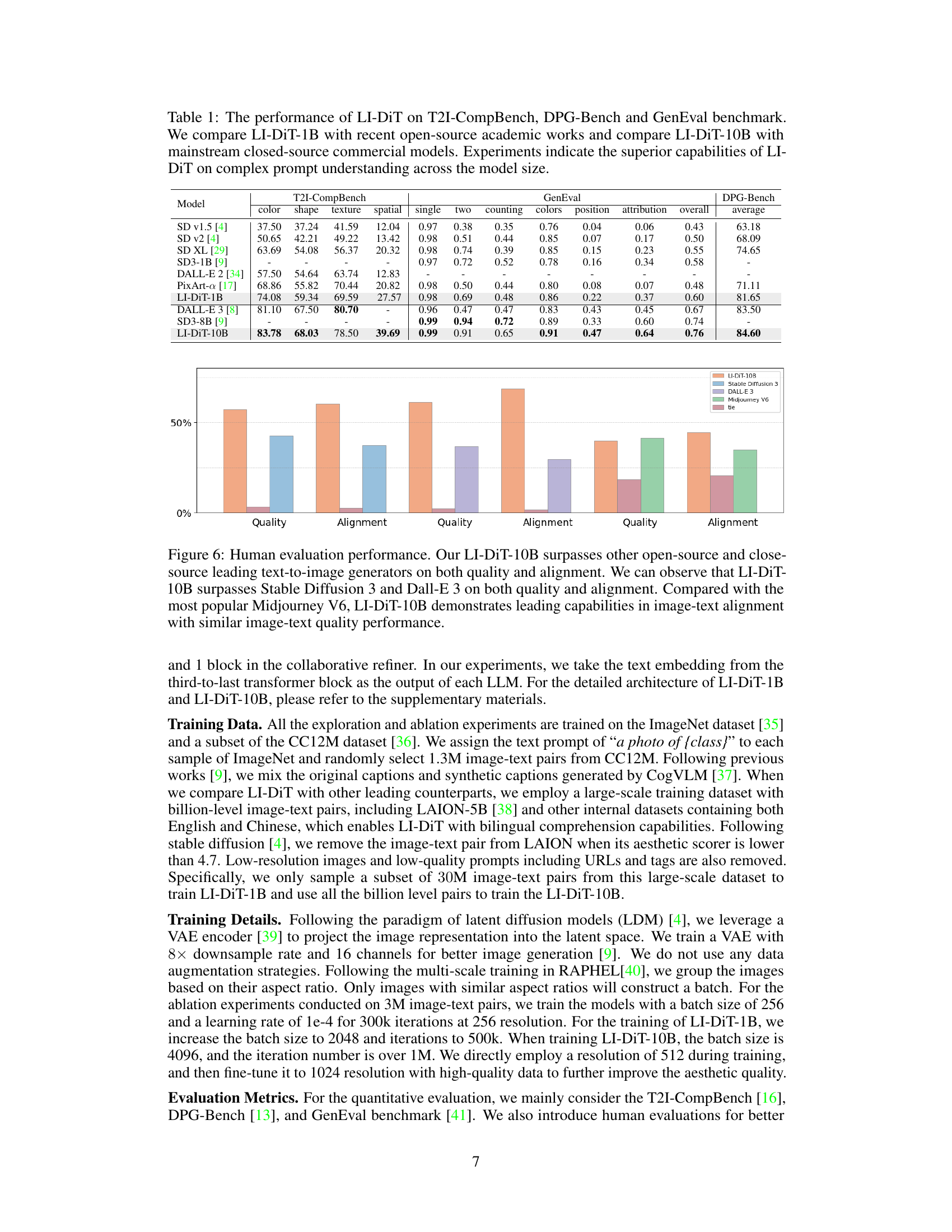
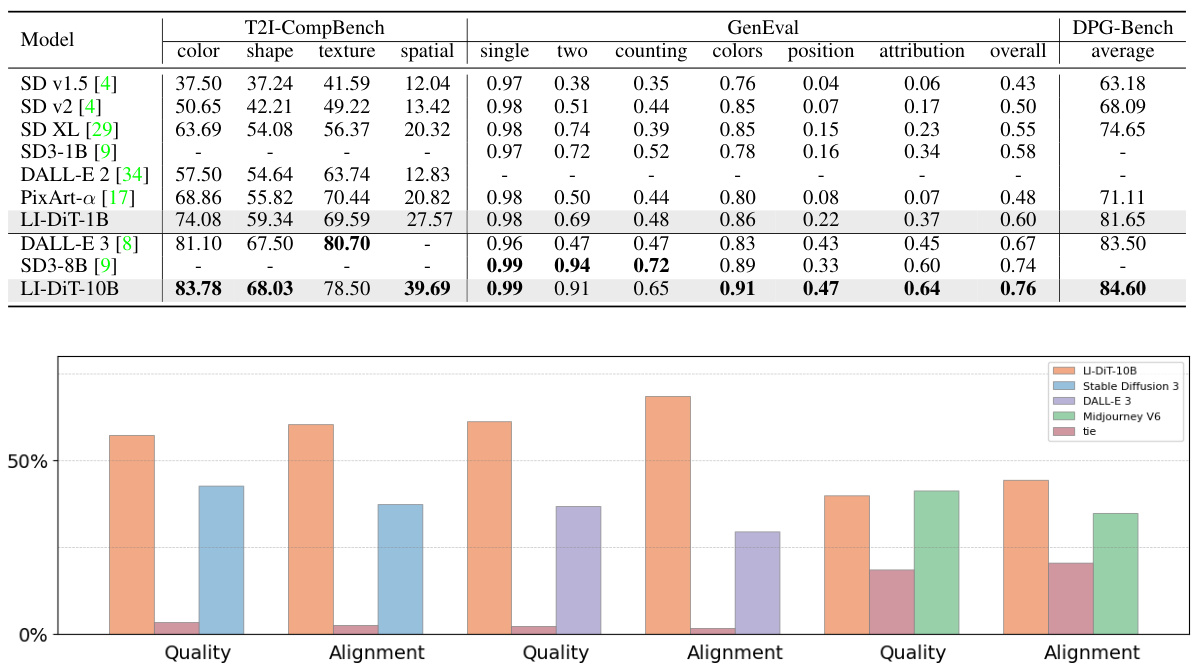
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of the LI-DiT model’s performance against other state-of-the-art text-to-image generation models on three benchmark datasets: T2I-CompBench, DPG-Bench, and GenEval. The results demonstrate LI-DiT’s superior performance across different model sizes (1B and 10B parameters), showcasing its ability to handle complex prompts and achieve high image quality. The comparison includes both open-source and closed-source commercial models to illustrate LI-DiT’s overall competitiveness.
read the caption
Table 1: The performance of LI-DiT on T2I-CompBench, DPG-Bench and GenEval benchmark. We compare LI-DiT-1B with recent open-source academic works and compare LI-DiT-10B with mainstream closed-source commercial models. Experiments indicate the superior capabilities of LI-DiT on complex prompt understanding across the model size.
In-depth insights#
LLM Prompt Encoding#
LLM prompt encoding is a crucial area in bridging the gap between natural language processing and image generation. The core challenge lies in effectively translating textual prompts into a format suitable for guiding diffusion models. This involves several complex steps, starting with understanding the nuances of the prompt itself - this is where the power of LLMs comes into play. LLMs excel at understanding complex language structures and contextual cues which would otherwise be lost with simpler encoding methods. However, simply using an LLM as a direct prompt encoder is often suboptimal. This is because LLMs are trained for next-token prediction, a task that differs fundamentally from the discriminative nature of prompt encoding required for image generation. This inherent misalignment leads to significant performance degradation in image quality and prompt adherence. Addressing this issue requires innovative approaches such as carefully crafting instruction formats to guide the LLM’s output, using multiple LLMs to improve robustness and accuracy, and employing techniques to mitigate inherent positional biases of decoder-only LLMs. These methods demonstrate that the full potential of LLMs for improved prompt encoding can be unlocked, yielding substantial gains in the quality and fidelity of generated images. The choice of LLM, and the design of the fusion framework significantly impact the final results and therefore are crucial points for research.
Diffusion Transformer#
Diffusion Transformers represent a significant advancement in generative modeling, combining the strengths of diffusion models and transformer architectures. Diffusion models excel at generating high-quality, diverse samples, but often lack the ability to effectively incorporate complex textual prompts. Transformers, known for their powerful sequence processing capabilities, offer a solution. By integrating transformers into the diffusion process, Diffusion Transformers allow for more nuanced control over the generated output based on detailed textual descriptions. This fusion enables the model to understand complex relationships within the text, translating them into precise image manipulations during the denoising process. However, challenges remain in optimizing the training process due to the increased complexity of the combined architecture. Efficient training strategies and careful attention to the interaction between the diffusion and transformer components are crucial for successful implementation. The effectiveness of Diffusion Transformers hinges on the ability to seamlessly integrate the semantic information from the transformer into the generative process of the diffusion model without sacrificing efficiency or quality.
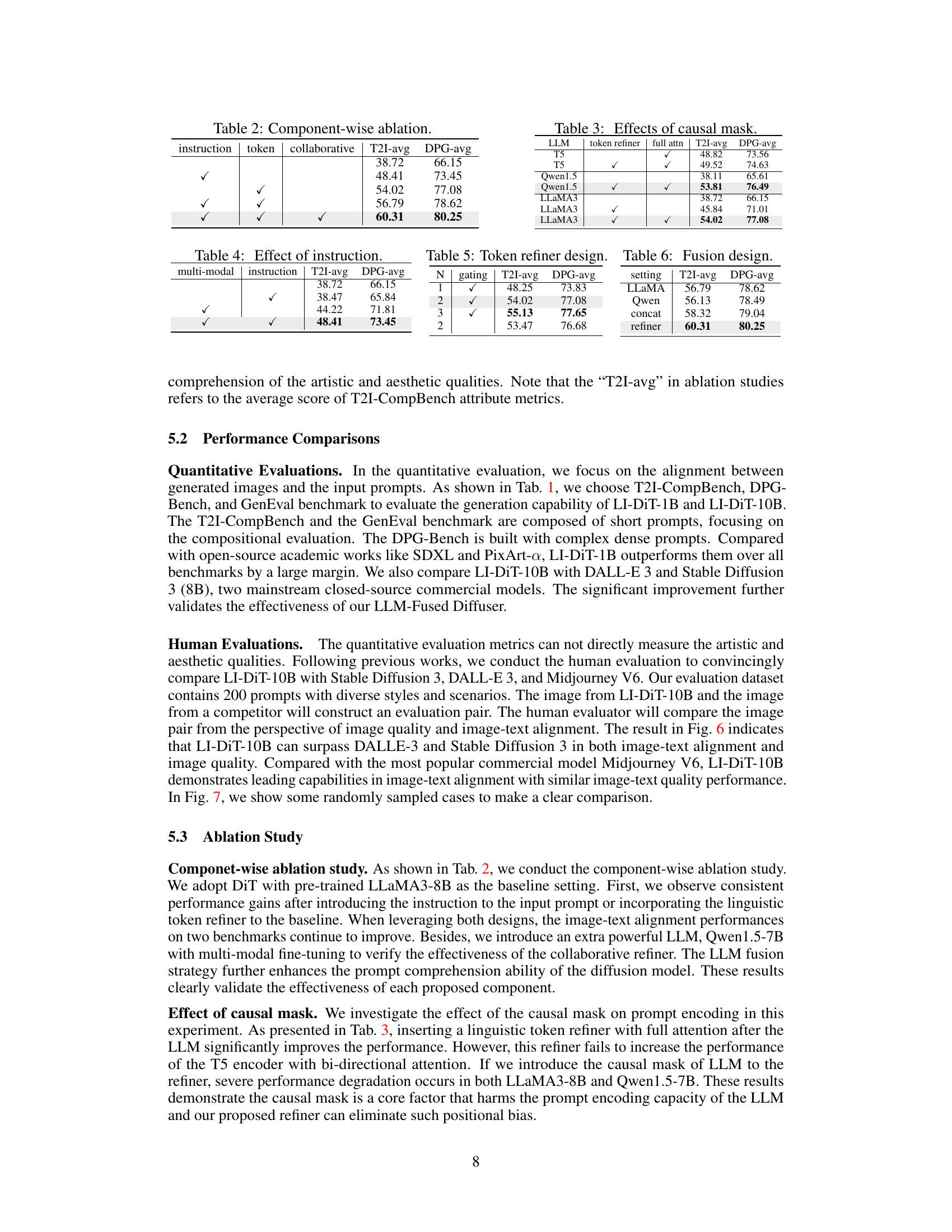
Ablation Studies#
Ablation studies systematically remove components of a model to assess their individual contributions. In the context of a text-to-image generation model, this might involve removing or modifying different elements such as the prompt encoder, the diffusion model itself, or specific modules within either. By observing the impact on performance metrics like image quality and text alignment after each ablation, researchers gain crucial insights into the efficacy and importance of each component. For example, removing the prompt encoder and relying on simpler text encoding might reveal its importance in nuanced prompt understanding. Similarly, modifying specific diffusion model components can reveal how various architectures affect the final image output. Analyzing results from these carefully controlled experiments is key to understanding the model’s inner workings and identifying areas ripe for improvement or optimization. Well-designed ablation studies are crucial for evaluating the relative importance of different model aspects and guiding future research directions.
Benchmark Results#
A dedicated ‘Benchmark Results’ section would ideally present a detailed quantitative analysis comparing the proposed model’s performance against existing state-of-the-art models. This would involve clear descriptions of the benchmark datasets used, emphasizing their diversity and relevance. Key performance metrics should be precisely defined and reported with appropriate error bars or confidence intervals, indicating the statistical significance of any observed differences. The choice of benchmarks should be justified, and any limitations acknowledged. Visualizations, such as tables and charts, would enhance understanding, showcasing relative performance across different metrics and models. A critical discussion of the results, addressing potential weaknesses and limitations, is crucial to present a balanced evaluation, ultimately demonstrating the strengths and potential impact of the proposed model in a fair and transparent manner. Qualitative analyses, supplementing the quantitative data, could further enrich the findings. For instance, visual comparisons of generated outputs might be included to illustrate improvements in image quality or adherence to user prompts.
Future of LLMs#
The future of LLMs is incredibly promising, yet also fraught with challenges. Scaling up model size and training data will continue to improve performance, but the computational costs are staggering, necessitating more efficient training methods and hardware advancements. Research into model architectures beyond the transformer is crucial for overcoming limitations in parallelization and long-range dependencies. Addressing bias and safety concerns is paramount; mitigating harmful outputs requires sophisticated techniques like reinforcement learning from human feedback and improved methods for detecting and preventing biases during training. Ensuring responsible deployment necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications, including transparency, accountability, and accessibility. Beyond text, multimodality is a key area of exploration, integrating LLMs with vision, audio, and other modalities to create more versatile and powerful AI systems. Finally, fundamental research into the nature of intelligence and learning is essential for developing truly robust and general-purpose LLMs that can understand and reason in a human-like manner.
More visual insights#
More on figures
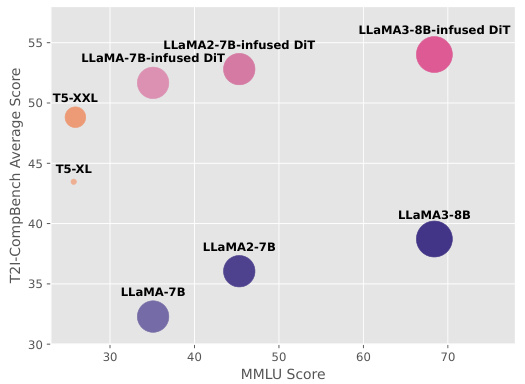
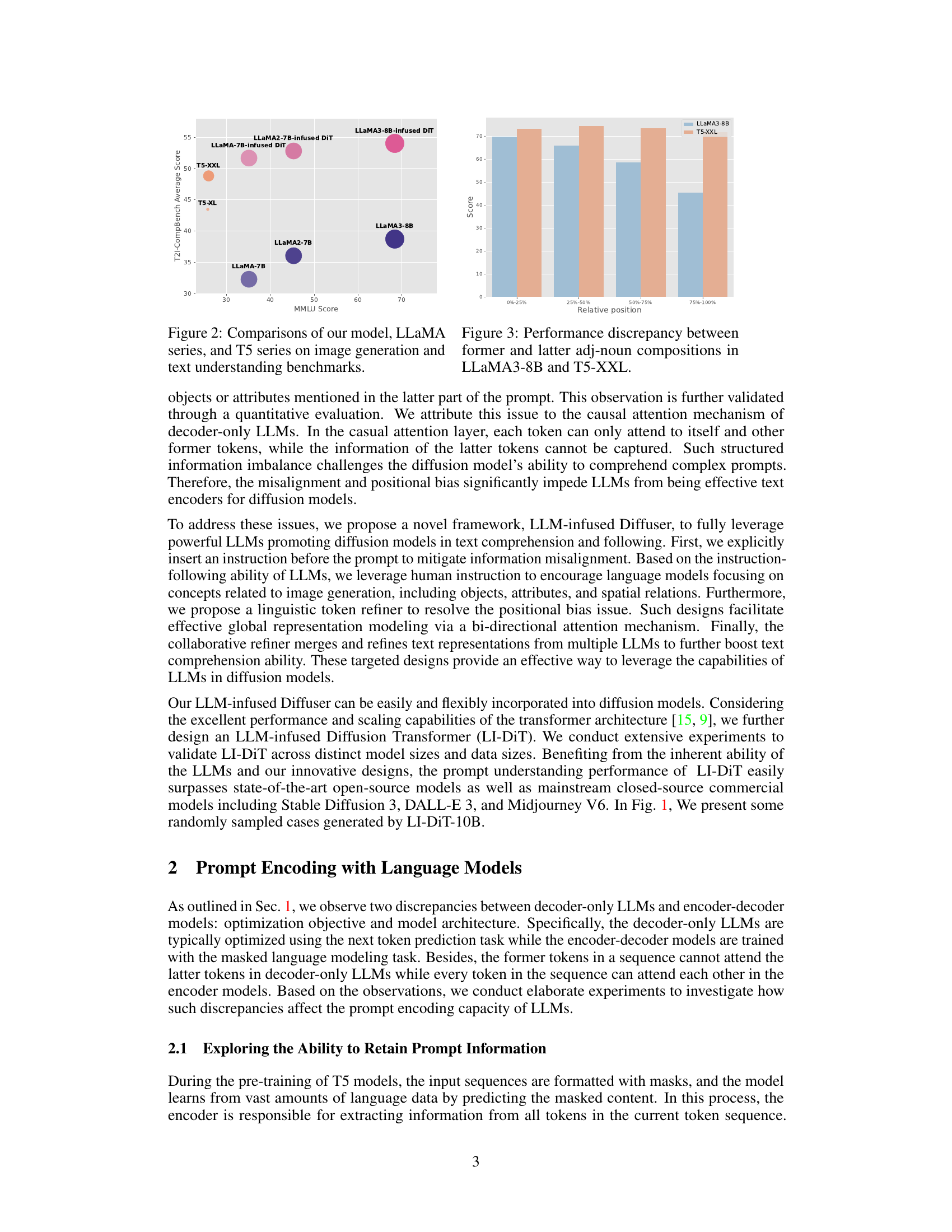
🔼 This figure compares the performance of the proposed LI-DiT model against several LLMs (LLaMA series) and encoder-decoder models (T5 series) across two benchmark datasets: image generation (T2I-CompBench) and text understanding (MMLU). The results illustrate that while larger LLMs such as LLaMA3-8B show superior text understanding, they do not directly translate to better image generation performance. The figure highlights the gap between raw LLM performance and effective prompt encoding within a diffusion model and motivates the need for a novel framework, such as the one proposed by the authors, to better leverage the power of LLMs in image generation. The performance of LI-DiT models (infused with different LLMs) is shown in relation to the base LLMs and T5 models, showcasing the improvement achieved by the proposed architecture.
read the caption
Figure 2: Comparisons of our model, LLAMA series, and T5 series on image generation and text understanding benchmarks.

🔼 This figure shows the performance discrepancy between the former and latter adjective-noun compositions in the LLaMA3-8B and T5-XXL models. It highlights the positional bias in decoder-only LLMs like LLaMA3-8B, where information in the latter part of a prompt is less effectively processed for image generation compared to encoder-decoder models such as T5-XXL. The x-axis represents the relative position of the adj-noun composition within the prompt, and the y-axis represents the performance score. The figure visually demonstrates that the LLaMA3-8B model struggles to capture information from the latter part of the prompt, whereas the T5-XXL model maintains consistent performance regardless of position.
read the caption
Figure 3: Performance discrepancy between former and latter adj-noun compositions in LLaMA3-8B and T5-XXL.

🔼 This figure demonstrates the difference in prompt encoding between different language models. When given a simple prompt (‘a blue backpack and a red orange’), T5-XXL simply repeats the prompt, showing a lack of understanding or generation capabilities. LLaMA3-8B generates an unrelated response, highlighting its tendency to focus on predicting the next token rather than representing the input’s meaning. However, when the same LLaMA3-8B model is fine-tuned with multimodal data and given an instruction to describe the image in detail, it produces a much more relevant and informative response. This highlights the effectiveness of multimodal fine-tuning and explicit instruction guidance in improving the capabilities of LLMs for prompt encoding in image generation tasks.
read the caption
Figure 4: The output of language models when feeding a prompt. We can observe that pre-trained LLaMA3-8B provides an unrelated expansion, and T5-XXL repeats the input prompt. LLaMA3-8B with multi-modal fine-tuning can provide detailed information based on human instruction.
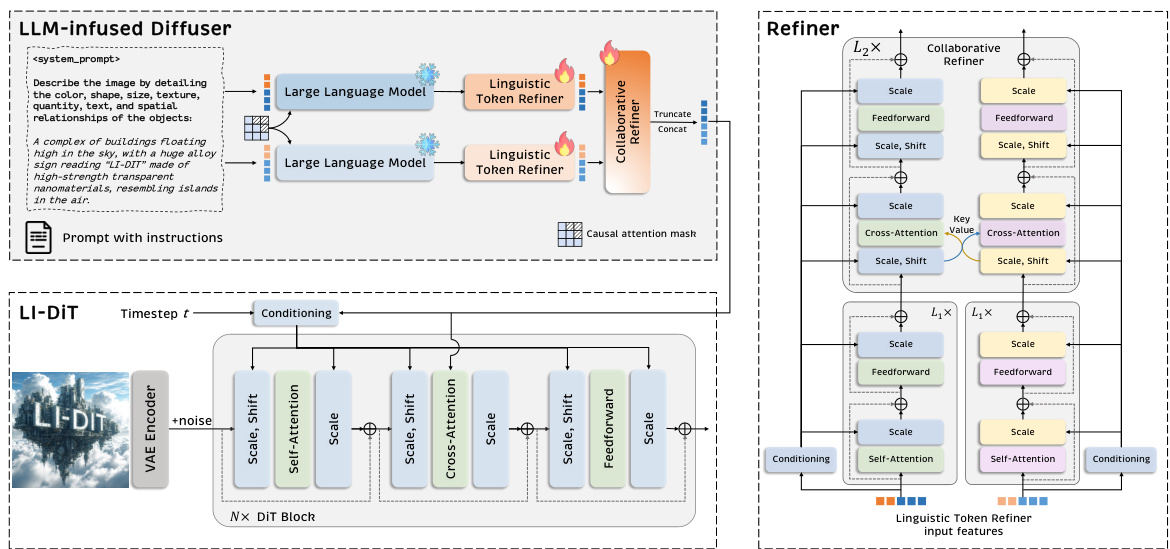
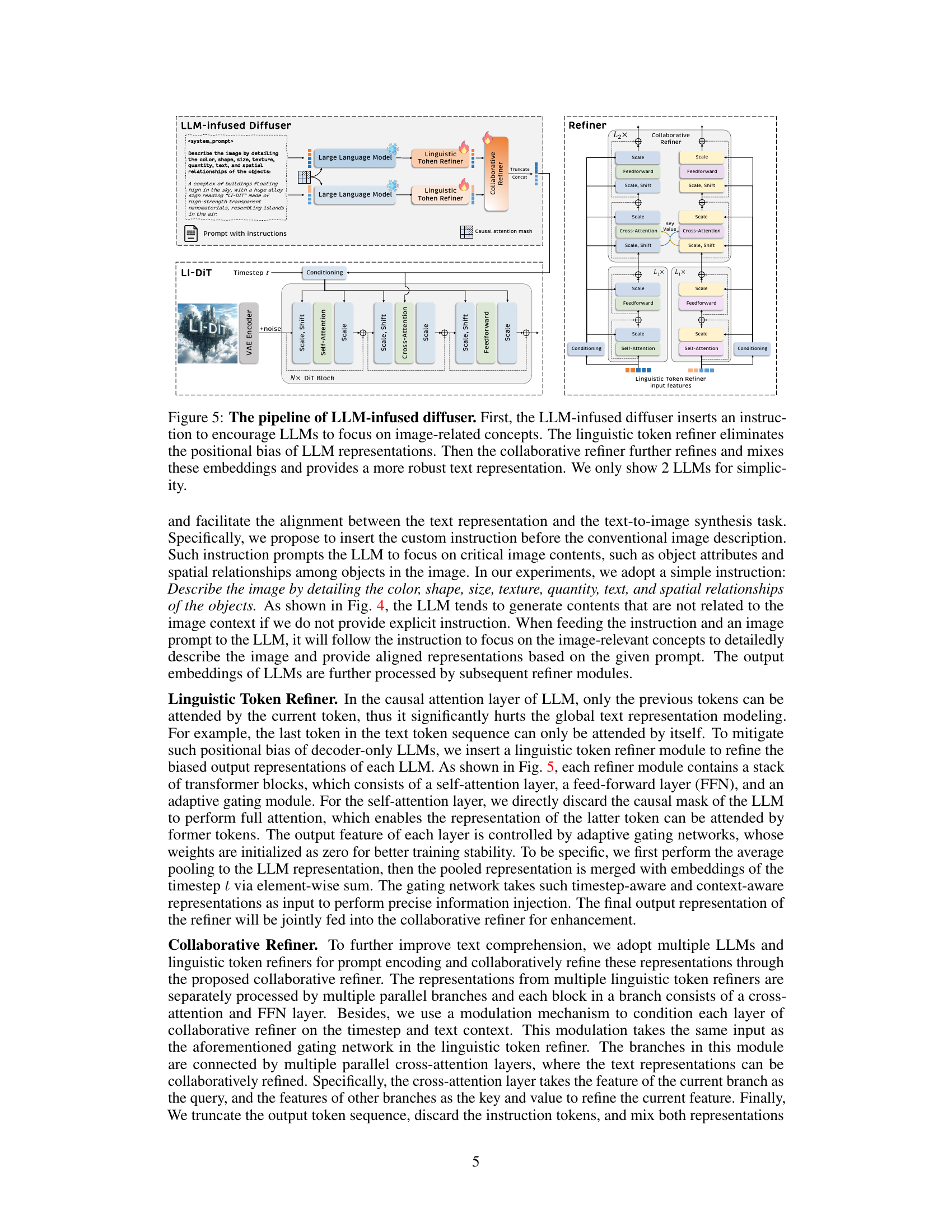
🔼 This figure illustrates the architecture of the LLM-infused diffuser, a novel framework proposed in the paper to leverage the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for prompt encoding in diffusion models. It shows a four-part pipeline: 1) Instruction insertion to guide LLMs toward image-relevant content; 2) Separate encoding of the prompt by multiple LLMs; 3) Linguistic token refiners to mitigate positional bias in LLM outputs; and 4) A collaborative refiner to merge and enhance representations from multiple LLMs, producing a robust text representation for the diffusion model. The diagram visually depicts the flow of information and the interaction between the different components of the framework.
read the caption
Figure 5: The pipeline of LLM-infused diffuser. First, the LLM-infused diffuser inserts an instruction to encourage LLMs to focus on image-related concepts. The linguistic token refiner eliminates the positional bias of LLM representations. Then the collaborative refiner further refines and mixes these embeddings and provides a more robust text representation. We only show 2 LLMs for simplicity.
🔼 This figure displays several high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately follow complex and diverse text prompts, resulting in high-quality outputs across different artistic styles and resolutions. The specific prompts used are listed in the appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.

🔼 This figure displays several high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately follow complex and diverse text prompts, producing high-quality results across different artistic styles and resolutions. The specific text prompts used are listed in the appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.

🔼 This figure showcases the high-quality image generation capabilities of the LI-DiT-10B model. It presents nine example images generated from diverse and complex prompts, highlighting the model’s proficiency in understanding and translating both simple and nuanced instructions, including those involving multiple objects and bilingual phrases. The results indicate LI-DiT-10B’s strength in accurately capturing the essence of complex descriptions and producing detailed, visually appealing images.
read the caption
Figure 8: LI-DiT-10B exhibits an astonishing ability to understand bilingual prompts, accurately generating images even with complex descriptions and combinations of objects.

🔼 This figure showcases the model’s ability to generate high-quality images from complex and creative prompts. The four example prompts demonstrate the model’s understanding of various artistic styles (anime, pixel art, realistic photography), scene descriptions, and object combinations. The generated images highlight LI-DiT-10B’s ability to accurately interpret and synthesize these prompts into visually coherent and appealing results.
read the caption
Figure 9: LI-DiT-10B exhibits an astonishing ability to understand prompts, accurately generating images even with complex descriptions and combinations of objects.

🔼 This figure displays several high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately represent complex prompts, generating images that match the specified styles and resolutions. The prompts used to generate these images can be found in the appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.

🔼 This figure displays high-resolution images generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately represent a wide range of complex prompts, showcasing its capabilities in various artistic styles and resolutions. The specific prompts used to generate each image can be found in the Appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.

🔼 This figure displays a diverse set of high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and accurately represent complex and diverse prompts, producing high-quality output across a wide range of styles and resolutions. The prompts used to generate these images can be found in the paper’s appendix.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.

🔼 This figure displays several high-resolution images (1024 pixels) generated by the LI-DiT-10B model. The images demonstrate the model’s ability to understand and follow complex and diverse prompts, producing high-quality results across different artistic styles and image resolutions. The specific prompts used to generate each image are listed in the appendix of the paper.
read the caption
Figure 1: High-resolution (1024px) samples from our LI-DiT-10B, showcasing its capabilities in complex prompt comprehension, precise prompt following, and high image quality across various styles and resolutions. Please refer to the appendix for the prompts.
Full paper#