↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Homepage ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Machine learning research heavily relies on understanding generalization—how well a model trained on a dataset performs on unseen data. Information-theoretic approaches, particularly using mutual information (MI), have shown promise but suffer from limitations, such as producing unbounded measures that don’t reflect true generalization error. Existing MI-based bounds often involve complex techniques that might not be easily applicable to various models and loss functions. Prior attempts to resolve these issues involved tightening existing bounds or using variants of mutual information, but they failed to achieve an accurate generalization measure for several cases.
This work introduces a novel framework based on conditional f-information, a broader concept than MI. The authors develop a generic method for deriving generalization bounds using this framework, applicable to diverse loss functions. This method avoids previous limitations by carefully selecting the measurable function to eliminate the problematic cumulant-generating function from the variational formula. Importantly, the derived bounds recover many prior results while enhancing our understanding of their limitations. Empirical evidence showcases the improvement of the new bounds against earlier approaches.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is crucial for researchers working on generalization bounds in machine learning. It offers novel information-theoretic bounds that improve upon existing methods, addressing key limitations like unboundedness. The introduction of the conditional f-information framework opens new avenues for research, potentially leading to tighter and more reliable generalization bounds for various machine learning algorithms and applications.
Visual Insights#
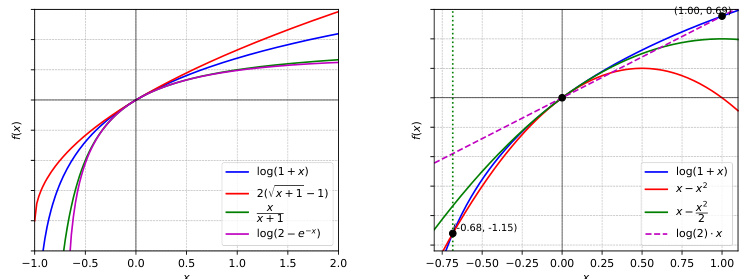
The figure compares various functions that can be used to lower-bound log(1+x), a key component in deriving f-information-based generalization bounds in the paper. The left panel shows the functions: log(1+x), 2(√x+1-1), x/(x+1), and log(2-e^-x), which are inverse functions of the convex conjugates of different f-divergences. The right panel zooms in on the region near x=0 to highlight how well x-ax² approximates the target log(1+x) function for various values of ‘a’. Different values of ‘a’ yield different levels of approximation.
Full paper#