↗ arXiv ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Hugging Face ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Current instruction-following diffusion models struggle with the detailed preservation of images and lack diverse instruction-following data for various image processing tasks, especially low-level ones. This significantly hampers the development of models that can effectively execute user-customized instructions. The stochastic nature of the diffusion process often leads to deficiencies in image generation or editing tasks.
To address these limitations, the authors introduce PromptFix, a comprehensive framework that enables diffusion models to follow detailed human instructions. It leverages a large-scale, instruction-following dataset, a high-frequency guidance sampling method to preserve image details, and an auxiliary prompting adapter using Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enhance prompt descriptions. Experimental results show that PromptFix outperforms existing methods in various image-processing tasks. The model demonstrates excellent zero-shot capabilities in blind restoration and combination tasks.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it addresses a critical limitation in current instruction-following diffusion models: their inability to handle diverse, low-level image-processing tasks effectively. The proposed solution, PromptFix, offers a unified framework that leverages a new large-scale dataset and innovative techniques to significantly improve performance. This could accelerate advancements in image editing and restoration, impacting various fields such as computer vision, digital art, and photography.
Visual Insights#

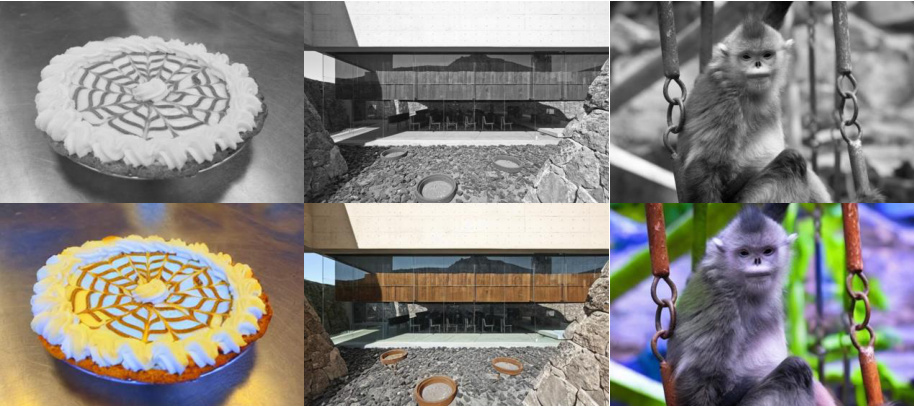
🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of the PromptFix model on various image editing and processing tasks. The examples show how the model successfully executes diverse instructions, maintaining high-frequency details and adapting to different image aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of different image restoration and editing methods on seven low-level image processing tasks. It compares expert models (specialized for individual tasks), generalist models (handling multiple tasks), and instruction-driven diffusion models. The metrics used are LPIPS and ManIQA, indicating perceptual similarity and image quality. Higher LPIPS values suggest less similarity, and higher ManIQA scores indicate better image quality.
read the caption
Table 1: Quantitative comparison is conducted across seven low-level datasets with a 512 × 512 input resolution. Expert models refer to approaches, such as Diff-plugin [46], which use non-generalizable training pipelines and maintain separate pre-trained weights for each of the four restoration tasks. Image Restoration Generalist Methods denote models that integrate multiple low-level tasks into a single framework. Instruction-driven Diffusion Methods represent diffusion generative baselines that follow human language instructions. ↑ indicates higher is better and ↓ indicates lower is better. The best and second best results are in bold and underlined, respectively.
In-depth insights#
PromptFix Framework#
The PromptFix framework presents a novel approach to enhancing the capabilities of diffusion models in image processing tasks by addressing limitations in instruction-following data and image preservation. A key innovation is the creation of a large-scale, diverse instruction-following dataset covering a wide range of tasks, including low-level image manipulation and object creation. This dataset significantly improves the model’s ability to understand and execute user-defined instructions. Further advancements include a high-frequency guidance sampling method that effectively controls the denoising process, preserving high-frequency details, and an auxiliary prompting adapter that leverages Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enrich textual prompts, boosting the model’s generalization abilities. The combination of these techniques results in a unified framework that surpasses existing methods in various image-processing tasks, demonstrating superior performance in both zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. The efficiency of the framework is also comparable to baseline models, making it a practical and powerful solution for instruction-guided image processing.
H-Freq Guidance#
The heading ‘H-Freq Guidance’ strongly suggests a technique focused on high-frequency component preservation during image processing. This is crucial because many image manipulation methods, especially those using diffusion models or VAEs, tend to lose fine details or high-frequency information during compression or processing. The method likely involves a strategy to explicitly control the denoising process, ensuring that the high-frequency information is not lost during reconstruction or generation. This could involve using specialized filters, loss functions weighted towards high frequencies, or a novel sampling method. Careful attention would need to be paid to balancing fidelity (preserving high-frequency details) and overall image quality (avoiding artifacts or noise amplification). The efficacy of this ‘H-Freq Guidance’ would likely be demonstrated by comparing its results to standard methods, possibly with quantitative metrics like PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, and qualitative assessments of image details.
VLM-based Adapter#
A VLM-based adapter enhances a diffusion model by incorporating external knowledge to improve instruction following, particularly for complex or ambiguous prompts. It bridges the gap between raw text instructions and the model’s internal representation, allowing for more nuanced and accurate image manipulation. By leveraging a pre-trained Vision-Language Model (VLM), the adapter translates natural language instructions into richer semantic embeddings. These embeddings provide the diffusion model with additional context, enabling it to better understand user intent and generate higher-quality results, especially when dealing with low-level image processing tasks that require precise control. This approach is particularly useful for handling complex tasks or scenarios where image degradation is severe. The integration of the VLM allows for a degree of zero-shot generalization, enabling the model to handle new instructions without explicit fine-tuning. However, the effectiveness hinges on the quality and relevance of the VLM’s output, and careful consideration needs to be given to integrating this additional information into the diffusion model’s architecture to avoid negative impacts on performance or efficiency.** The resulting system demonstrates superior image fidelity and adherence to user instructions compared to models that rely solely on text prompts.
Dataset Creation#
Creating a robust dataset is crucial for training effective instruction-following models in image processing. A well-designed dataset should encompass a wide variety of image manipulation tasks, including low-level operations like dehazing and super-resolution, as well as higher-level tasks such as object removal and creation. Data augmentation techniques are essential to increase the size and diversity of the dataset, ensuring that the model generalizes well to unseen images and instructions. Careful consideration of data labeling is also critical, with clear and consistent annotations being crucial for model training. The choice of source images also significantly impacts the quality and diversity of the final dataset. Utilizing a combination of existing datasets and newly generated images can provide a robust balance between leveraging existing resources and controlling specific aspects of the dataset. The dataset creation process should also strive for balance in terms of complexity and diversity, ensuring that the model is trained on a range of image characteristics, degradation levels, and instruction types.
Ablation Studies#
Ablation studies systematically remove components of a model to assess their individual contributions. In a deep learning context, this might involve removing layers from a neural network, disabling specific regularization techniques, or altering hyperparameters. The goal is to isolate the impact of each component and understand its role in the overall performance. Well-designed ablation studies are crucial for establishing causality and justifying design choices. For instance, if removing a specific layer significantly degrades performance, it highlights the layer’s importance. Conversely, if removing a component has minimal effect, it suggests that the component is either redundant or less critical. Thorough ablation studies strengthen a paper’s claims by providing strong empirical evidence, supporting the model’s architecture, training strategy, and parameter choices. They also help in identifying potential weaknesses, guiding future improvements, and enabling a more nuanced understanding of the model’s behavior. The results of ablation studies should be presented clearly, often in tabular format, illustrating the quantitative impact of removing each component. A well-conducted ablation study helps establish the relative importance of different model aspects and ensures that the reported contributions are not merely due to chance or an artifact of the specific experimental setup.
More visual insights#
More on figures

🔼 PromptFix takes user-customized instructions and input images as input. It uses a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to generate auxiliary prompts that describe the image and its flaws. These prompts, along with the user instructions, are processed using CLIP to generate embeddings. These embeddings are then fed into a diffusion model (U-Net) that uses a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) for encoding and decoding. The output is a processed image that meets the user’s instructions.
read the caption
Figure 2: The architecture of our proposed PromptFix.
🔼 The figure shows the architecture of PromptFix, a unified diffusion model for image processing tasks. It consists of several components, including an instruction embedding module, a CLIP encoder, a cross-attention module, a VAE encoder and decoder, and a U-Net. The model takes as input an image and a user-customized instruction. The instruction is processed by the instruction embedding module and combined with the image features from the CLIP encoder. The combined features are then passed through the cross-attention module, which allows the model to attend to both the image and the instruction. Finally, the features are passed through the VAE encoder and decoder, and the U-Net, which generates the output image. The model also includes an auxiliary prompt module, which takes as input an auxiliary prompt and combines it with the image features and the instruction. This auxiliary prompt is used to help the model to generate more realistic and accurate images.
read the caption
Figure 2: The architecture of our proposed PromptFix.

🔼 This figure displays a qualitative comparison of various image processing methods. It showcases the results of different models (PromptFix, InstructP2P, InstructDiff, MGIE, PromptIR, AirNet, Diff-Plugin) on several image processing tasks (colorization, watermark removal, desnowing, low-light enhancement, super-resolution, dehazing). The results are shown alongside the ground truth images to illustrate the strengths and weaknesses of each approach in preserving image details and adhering to user instructions.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure shows examples of blind image restoration using PromptFix. The model takes a degraded image as input and, without any explicit instructions, uses a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to generate an auxiliary prompt that describes the image and its defects. The model then uses this auxiliary prompt to perform the restoration. The examples showcase successful restoration for desnowing, dehazing, and low-light enhancement, highlighting the zero-shot capabilities of the proposed method.
read the caption
Figure 4: Qualitative analysis of VLM-guided blind restoration for desnowing, dehazing, and low-light enhancement. The results are obtained from PromptFix without explicit task instructions, relying solely on the input image. The auxiliary prompt, automatically generated by a VLM during inference, includes semantic captions and defect descriptions, indicated byand tags, respectively.
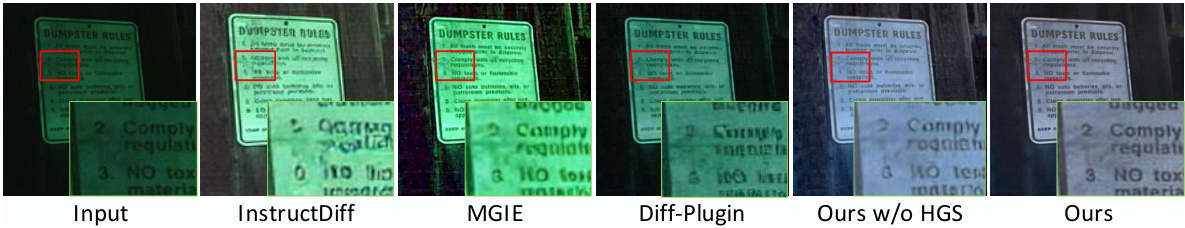
🔼 This figure demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed High-frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method in preserving low-level image details during image restoration. It compares the results of HGS with those of several VAE-based baselines using stable diffusion architecture. The comparison highlights HGS’s ability to maintain high-frequency information, such as text, which is often lost during VAE compression in other methods.
read the caption
Figure 5: Preservation of low-level image details using the proposed High-frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method, compared to previous VAE-based baselines [21, 23, 46] utilizing stable-diffusion architecture.

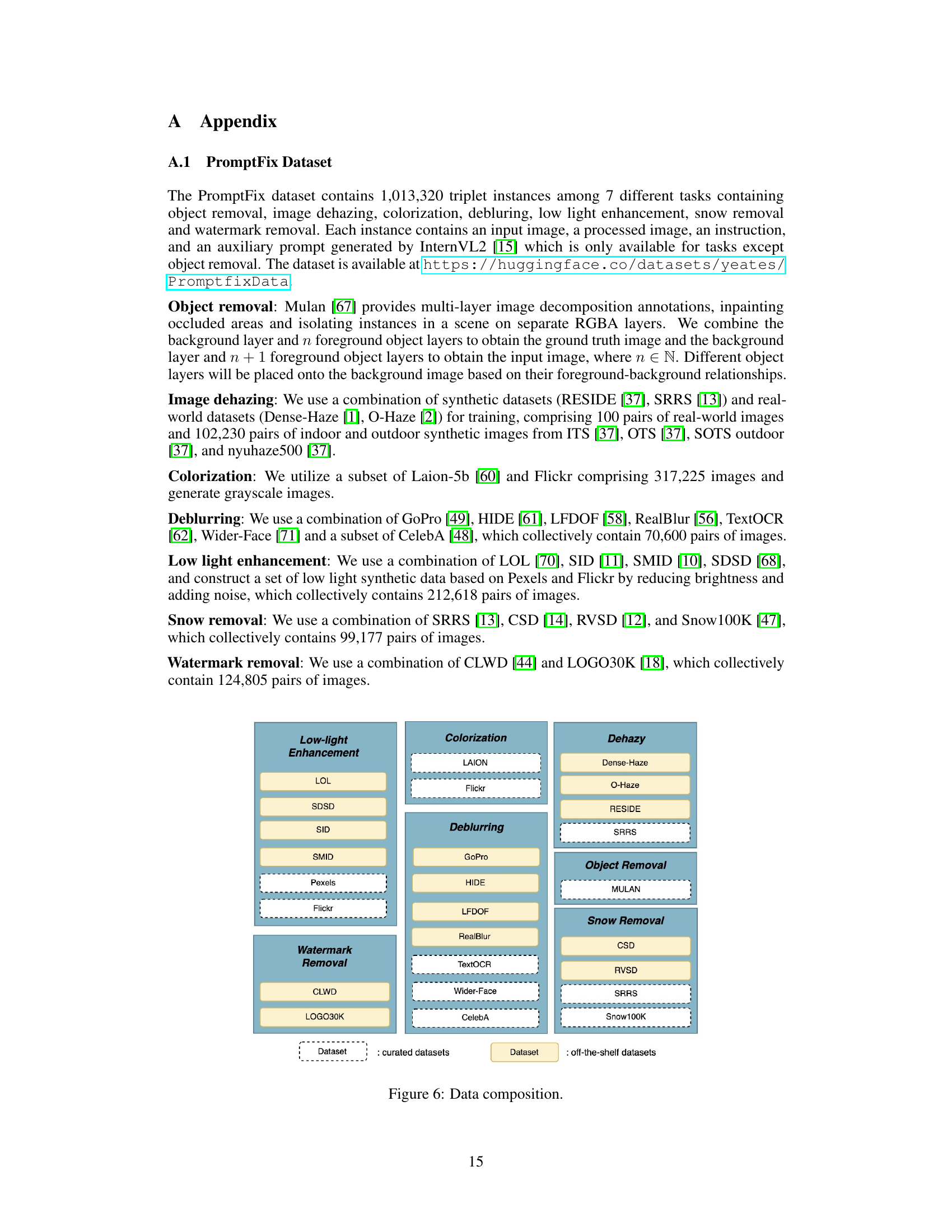
🔼 This figure shows the composition of datasets used for training the PromptFix model. It breaks down the datasets used for each of the seven tasks: Low-light Enhancement, Colorization, Dehazy, Deblurring, Object Removal, Snow Removal, and Watermark Removal. Each task lists the specific datasets used. The datasets are categorized as either ‘curated datasets’ or ‘off-the-shelf datasets’.
read the caption
Figure 6: Data composition.
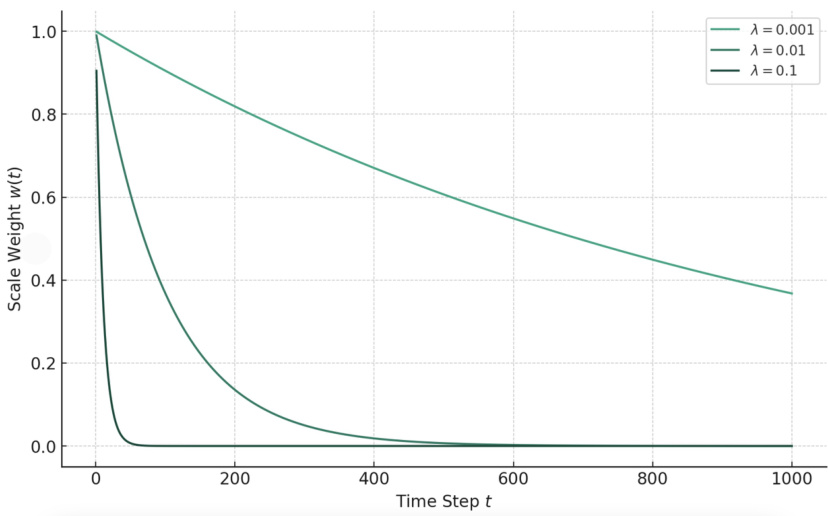
🔼 This figure shows the exponential decay weight functions used in the high-frequency guidance sampling method. The x-axis represents the time step (t) during the denoising process, and the y-axis represents the scale weight (w(t)). Three lines are plotted, each representing a different value of the hyperparameter λ (lambda): 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1. As λ increases, the weight decays more rapidly, meaning the fidelity constraint (preservation of high-frequency details) has less influence at later timesteps of the denoising process.
read the caption
Figure 7: Exponential Decay Weight Functions.

🔼 This figure demonstrates the capability of PromptFix to perform multiple image processing tasks simultaneously. The top row shows an input image with snow and haze, and the corresponding output image after applying PromptFix with instructions to remove the haze and snow, and enhance the resolution. The bottom row shows a similar example, but with instructions to colorize the image, remove a watermark, and enhance clarity.
read the caption
Figure 8: Visual results for Multi-task processing.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a unified diffusion model, in performing various image processing tasks such as image editing and object removal with high quality. The model effectively follows user-specified instructions, preserves high-frequency information during processing, and handles images with different aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a novel diffusion model designed to handle various image-processing tasks based on user-provided instructions. It highlights the model’s ability to maintain high-quality image details, even after processing, and its versatility in handling images of diverse aspect ratios. The images demonstrate different types of editing tasks, from object removal and creation to style transfer and restoration.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.
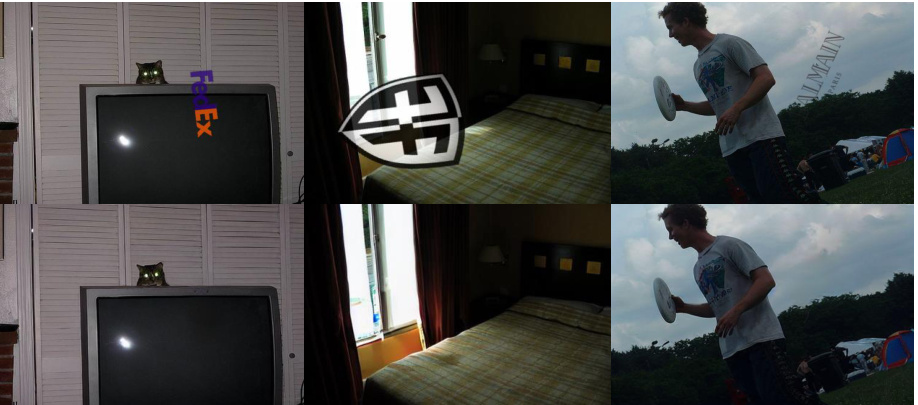

🔼 This figure shows example results of PromptFix, demonstrating its ability to perform various image processing tasks from different image types and aspect ratios. The model successfully edits images according to complex user instructions, while preserving high-frequency details and maintaining overall image quality.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases examples of various image editing tasks accomplished by the proposed PromptFix model. It highlights the model’s ability to understand and execute user-specific instructions while preserving high-frequency details in the images, a key advantage over existing methods. The examples demonstrate the model’s versatility in handling diverse image types and aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of the PromptFix model by illustrating its ability to perform various image editing tasks. It highlights the model’s ability to understand and follow user-defined instructions, and it demonstrates the model’s ability to preserve high-frequency information, leading to high-quality results. Different examples show the model’s versatility in handling images with varying aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.
🔼 This figure shows several examples of image editing tasks performed by PromptFix. It highlights the model’s ability to understand and execute diverse user instructions while maintaining high-frequency details in the images. The examples demonstrate the model’s versatility in handling various image types and aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows examples of various image editing tasks performed by the PromptFix model. The model takes user instructions as input and modifies the image accordingly. Examples include removing a person from an image, enhancing an image by removing haze, colorizing an image, removing snow from an image, brightening an image, and removing a watermark from an image. The figure highlights PromptFix’s ability to handle various image types and aspect ratios while preserving high-frequency details.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.
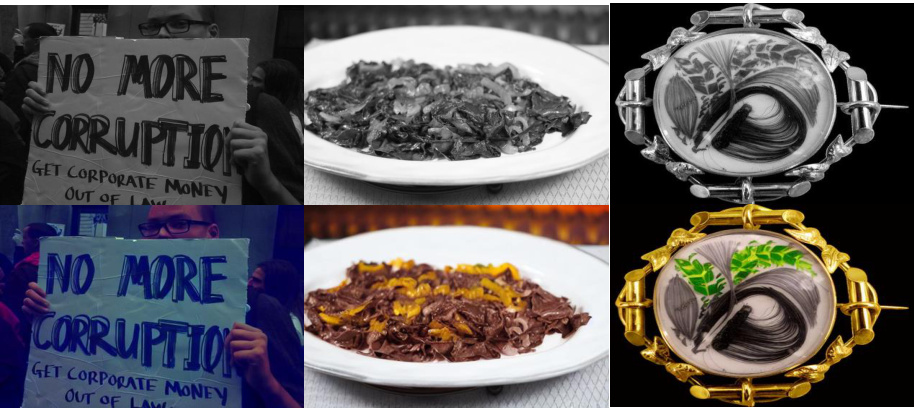

🔼 This figure shows several examples of image colorization results produced by the proposed PromptFix model. The input images are grayscale, and the corresponding colorized images demonstrate the model’s ability to accurately and realistically restore colors based on context and instructions. The diverse range of objects and scenes highlights the model’s generalizability across different types of imagery.
read the caption
Figure 10: More results for image colorization.

🔼 PromptFix is a unified diffusion model designed for various image-processing tasks. It excels at following user instructions for both high-level and low-level image editing and enhancement. A key feature is the preservation of high-frequency details during processing, maintaining image quality. The model handles images of diverse aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

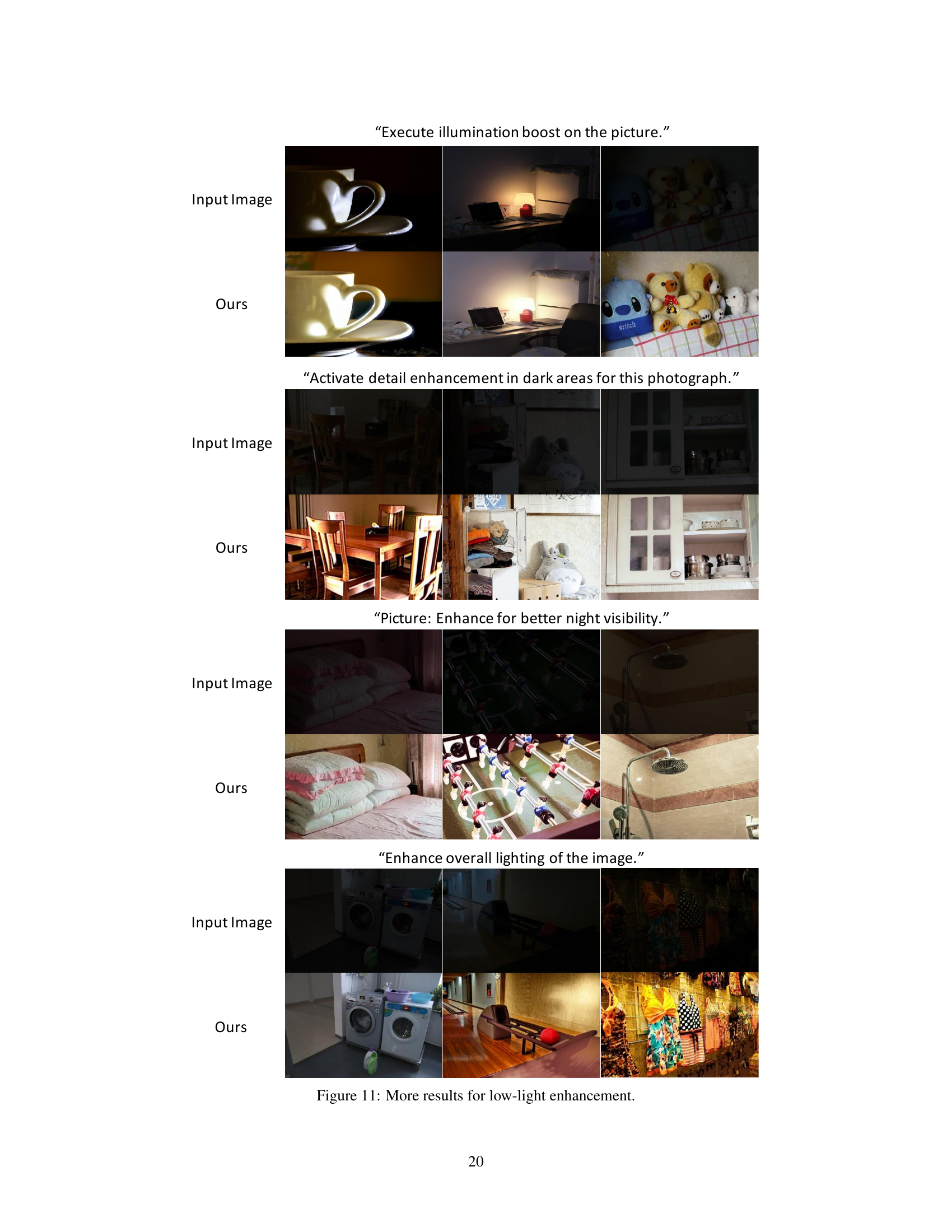
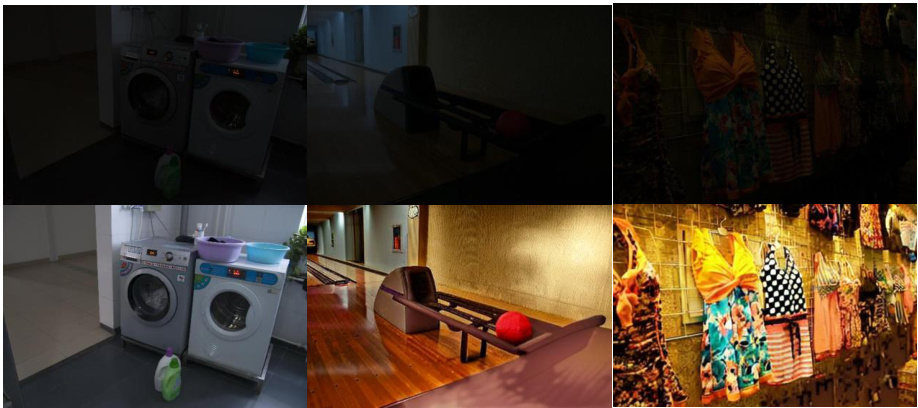
🔼 This figure shows more results of low-light enhancement, demonstrating the capabilities of the PromptFix model to enhance details and improve the visibility of images with low lighting. Each row presents an input image and the corresponding result processed by PromptFix, accompanied by instruction prompts that specify the enhancement task. The variety of scenes and improvements shown highlights the model’s adaptability and effectiveness across different low-light image scenarios.
read the caption
Figure 11: More results for low-light enhancement.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a novel diffusion model designed for image processing tasks. It demonstrates the model’s ability to accurately follow diverse user instructions for various image editing and manipulation tasks. The model’s preservation of high-frequency detail in images is a key highlight, ensuring that even fine details are maintained after processing. The figure also shows PromptFix is capable of handling images with varied aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a unified diffusion model designed for various image processing tasks. It demonstrates the model’s ability to follow custom instructions for image editing and generation, maintaining high-frequency details even after compression. The figure highlights the model’s versatility in handling images with diverse aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the image processing results between PromptFix and several other methods across different tasks. PromptFix is compared against instruction-driven diffusion models (InstructP2P, InstructDiff, MGIE) and generalist image restoration methods (PromptIR, AirNet, Diff-Plugin). The comparison highlights PromptFix’s superior performance in various image processing and restoration tasks.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the results of different image processing methods on various tasks. It compares PromptFix’s performance against several other instruction-driven diffusion models (InstructP2P, InstructDiff, MGIE) and general low-level image restoration techniques (PromptIR, AirNet, Diff-Plugin). Each row represents a different image processing task (colorization, watermark removal, desnowing, low-light enhancement, super-resolution, dehazing), showing the input image and the output images generated by each method. This allows for a visual assessment of the relative quality and effectiveness of different approaches.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure presents a qualitative comparison of different methods for image processing tasks, including colorization, watermark removal, desnowing, low-light enhancement, super-resolution, and dehazing. It compares PromptFix against other instruction-driven diffusion models (InstructP2P, InstructDiff, MGIE) and general low-level image restoration techniques (PromptIR, AirNet, Diff-Plugin). The comparison is shown visually through the results produced by each method for various input images.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure shows a qualitative comparison of the image processing results between PromptFix and other state-of-the-art methods for various low-level image processing tasks. It demonstrates PromptFix’s superior performance in terms of image quality and detail preservation, particularly when compared to instruction-driven diffusion methods and generalist models.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure shows a comparison of image details preservation using different methods for low-level image processing tasks. The top row shows the input image with snow effects added artificially. The second row shows the corresponding results by removing snow using four different methods. The first three methods are existing VAE-based methods, which fail to preserve high-frequency details like the text on the signboard, while the proposed method preserves these details successfully.
read the caption
Figure 5: Preservation of low-level image details using the proposed High-frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method, compared to previous VAE-based baselines [21, 23, 46] utilizing stable-diffusion architecture.

🔼 This figure demonstrates the importance of the proposed high-frequency guidance sampling method in preserving fine details during image restoration, particularly for tasks like low-light enhancement where such details are critical. It compares the results of the proposed method with those of several VAE-based baseline methods, highlighting its superior performance in maintaining high-frequency information such as text, which is often lost in the compression process of traditional VAEs. The comparison visually showcases how the baseline methods (InstructDiff, MGIE, Diff-Plugin) lose spatial information (text in this case) during the image restoration process, whereas the proposed method effectively preserves it.
read the caption
Figure 5: Preservation of low-level image details using the proposed High-frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method, compared to previous VAE-based baselines [21, 23, 46] utilizing stable-diffusion architecture.

🔼 This figure compares the performance of the proposed High-Frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method against three other VAE-based methods (InstructDiff, MGIE, and Diff-Plugin) in preserving low-level image details, specifically focusing on a low-light enhancement task. The top row shows the degraded input images, while the bottom row presents the results after processing by each method. The comparison highlights HGS’s ability to retain fine details such as text during the denoising process, showcasing its superior performance in maintaining spatial consistency and fidelity compared to baseline methods.
read the caption
Figure 5: Preservation of low-level image details using the proposed High-frequency Guidance Sampling (HGS) method, compared to previous VAE-based baselines [21, 23, 46] utilizing stable-diffusion architecture.

🔼 This figure presents a qualitative comparison of the results obtained by PromptFix and several other methods on various image processing tasks. These tasks include colorization, watermark removal, desnowing, low-light enhancement, super-resolution, and dehazing. The comparison includes both instruction-driven diffusion methods and low-level generalist techniques, showcasing the performance of PromptFix in comparison to other state-of-the-art approaches.
read the caption
Figure 3: Qualitative comparison between PromptFix and other instruct-driven diffusion methods (InstructP2P [7], InstructDiff [23], and MGIE [21]) for image processing, as well as low-level generalist techniques (PromptIR [52], AirNet [38], and Diff-Plugin [46]) for image restoration.

🔼 This figure shows examples of various image editing tasks performed by the PromptFix model. It highlights the model’s ability to understand and execute user instructions accurately while preserving high-frequency details in the images. The examples showcase different aspect ratios of input images to demonstrate the model’s versatility.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of the PromptFix model by displaying various examples of image editing tasks. Each example shows an original image with a user-specified task (e.g., ‘remove the man,’ ’enhance the image’). The corresponding processed images are shown demonstrating the model’s ability to perform various image editing tasks accurately while preserving image details.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a novel diffusion model designed for versatile image processing tasks. It demonstrates the model’s ability to understand and execute user-specified edits while maintaining high-quality image details and accommodating various image aspect ratios. Several example image manipulation tasks with their respective instructions and results are presented to illustrate this capability.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows examples of various image editing tasks accomplished by PromptFix. The model successfully performs diverse image manipulations, preserving high-frequency details even after VAE decoding. The example images demonstrate the model’s ability to handle a range of input image aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows examples of different image editing tasks accomplished by PromptFix. It highlights the model’s ability to understand and execute diverse instructions while maintaining high-frequency details in the output images. The variety of images with different aspect ratios demonstrates the model’s generalizability.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows the composition of the PromptFix dataset. It details the specific datasets used for each of the seven image processing tasks: Low-light Enhancement, Colorization, Deblurring, Object Removal, Snow Removal, Watermark Removal, and Dehazing. For each task, the figure lists both curated and off-the-shelf datasets that were combined to create the PromptFix dataset.
read the caption
Figure 6: Data composition.

🔼 This figure showcases the capabilities of PromptFix, a novel diffusion model. It demonstrates its ability to handle various image-processing tasks (including object removal, colorization, and image restoration) while preserving high-frequency details. The images shown highlight the versatility of the model in handling different aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows several examples of image editing tasks performed by PromptFix, highlighting its ability to understand and execute various instructions with high quality, while maintaining high-frequency details. It showcases the model’s versatility in handling different image types and aspect ratios.
read the caption
Figure 1: We propose PromptFix, a unified diffusion model capable of performing multiple image-processing tasks. It can understand user-customized editing instructions and perform the corresponding tasks with high quality. One of the key advantages of PromptFix is high-frequency information preservation, ensuring that image details are maintained throughout VAE decoding. PromptFix can handle various images with different aspect ratios.

🔼 This figure shows four examples of object removal using bounding boxes. Each row presents the input image with the object to be removed highlighted in a red bounding box, followed by the output image generated by the PromptFix model, demonstrating the model’s ability to effectively remove the specified objects while preserving the overall context of the image.
read the caption
Figure 15: More results for object removal by a bounding box.

🔼 This figure shows the results of VLM-guided blind restoration on several images. The top row displays the input images, each exhibiting various degrees of degradation (e.g., snow, haze). The bottom row presents the corresponding outputs generated by the PromptFix model using only the image as input (no explicit instructions). The model leverages the VLM to interpret the image content and automatically generate suitable prompts for restoration, demonstrating the model’s zero-shot capability in image restoration tasks.
read the caption
Figure 16: Visual results for VLM-guided blind restoration.
More on tables
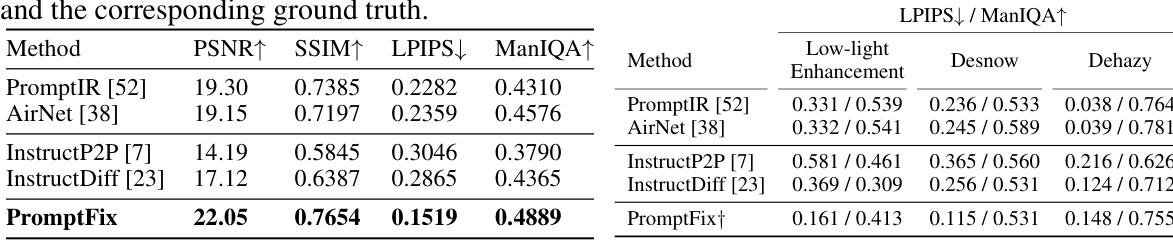
🔼 This table presents a quantitative comparison of different image restoration and editing methods across seven low-level image processing tasks. It compares the performance of expert models (trained specifically for individual tasks), generalist models (handling multiple tasks), and instruction-driven diffusion models. The metrics used are LPIPS and ManIQA, indicating perceptual similarity and overall image quality respectively. Higher LPIPS scores indicate better quality and vice versa for ManIQA scores. The table highlights PromptFix’s superior performance across several tasks, particularly compared to instruction-driven baselines.
read the caption
Table 1: Quantitative comparison is conducted across seven low-level datasets with a 512 × 512 input resolution. Expert models refer to approaches, such as Diff-plugin [46], which use non-generalizable training pipelines and maintain separate pre-trained weights for each of the four restoration tasks. Image Restoration Generalist Methods denote models that integrate multiple low-level tasks into a single framework. Instruct-driven Diffusion Methods represent diffusion generative baselines that follow human language instructions. ↑ indicates higher is better and ↓ indicates lower is better. The best and second best results are in bold and underlined, respectively.

🔼 This table presents the results of an ablation study that investigates the impact of different types of instruction prompts on the performance of the PromptFix model. Three types of prompts were used: instructions from the training dataset (A), short instructions (less than 20 words) from outside the training dataset (B), and long instructions (40-70 words) from outside the training dataset (C). The table shows that the model is robust to different prompt lengths, with only a slight decrease in performance observed for longer prompts (C).
read the caption
Table 5: Ablation Study on Different Types of Instruction Prompt. A: instructions used during training; B: out-of-training human instructions with fewer than 20 words; C: out-of-training human instructions with 40-70 words.

🔼 This table compares the performance of PromptFix against other methods for seven low-level image processing tasks. It categorizes methods into three groups: expert models (trained for specific tasks), generalist models (handling multiple tasks), and instruction-driven diffusion models (following text instructions). Performance is measured using LPIPS and ManIQA metrics, indicating higher values are better for ManIQA and lower for LPIPS.
read the caption
Table 1: Quantitative comparison is conducted across seven low-level datasets with a 512 × 512 input resolution. Expert models refer to approaches, such as Diff-plugin [46], which use non-generalizable training pipelines and maintain separate pre-trained weights for each of the four restoration tasks. Image Restoration Generalist Methods denote models that integrate multiple low-level tasks into a single framework. Instruct-driven Diffusion Methods represent diffusion generative baselines that follow human language instructions. ↑ indicates higher is better and ↓ indicates lower is better. The best and second best results are in bold and underlined, respectively.
Full paper#