↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Homepage ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Online optimization problems with long-term constraints are challenging due to the need to balance immediate rewards with future resource limitations. Existing methods often make simplifying assumptions or have high computational costs. This paper tackles the problem of online monotone DR-submodular maximization with stochastic long-term constraints, a setting relevant to various applications, particularly those involving resource allocation or budget management. The challenge lies in the uncertainty of both future rewards and resource availability.
The researchers address these challenges by proposing novel gradient ascent-based algorithms. These algorithms handle both semi-bandit and full-information feedback settings, offering improved efficiency. They achieve O(√T) regret and O(T3/4) constraint violation with high probability, demonstrating a significant improvement in query complexity compared to previous state-of-the-art methods. The stochastic nature of the problem is carefully considered in the theoretical analysis, leading to robust performance guarantees. The results provide valuable insights into the design and analysis of online algorithms for challenging real-world problems.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it presents the first algorithms for online DR-submodular maximization with stochastic long-term constraints, a crucial problem in many machine learning applications. It significantly improves upon existing methods in terms of query complexity, opening new avenues for research in online optimization under uncertainty. The findings are highly relevant to researchers working on resource allocation, online advertising, and other problems involving sequential decision-making under budgetary constraints. The high-probability bounds provided by the algorithms offer strong theoretical guarantees.
Visual Insights#
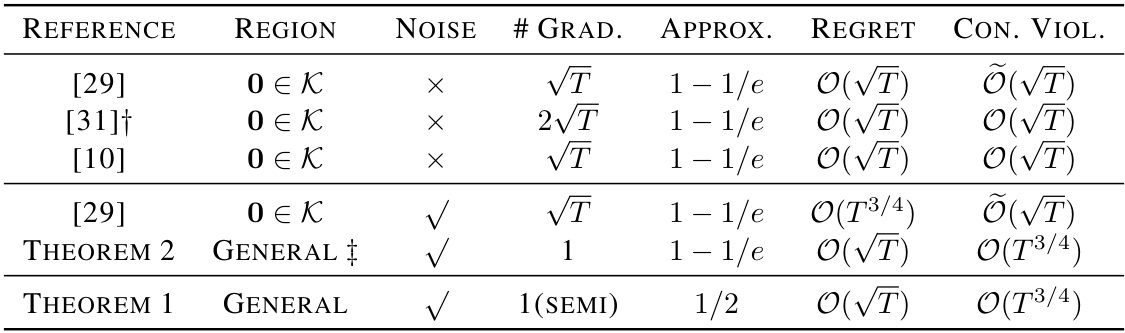
This table compares the proposed algorithms in this paper to existing state-of-the-art algorithms for online DR-submodular maximization with long-term constraints. It shows the region (whether 0 is in the constraint set K), whether the gradient information is exact or noisy, the number of gradient evaluations per round, the approximation ratio achieved, the regret bound, and the constraint violation bound for each algorithm.
Full paper#



















