↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Homepage ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Reinforcement learning (RL) typically focuses on stationary environments with linear reward functions, but real-world scenarios often involve non-stationary environments and complex, non-linear objective functions. Concave Utility Reinforcement Learning (CURL) addresses the latter, but existing solutions fail to address non-stationarity. This presents a challenge because agents need to adapt to changing environments and objectives to maintain optimal performance. Traditional approaches often assume prior knowledge of environmental changes or focus on static regret, which is less useful for dynamic settings.
This paper introduces MetaCURL, an algorithm designed for non-stationary CURL problems. It cleverly uses a meta-algorithm that runs several instances of black-box algorithms over different time intervals, aggregating their outputs using a sleeping expert framework. This approach handles uncertainty due to partial information about the environment by dynamically weighting the learning rates and instances. The key result is that MetaCURL achieves near-optimal dynamic regret, adapting to unpredictable changes in the environment and objective functions without needing prior knowledge. This means MetaCURL performs nearly as well as an oracle that knows the future changes in advance. This is a major advance for applying RL to non-stationary real-world problems.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is important because it introduces MetaCURL, the first algorithm to address non-stationary Concave Utility Reinforcement Learning (CURL) problems. This is significant because many real-world machine learning problems are non-stationary and involve non-linear objective functions, which are addressed by CURL. MetaCURL’s ability to handle adversarial losses and achieve near-optimal dynamic regret makes it a valuable tool for researchers dealing with such problems. The paper also presents a novel approach to handling uncertainty in non-stationary environments, which opens new avenues for further research in reinforcement learning.
Visual Insights#
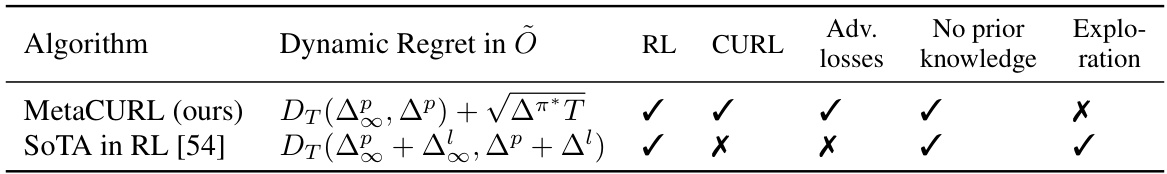
This table compares the dynamic regret bounds achieved by MetaCURL with those of the state-of-the-art non-stationary RL algorithms. It highlights that MetaCURL achieves optimal dynamic regret without prior knowledge of MDP changes and handles adversarial losses, unlike other methods.
Full paper#



















