↗ OpenReview ↗ NeurIPS Proc. ↗ Chat
TL;DR#
Machine learning models often fail in real-world scenarios due to distribution shift, where training and test data differ. Existing approaches for handling this issue either have high computational costs or are too sensitive to even minor shifts. This necessitates new methods that are both efficient and tolerant to significant distribution variations.
This work provides novel algorithms that address these limitations. The authors introduce efficient learning algorithms that permit classifiers to strategically abstain from predictions when faced with adversarial test distributions. This approach is contrasted with a tolerant TDS (Testable Distribution Shift) learning method which allows the algorithm to abstain from the entire test set if a significant shift is detected. Improved analysis of spectral outlier removal techniques is a key component, providing stronger bounds on polynomial moments after outlier removal and enabling tolerance of significant levels of distribution shift.
Key Takeaways#
Why does it matter?#
This paper is crucial because it tackles the critical problem of learning under distribution shifts, a common challenge in real-world machine learning deployments. The efficient algorithms provided offer practical solutions, advancing the field and opening new avenues for research in robust and reliable machine learning.
Visual Insights#
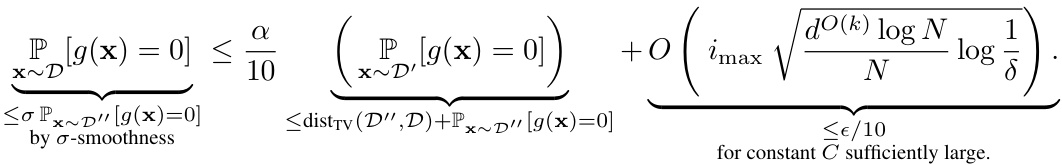
This table summarizes the runtime complexities of the proposed algorithms for PQ learning and tolerant TDS learning. It shows the runtime for different concept classes (halfspaces, intersections of halfspaces, decision trees, and formulas) under various training distributions (Gaussian, uniform). The first row represents the realizable setting, while the remaining rows consider the agnostic noise model, meaning the training labels can be arbitrarily noisy. The table highlights that the algorithms achieve dimension-efficient runtimes for PQ learning and tolerate moderate distribution shift for TDS learning.
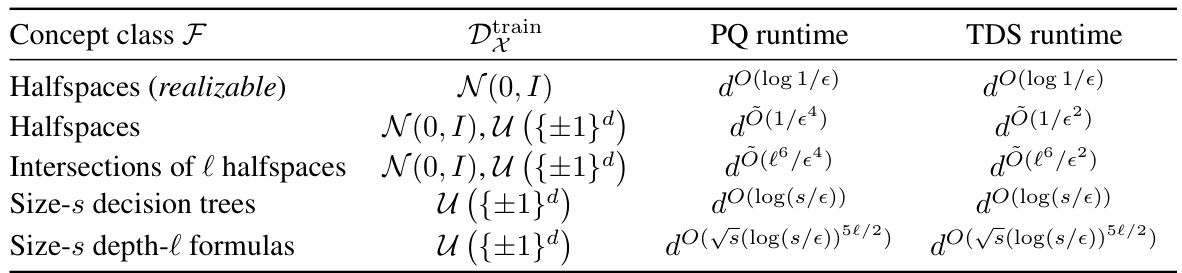
This table summarizes the results of the paper on PQ learning and tolerant TDS learning algorithms. It shows the runtime complexities for several concept classes (halfspaces, intersections of halfspaces, decision trees, and depth-l formulas) under different training distributions (Gaussian and uniform). The first row represents the realizable case, while the rest consider the agnostic noise model, where there is uncertainty in the labels. The PQ runtime column indicates the efficiency of the proposed PQ learning algorithms, while TDS runtime shows the efficiency of the tolerant TDS learning algorithms. Dimensionality (d), error rate (ε), size (s) and depth (l) influence the runtime.
Full paper#



















